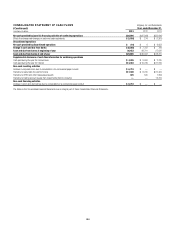
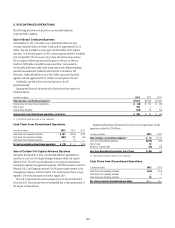
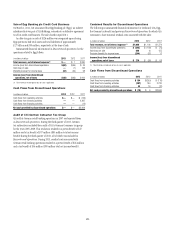
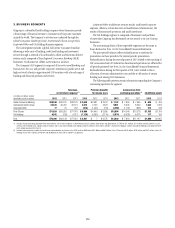
Citibank 2013 Annual Report Download - page 182
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 182 of the 2013 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.164
floating-rate debt and floating-rate assets, including loans and securities
purchased under agreement to resell, as well as rollovers of short-term fixed-
rate liabilities and floating-rate liabilities and forecasted debt issuances.
For net investment hedges in which derivatives hedge the foreign
currency exposure of a net investment in a foreign operation, the accounting
treatment will similarly depend on the effectiveness of the hedge. The effective
portion of the change in fair value of the derivative, including any forward
premium or discount, is reflected in Accumulated other comprehensive
income (loss) as part of the foreign currency translation adjustment.
For those accounting hedge relationships that are terminated or when
hedge designations are removed, the hedge accounting treatment described
in the paragraphs above is no longer applied. Instead, the end-user derivative
is terminated or transferred to the trading account. For fair value hedges, any
changes in the fair value of the hedged item remain as part of the basis of the
asset or liability and are ultimately reflected as an element of the yield. For
cash flow hedges, any changes in fair value of the end-user derivative remain
in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and are included in
earnings of future periods when the hedged cash flows impact earnings.
However, if it becomes probable that the hedged forecasted transaction will
not occur, any amounts that remain in Accumulated other comprehensive
income (loss) are immediately reflected in Other revenue.
End-user derivatives that are economic hedges, rather than qualifying
for hedge accounting, are also carried at fair value, with changes in value
included in Principal transactions or Other revenue. Citigroup often
uses economic hedges when qualifying for hedge accounting would be too
complex or operationally burdensome; examples are hedges of the credit
risk component of commercial loans and loan commitments. Citigroup
periodically evaluates its hedging strategies in other areas and may designate
either a qualifying hedge or an economic hedge, after considering the
relative cost and benefits. Economic hedges are also employed when the
hedged item itself is marked to market through current earnings, such as
hedges of commitments to originate one-to-four-family mortgage loans to be
held for sale and MSRs. See Note 23 to the Consolidated Financial Statements
for a further discussion of the Company’s hedging and derivative activities.
Employee Benefits Expense
Employee benefits expense includes current service costs of pension and
other postretirement benefit plans (which are accrued on a current basis),
contributions and unrestricted awards under other employee plans, the
amortization of restricted stock awards and costs of other employee benefits.
See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company recognizes compensation expense related to stock and option
awards over the requisite service period, generally based on the instruments’
grant-date fair value, reduced by expected forfeitures. Compensation
cost related to awards granted to employees who meet certain age plus
years-of-service requirements (retirement eligible employees) is accrued in
the year prior to the grant date, in the same manner as the accrual for cash
incentive compensation. Certain stock awards with performance conditions
or certain clawback provisions are subject to variable accounting, pursuant
to which the associated compensation expense fluctuates with changes in
Citigroup’s stock price. See Note 7 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Income Taxes
The Company is subject to the income tax laws of the U.S. and its states and
municipalities, and the foreign jurisdictions in which it operates. These tax
laws are complex and subject to different interpretations by the taxpayer and
the relevant governmental taxing authorities. In establishing a provision for
income tax expense, the Company must make judgments and interpretations
about the application of these inherently complex tax laws. The Company
must also make estimates about when in the future certain items will affect
taxable income in the various tax jurisdictions, both domestic and foreign.
Disputes over interpretations of the tax laws may be subject to review and
adjudication by the court systems of the various tax jurisdictions or may be
settled with the taxing authority upon examination or audit. The Company
treats interest and penalties on income taxes as a component of Income
tax expense.
Deferred taxes are recorded for the future consequences of events that
have been recognized for financial statements or tax returns, based upon
enacted tax laws and rates. Deferred tax assets are recognized subject to
management’s judgment that realization is more-likely-than-not. FASB
Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes”
(FIN 48) (now incorporated into ASC 740, Income Taxes), sets out a
consistent framework to determine the appropriate level of tax reserves to
maintain for uncertain tax positions. This interpretation uses a two-step
approach wherein a tax benefit is recognized if a position is more-likely-
than-not to be sustained. The amount of the benefit is then measured to be
the highest tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely to be realized. FIN 48
also sets out disclosure requirements to enhance transparency of an entity’s
tax reserves.
See Note 9 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a further
description of the Company’s tax provision and related income tax assets
and liabilities.
Commissions, Underwriting and Principal Transactions
Commissions revenues are recognized in income generally when earned.
Underwriting revenues are recognized in income typically at the closing of
the transaction. Principal transactions revenues are recognized in income on
a trade-date basis. See Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a
description of the Company’s revenue recognition policies for commissions
and fees, and Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for details of
Principal Transactions revenue.