Citibank 2010 Annual Report Download - page 263
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 263 of the 2010 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.261
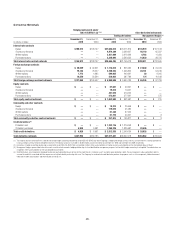
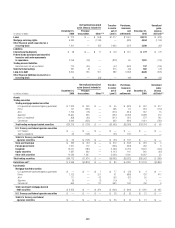
Trading account assets and liabilities—derivatives
Exchange-traded derivatives are generally fair valued using quoted market
(i.e., exchange) prices and so are classified as Level 1 of the fair value
hierarchy.
The majority of derivatives entered into by the Company are executed
over the counter and so are valued using internal valuation techniques as no
quoted market prices exist for such instruments. The valuation techniques
and inputs depend on the type of derivative and the nature of the underlying
instrument. The principal techniques used to value these instruments are
discounted cash flows, Black-Scholes and Monte Carlo simulation. The fair
values of derivative contracts reflect cash the Company has paid or received
(for example, option premiums paid and received).
The key inputs depend upon the type of derivative and the nature of
the underlying instrument and include interest rate yield curves, foreign-
exchange rates, the spot price of the underlying volatility and correlation.
The item is placed in either Level 2 or Level 3 depending on the observability
of the significant inputs to the model. Correlation and items with longer
tenors are generally less observable.
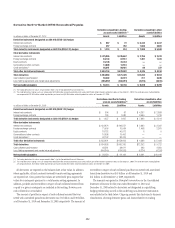
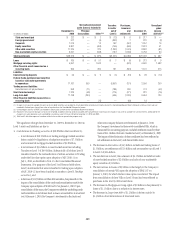
Subprime-related direct exposures in CDOs
The valuation of high-grade and mezzanine asset-backed security (ABS)
CDO positions uses trader prices based on the underlying assets of each high-
grade and mezzanine ABS CDO. The high-grade and mezzanine positions
are now largely hedged through the ABX and bond short positions, which are
trader priced. This results in closer symmetry in the way these long and short
positions are valued by the Company. Citigroup intends to use trader marks
to value this portion of the portfolio going forward so long as it remains
largely hedged.
For most of the lending and structuring direct subprime exposures,
fair value is determined utilizing observable transactions where available,
other market data for similar assets in markets that are not active and other
internal valuation techniques.
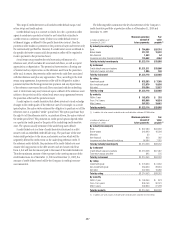
Investments
The investments category includes available-for-sale debt and marketable
equity securities, whose fair value is determined using the same procedures
described for trading securities above or, in some cases, using vendor prices
as the primary source.
Also included in investments are nonpublic investments in private equity
and real estate entities held by the S&B business. Determining the fair
value of nonpublic securities involves a significant degree of management
resources and judgment as no quoted prices exist and such securities are
generally very thinly traded. In addition, there may be transfer restrictions
on private equity securities. The Company uses an established process for
determining the fair value of such securities, using commonly accepted
valuation techniques, including the use of earnings multiples based on
comparable public securities, industry-specific non-earnings-based multiples
and discounted cash flow models. In determining the fair value of nonpublic
securities, the Company also considers events such as a proposed sale of
the investee company, initial public offerings, equity issuances or other
observable transactions. As discussed in Note 15, the Company uses NAV to
value certain of these entities.
Private equity securities are generally classified as Level 3 of the fair value
hierarchy.
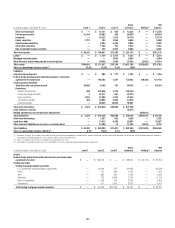
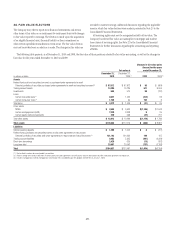
Short-term borrowings and long-term debt
Where fair value accounting has been elected, the fair values of
non-structured liabilities are determined by discounting expected cash
flows using the appropriate discount rate for the applicable maturity. Such
instruments are generally classified as Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy as
all inputs are readily observable.
The Company determines the fair values of structured liabilities (where
performance is linked to structured interest rates, inflation or currency risks)
and hybrid financial instruments (performance linked to risks other than
interest rates, inflation or currency risks) using the appropriate derivative
valuation methodology (described above) given the nature of the embedded
risk profile. Such instruments are classified as Level 2 or Level 3 depending
on the observability of significant inputs to the model.
Market valuation adjustments
Liquidity adjustments are applied to items in Level 2 and Level 3 of the
fair value hierarchy to ensure that the fair value reflects the price at which
the entire position could be liquidated in an orderly manner. The liquidity
reserve is based on the bid-offer spread for an instrument, adjusted to take
into account the size of the position consistent with what Citi believes a
market participant would consider.
Counterparty credit-risk adjustments are applied to derivatives, such
as over-the-counter derivatives, where the base valuation uses market
parameters based on the LIBOR interest rate curves. Not all counterparties
have the same credit risk as that implied by the relevant LIBOR curve, so it is
necessary to consider the market view of the credit risk of a counterparty in
order to estimate the fair value of such an item.