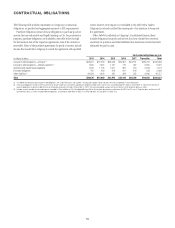
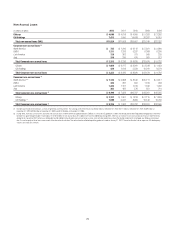
Citibank 2012 Annual Report Download - page 91
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 91 of the 2012 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.69
Citi’s Operational Systems and Networks Have Been, and
Will Continue to Be, Subject to an Increasing Risk of
Continually Evolving Cybersecurity or Other Technological
Risks, Which Could Result in the Disclosure of Confidential
Client or Customer Information, Damage to Citi’s
Reputation, Additional Costs to Citi, Regulatory Penalties
and Financial Losses.
A significant portion of Citi’s operations relies heavily on the secure
processing, storage and transmission of confidential and other information
as well as the monitoring of a large number of complex transactions on a
minute-by-minute basis. For example, through its global consumer banking,
credit card and Transaction Services businesses, Citi obtains and stores an
extensive amount of personal and client-specific information for its retail,
corporate and governmental customers and clients and must accurately
record and reflect their extensive account transactions. With the evolving
proliferation of new technologies and the increasing use of the Internet and
mobile devices to conduct financial transactions, large, global financial
institutions such as Citi have been, and will continue to be, subject to an
increasing risk of cyber incidents from these activities.
Although Citi devotes significant resources to maintain and regularly
upgrade its systems and networks with measures such as intrusion and
detection prevention systems and monitoring firewalls to safeguard critical
business applications, there is no guarantee that these measures or any other
measures can provide absolute security. Citi’s computer systems, software and
networks are subject to ongoing cyber incidents such as unauthorized access;
loss or destruction of data (including confidential client information);
account takeovers; unavailability of service; computer viruses or other
malicious code; cyber attacks; and other events. These threats may derive
from human error, fraud or malice on the part of employees or third parties,
or may result from accidental technological failure. Additional challenges
are posed by external extremist parties, including foreign state actors, in
some circumstances as a means to promote political ends. If one or more
of these events occurs, it could result in the disclosure of confidential client
information, damage to Citi’s reputation with its clients and the market,
customer dissatisfaction, additional costs to Citi (such as repairing systems
or adding new personnel or protection technologies), regulatory penalties,
exposure to litigation and other financial losses to both Citi and its clients
and customers. Such events could also cause interruptions or malfunctions
in the operations of Citi (such as the lack of availability of Citi’s online
banking system), as well as the operations of its clients, customers or other
third parties. Given Citi’s global footprint and high volume of transactions
processed by Citi, certain errors or actions may be repeated or compounded
before they are discovered and rectified, which would further increase these
costs and consequences.
Citi has been subject to intentional cyber incidents from external
sources, including (i) denial of service attacks, which attempted to interrupt
service to clients and customers; (ii) data breaches, which aimed to obtain
unauthorized access to customer account data; and (iii) malicious software
attacks on client systems, which attempted to allow unauthorized entrance
to Citi’s systems under the guise of a client and the extraction of client data.
For example, in 2012 Citi and other U.S. financial institutions experienced
distributed denial of service attacks which were intended to disrupt consumer
online banking services. While Citi’s monitoring and protection services were
able to detect and respond to these incidents before they became significant,
they still resulted in certain limited losses in some instances as well as
increases in expenditures to monitor against the threat of similar future
cyber incidents. There can be no assurance that such cyber incidents will not
occur again, and they could occur more frequently and on a more significant
scale. In addition, because the methods used to cause cyber attacks change
frequently or, in some cases, are not recognized until launched, Citi may be
unable to implement effective preventive measures or proactively address
these methods.
Third parties with which Citi does business may also be sources of
cybersecurity or other technological risks. Citi outsources certain functions,
such as processing customer credit card transactions, uploading content
on customer-facing websites, and developing software for new products and
services. These relationships allow for the storage and processing of customer
information, by third party hosting of or access to Citi websites, which could
result in service disruptions or website defacements, and the potential to
introduce vulnerable code, resulting in security breaches impacting Citi
customers. While Citi engages in certain actions to reduce the exposure
resulting from outsourcing, such as performing onsite security control
assessments, limiting third-party access to the least privileged level necessary
to perform job functions, and restricting third-party processing to systems
stored within Citi’s data centers, ongoing threats may result in unauthorized
access, loss or destruction of data or other cyber incidents with increased
costs and consequences to Citi such as those discussed above. Furthermore,
because financial institutions are becoming increasingly interconnected
with central agents, exchanges and clearing houses, including through the
derivatives provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act, Citi has increased exposure to
operational failure or cyber attacks through third parties.
While Citi maintains insurance coverage that may, subject to policy terms
and conditions including significant self-insured deductibles, cover certain
aspects of cyber risks, such insurance coverage may be insufficient to cover
all losses.