Citibank 2012 Annual Report Download - page 128
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 128 of the 2012 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324
 |
 |
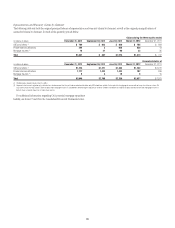
106
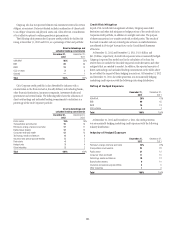
disclosure purposes, these differences are due to the fact that certain positions
included for external market risk purposes are not eligible for market risk
treatment under the U.S. regulatory capital rules, either as currently in effect
under Basel I or under the final market risk capital rules under Basel II.5/III
(e.g., the interest rate sensitivity of repos and reverse repos and the credit
and market sensitivities of the derivatives CVA are included for external
market risk disclosure purposes, but are not included for regulatory capital
purposes). The applicability of the VAR model for positions eligible for market
risk treatment under U.S. regulatory capital rules is periodically reviewed and
approved by Citi’s U.S. banking regulators.
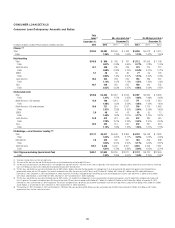
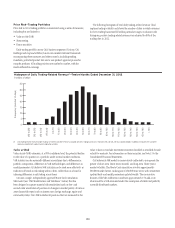
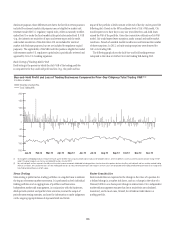
Back-Testing of Trading Market Risk
Back-testing is the process in which the daily VAR of the trading portfolio
is compared to the buy-and-hold profit and loss (e.g., the profit and loss
impact if the portfolio is held constant at the end of the day and re-priced the
following day). Based on the 99% confidence level of Citi’s VAR model, Citi
would expect two to three days in any one year where buy-and-hold losses
exceed the VAR of the portfolio. Given the conservative calibration of its VAR
model, Citi would expect fewer exceptions under normal and stable market
conditions. Periods of unstable market conditions could increase the number
of these exceptions. In 2012, no back-testing exceptions were observed for
Citi’s total trading VAR.
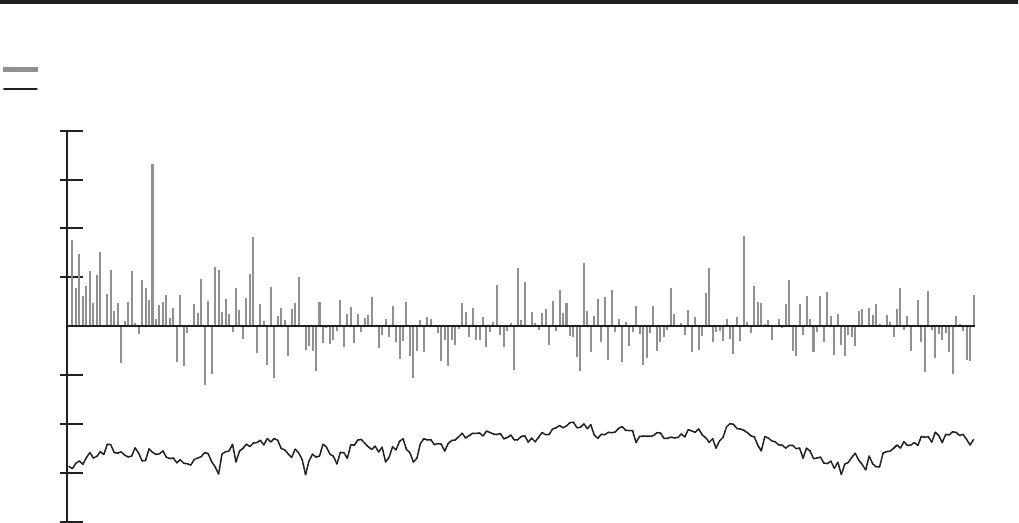
The following graph shows the daily buy-and-hold trading revenue
compared to the value at risk for Citi’s total trading VAR during 2012.
Buy-and-Hold Profit and Loss of Trading Businesses Compared to Prior-Day Citigroup Total Trading VAR(1)(2)
In millions of dollars
-200
-150
-100
-50
0
50
100
150
200
Total Buy-and-hold P&L
Total Trading VAR
Jan-12 Feb-12 Mar-12 Apr-12 May-12 Jun-12 Jul-12 Aug-12 Sep-12 Oct-12 Nov-12 Dec-12
(1) Citi changed its methodology for back-testing in the fourth quarter of 2012 from using actual profit and loss to buy-and-hold profit and loss, which Citi believes is more accurate for purposes of back-testing the VAR
model. The above histogram uses the buy-and-hold profit and loss for all of 2012.
(2) Buy-and-hold profit and loss represents the daily mark-to-market revenue movement attributable to trading positions from the close of the previous business day. Buy-and-hold profit and loss excludes realized trading
revenue, net interest, fees and commissions, intra-day trading profit and loss on new and terminated trades and changes in reserves and is not comparable to the trading-related revenue presented in the histogram of
Daily Trading-Related Revenue set forth above.
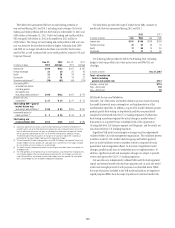
Stress Testing
Stress testing is performed on trading portfolios on a regular basis to estimate
the impact of extreme market movements. It is performed on both individual
trading portfolios and on aggregations of portfolios and businesses.
Independent market risk management, in conjunction with the businesses,
develops both systemic and specific stress scenarios, reviews the output of
periodic stress-testing exercises, and uses the information to make judgments
on the ongoing appropriateness of exposure levels and limits.
Factor Sensitivities
Factor sensitivities are expressed as the change in the value of a position for
a defined change in a market risk factor, such as a change in the value of a
Treasury bill for a one-basis-point change in interest rates. Citi’s independent
market risk management ensures that factor sensitivities are calculated,
monitored, and in most cases, limited, for all relevant risks taken in a
trading portfolio.
