Citibank 2012 Annual Report Download - page 257
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 257 of the 2012 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.235
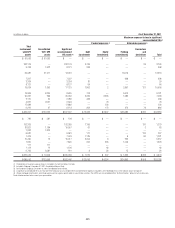
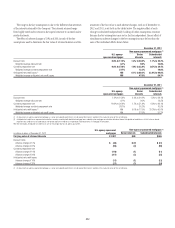
The Company also re-securitizes U.S. government-agency guaranteed
mortgage-backed (agency) securities. During the 12 months ended December
31, 2012, Citi transferred agency securities with a fair value of approximately
$30.3 billion to re-securitization entities. As of December 31, 2012, the fair
value of Citi-retained interests in agency re-securitization transactions
structured by Citi totaled approximately $1.7 billion ($1.1 billion of which
related to re-securitization transactions executed in 2012) and is recorded in
Trading account assets. The original fair value of agency re-securitization
transactions in which Citi holds a retained interest as of December 31, 2012
was approximately $71.2 billion.
As of December 31, 2012, the Company did not consolidate any private-
label or agency re-securitization entities.
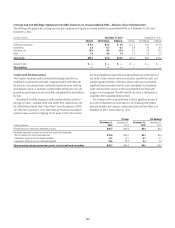
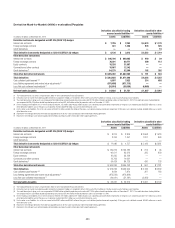
Citi-Administered Asset-Backed Commercial Paper Conduits
The Company is active in the asset-backed commercial paper conduit
business as administrator of several multi-seller commercial paper conduits
and also as a service provider to single-seller and other commercial paper
conduits sponsored by third parties.
Citi’s multi-seller commercial paper conduits are designed to provide
the Company’s clients access to low-cost funding in the commercial paper
markets. The conduits purchase assets from or provide financing facilities to
clients and are funded by issuing commercial paper to third-party investors.
The conduits generally do not purchase assets originated by the Company.
The funding of the conduits is facilitated by the liquidity support and credit
enhancements provided by the Company.
As administrator to Citi’s conduits, the Company is generally responsible
for selecting and structuring assets purchased or financed by the conduits,
making decisions regarding the funding of the conduits, including
determining the tenor and other features of the commercial paper issued,
monitoring the quality and performance of the conduits’ assets, and
facilitating the operations and cash flows of the conduits. In return, the
Company earns structuring fees from customers for individual transactions
and earns an administration fee from the conduit, which is equal to the
income from the client program and liquidity fees of the conduit after
payment of conduit expenses. This administration fee is fairly stable, since
most risks and rewards of the underlying assets are passed back to the clients
and, once the asset pricing is negotiated, most ongoing income, costs and
fees are relatively stable as a percentage of the conduit’s size.
The conduits administered by the Company do not generally invest
in liquid securities that are formally rated by third parties. The assets are
privately negotiated and structured transactions that are designed to be
held by the conduit, rather than actively traded and sold. The yield earned
by the conduit on each asset is generally tied to the rate on the commercial
paper issued by the conduit, thus passing interest rate risk to the client. Each
asset purchased by the conduit is structured with transaction-specific credit
enhancement features provided by the third-party client seller, including
over collateralization, cash and excess spread collateral accounts, direct
recourse or third-party guarantees. These credit enhancements are sized with
the objective of approximating a credit rating of A or above, based on the
Company’s internal risk ratings.
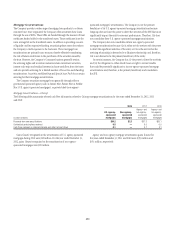
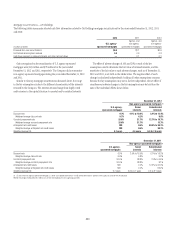
Substantially all of the funding of the conduits is in the form of short-
term commercial paper, with a weighted average life generally ranging
from 25 to 45 days. At the respective period ends December 31, 2012 and
December 31, 2011, the weighted average lives of the commercial paper
issued by consolidated and unconsolidated conduits were approximately 38
and 37 days, respectively.
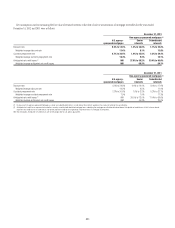
The primary credit enhancement provided to the conduit investors is in
the form of transaction-specific credit enhancement described above. In
addition, each consolidated conduit has obtained a letter of credit from the
Company, which needs to be sized to at least 8–10% of the conduit’s assets
with a floor of $200 million. The letters of credit provided by the Company
to the consolidated conduits total approximately $2.1 billion. The net result
across all multi-seller conduits administered by the Company is that, in the
event defaulted assets exceed the transaction-specific credit enhancements
described above, any losses in each conduit are allocated first to the Company
and then the commercial paper investors.
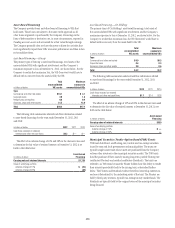
The Company also provides the conduits with two forms of liquidity
agreements that are used to provide funding to the conduits in the event
of a market disruption, among other events. Each asset of the conduits is
supported by a transaction-specific liquidity facility in the form of an asset
purchase agreement (APA). Under the APA, the Company has generally
agreed to purchase non-defaulted eligible receivables from the conduit at par.
The APA is not generally designed to provide credit support to the conduit,
as it generally does not permit the purchase of defaulted or impaired assets.
Any funding under the APA will likely subject the underlying borrower to
the conduits to increased interest costs. In addition, the Company provides
the conduits with program-wide liquidity in the form of short-term lending
commitments. Under these commitments, the Company has agreed to lend
to the conduits in the event of a short-term disruption in the commercial
paper market, subject to specified conditions. The Company receives fees for
providing both types of liquidity agreements and considers these fees to be on
fair market terms.