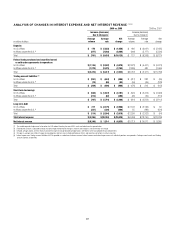
Citibank 2009 Annual Report Download - page 110
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 110 of the 2009 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
100
DERIVATIVES
See Note 24 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion
and disclosures relate to Citigroup’s derivative activities. The following
discussions relate to the Derivative Obligor Information, the Fair Valuation
for Derivatives and Credit Derivatives activities.
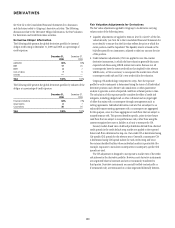
Derivative Obligor Information
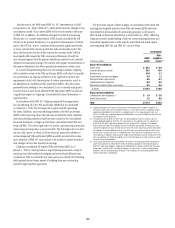
The following table presents the global derivatives portfolio by internal
obligor credit rating at December 31, 2009 and 2008, as a percentage of
credit exposure:
December 31,
2009
December 31,
2008
AAA/AA/A 68% 68%
BBB 17 20
BB/B 87
CCC or below 75
Unrated ——
Total 100% 100%
The following table presents the global derivatives portfolio by industry of the
obligor as a percentage of credit exposure:
December 31,
2009
December 31,
2008
Financial institutions 64% 73%
Governments 87
Corporations 28 20
Total 100% 100%
Fair Valuation Adjustments for Derivatives
The fair value adjustments applied by Citigroup to its derivative carrying
values consist of the following items:
Liquidity adjustments are applied to items in Level 2 or Level 3 of the fair-•
value hierarchy (see Note 26 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for
more details) to ensure that the fair value reflects the price at which the
entire position could be liquidated. The liquidity reserve is based on the
bid/offer spread for an instrument, adjusted to take into account the size
of the position.
Credit valuation adjustments (CVA) are applied to over-the-counter •
derivative instruments, in which the base valuation generally discounts
expected cash flows using LIBOR interest rate curves. Because not all
counterparties have the same credit risk as that implied by the relevant
LIBOR curve, a CVA is necessary to incorporate the market view of both
counterparty credit risk and Citi’s own credit risk in the valuation.
Citigroup CVA methodology comprises two steps. First, the exposure
profile for each counterparty is determined using the terms of all individual
derivative positions and a Monte Carlo simulation or other quantitative
analysis to generate a series of expected cash flows at future points in time.
The calculation of this exposure profile considers the effect of credit risk
mitigants, including pledged cash or other collateral and any legal right
of offset that exists with a counterparty through arrangements such as
netting agreements. Individual derivative contracts that are subject to an
enforceable master netting agreement with a counterparty are aggregated
for this purpose, since it is those aggregate net cash flows that are subject to
nonperformance risk. This process identifies specific, point-in-time future
cash flows that are subject to nonperformance risk, rather than using the
current recognized net asset or liability as a basis to measure the CVA.
Second, market-based views of default probabilities derived from observed
credit spreads in the credit default swap market are applied to the expected
future cash flows determined in step one. Own-credit CVA is determined using
Citi-specific CDS spreads for the relevant tenor. Generally, counterparty CVA
is determined using CDS spread indices for each credit rating and tenor.
For certain identified facilities where individual analysis is practicable (for
example, exposures to monoline counterparties) counterparty-specific CDS
spreads are used.
The CVA adjustment is designed to incorporate a market view of the credit
risk inherent in the derivative portfolio. However, most derivative instruments
are negotiated bilateral contracts and are not commonly transferred to
third parties. Derivative instruments are normally settled contractually, or
if terminated early, are terminated at a value negotiated bilaterally between