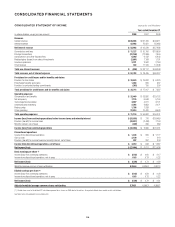
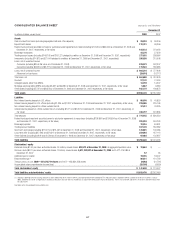
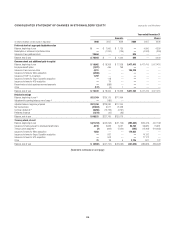
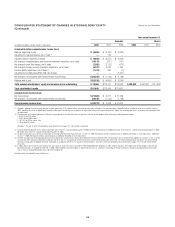
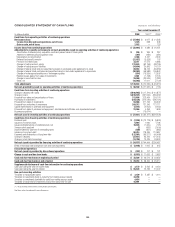
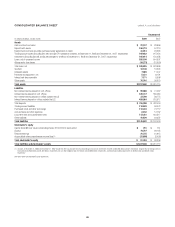
Citibank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 132
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 132 of the 2008 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.equipment, end-user derivatives in a net receivable position, repossessed
assets, and other receivables.
Other liabilities includes, among other items, accrued expenses and other
payables, deferred tax liabilities, minority interest, end-user derivatives in a
net payable position, and reserves for legal, taxes, restructuring, unfunded
lending commitments, and other matters.
Repossessed Assets
Upon repossession, loans are adjusted, if necessary, to the estimated fair
value of the underlying collateral and transferred to repossessed assets. This
is reported in Other assets, net of a valuation allowance for selling costs and
net declines in value as appropriate.
Securitizations
The Company primarily securitizes credit card receivables and mortgages.
Other types of securitized assets include corporate debt instruments (in cash
and synthetic form) and student loans.
There are two key accounting determinations that must be made relating
to securitizations. First, in the case where Citigroup originated or owned the
financial assets transferred to the securitization entity, a decision must be
made as to whether that transfer is considered a sale under U.S. Generally
Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). If it is a sale, the transferred assets
are removed from the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet with a gain or
loss recognized. Alternatively, when the transfer would be considered to be a
financing rather than a sale, the assets will remain on the Company’s
Consolidated Balance Sheet with an offsetting liability recognized in the
amount of proceeds received.
Second, a determination must be made as to whether the securitization
entity would be included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial
Statements. For each securitization entity with which it is involved, the
Company makes a determination of whether the entity should be considered
a subsidiary of the Company and be included in its Consolidated Financial
Statements or whether the entity is sufficiently independent that it does not
need to be consolidated. If the securitization entity’s activities are sufficiently
restricted to meet accounting requirements to be a qualifying special purpose
entity (QSPE), the securitization entity is not consolidated by the seller of the
transferred assets. If the securitization entity is determined to be a VIE, the
Company consolidates the VIE if it is the primary beneficiary.
For all other securitization entities determined not to be VIEs in which
Citigroup participates, a consolidation decision is made by evaluating several
factors, including how much of the entity’s ownership is in the hands of
third-party investors, who controls the securitization entity, and who reaps
the rewards and bears the risks of the entity. Only securitization entities
controlled by Citigroup are consolidated.
Interests in the securitized and sold assets may be retained in the form of
subordinated interest-only strips, subordinated tranches, spread accounts,
and servicing rights. In credit card securitizations, the Company retains a
seller’s interest in the credit card receivables transferred to the trusts, which is
not in securitized form. Accordingly, the seller’s interest is carried on a
historical cost basis and classified as Consumer loans. Retained interests in
securitized mortgage loans and student loans are classified as Trading
account assets, as is a majority of the retained interests in securitized credit
card receivables. Certain other retained interests are recorded as
available-for-sale investments, but servicing rights are included in
Intangible assets. However, since January 1, 2006, servicing rights are
initially recorded at fair value. Gains or losses on securitization and sale
depend in part on the previous carrying amount of the loans involved in the
transfer and, prior to January 1, 2006, were allocated between the loans sold
and the retained interests based on their relative fair values at the date of
sale. Gains are recognized at the time of securitization and are reported in
Other revenue.
The Company values its securitized retained interests at fair value using
quoted market prices, if such positions are actively traded, or financial
models that incorporate observable and unobservable inputs. More
specifically, these models estimate the fair value of these retained interests by
determining the present value of expected future cash flows, using modeling
techniques that incorporate management’s best estimates of key
assumptions, including prepayment speeds, credit losses and discount rates,
when observable inputs are not available. In addition, internally calculated
fair values of retained interests are compared to recent sales of similar assets,
if available.
Additional information on the Company’s securitization activities can be
found in Note 23 to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 175.
Transfers of Financial Assets
For a transfer of financial assets to be considered a sale, the assets must have
been isolated from the Company, even in bankruptcy or other receivership;
the purchaser must have the right to sell the assets transferred or the
purchaser must be a QSPE; and the Company may not have an option or any
obligation to reacquire the assets. If these sale requirements are met, the
assets are removed from the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet. If the
conditions for sale are not met, the transfer is considered to be a secured
borrowing, the assets remain on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, and the
sale proceeds are recognized as the Company’s liability. A legal opinion on a
sale is generally obtained for complex transactions or where the Company
has continuing involvement with assets transferred or with the securitization
entity. For a transfer to be eligible for sale accounting, those opinions must
state that the asset transfer is considered a sale and that the assets transferred
would not be consolidated with the Company’s other assets in the event of
the Company’s insolvency.
See Note 23 to the Consolidated Financial Statements on page 175.
Risk Management Activities—Derivatives Used for
Non-Trading Purposes
The Company manages its exposures to market rate movements outside its
trading activities by modifying the asset and liability mix, either directly or
through the use of derivative financial products, including interest rate
swaps, futures, forwards, and purchased option positions, as well as foreign-
exchange contracts. These end-user derivatives are carried at fair value in
Other assets or Other liabilities.
To qualify as a hedge, a derivative must be highly effective in offsetting
the risk designated as being hedged. The hedge relationship must be
formally documented at inception, detailing the particular risk management
objective and strategy for the hedge, which includes the item and risk that is
being hedged and the derivative that is being used, as well as how
effectiveness will be assessed and ineffectiveness measured. The effectiveness
of these hedging relationships is evaluated on a retrospective and prospective
basis, typically using quantitative measures of correlation with hedge
ineffectiveness measured and recorded in current earnings. If a hedge
relationship is found to be ineffective, it no longer qualifies as a hedge and
126