Citibank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 108
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 108 of the 2008 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.LIQUIDITY
Overview
Citigroup’s liquidity management is structured to ensure the availability of
funds and to optimize the free flow of funds through the Company’s legal
and regulatory structure. Principal constraints relate to legal and regulatory
limitations, sovereign risk and tax considerations. Consistent with these
constraints and the consolidated funding activities described in the
“Funding” section on page 98, Citigroup’s primary objectives for liquidity
management are established by entity and in aggregate across three main
operating entities as follows:
• Holding Company (Parent);
• Broker-Dealer (CGMHI); and
• Bank Entities.
Management of Liquidity
Management of liquidity at Citigroup is the responsibility of the Treasurer. A
uniform liquidity risk management policy exists for Citigroup and its major
operating subsidiaries. Under this policy, there is a single set of standards for
the measurement of liquidity risk in order to ensure consistency across
businesses, stability in methodologies and transparency of risk. Management
of liquidity at each operating subsidiary and/or country is performed on a
daily basis and is monitored by Corporate Treasury and independent risk
management.
The basis of Citigroup’s liquidity management is strong decentralized
liquidity management at each of its principal operating subsidiaries and in
each of its countries, combined with an active corporate oversight function.
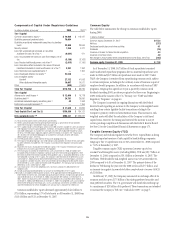
As discussed in “Capital Resources” on page 94, Citigroup’s FinALCO
undertakes this oversight responsibility along with the Treasurer. One of the
objectives of the FinALCO is to monitor and review the overall liquidity and
balance sheet positions of Citigroup and its principal subsidiaries. Similarly,
Asset and Liability Committees are also established for each country and/or
major line of business.
Monitoring Liquidity
Each principal operating subsidiary and/or country must prepare an annual
funding and liquidity plan for review by the Treasurer and approval by
independent risk management. The funding and liquidity plan includes
analysis of the balance sheet, as well as the economic and business
conditions impacting the liquidity of the major operating subsidiary and/or
country. As part of the funding and liquidity plan, liquidity limits, liquidity
ratios, market triggers, and assumptions for periodic stress tests are
established and approved. At a minimum, these parameters are reviewed on
an annual basis.
Liquidity Limits
Liquidity limits establish boundaries for market access in business-as-usual
conditions and are monitored against the liquidity position on a daily basis.
These limits are established based on the size of the balance sheet, depth of
the market, experience level of local management, stability of the liabilities
and liquidity of the assets. Finally, the limits are subject to the evaluation of
the entities’ stress test results. Generally, limits are established such that in
stress scenarios, entities are self-funded or net providers of liquidity. Thus,
the risk tolerance of the liquidity position is limited based on the capacity to
cover the position in a stressed environment. These limits are the key daily
risk-management tool for the Parent and Bank Entities.
Within this construct, there is a funding framework for the Company’s
activities. The primary benchmark for the Parent and Broker-Dealer is that,
on a combined basis, Citigroup maintains sufficient liquidity to meet all
maturing unsecured debt obligations due within one year without accessing
the unsecured markets. The resulting “short-term ratio” is monitored on a
daily basis. The short-term ratio consists of the following significant
components:
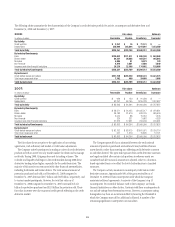
Liquidity Sources
•Cash and Liquid Securities Portfolio
The Company maintains cash and a portfolio of highly liquid/highly-
rated securities that could be sold or financed on a secured basis. The
cash balances are available for same-day settlement.
•Unencumbered Securities of the Broker-Dealer
CGMHI has unencumbered securities that are available for sale or can be
financed on a secured basis. The liquidity assumptions are reviewed
periodically to assess liquidation horizons and required margins in line
with market conditions.
•23A Capacity
As discussed further in the “Funding” section beginning on page 98,
some of Citigroup’s non-bank subsidiaries, including CGMHI, have credit
facilities with Citigroup’s subsidiary depository institutions, including
Citibank, N.A. Borrowings under these facilities must be secured in
accordance with Section 23A of the Federal Reserve Act.
Liquidity Obligations
•Commercial Paper
Maturing commercial paper issued by CFI. See Note 20 to the
Consolidated Financial Statements on page 169 for further information.
•LT Debt Maturing Within 12 Months
This includes debt maturing within the next 12 months of Citigroup, CFI
and CGMHI.
•Guaranteed Money Market Notes
Represents a portion of notes issued through Citi’s Private Bank via a
non-bank subsidiary that is an element of Parent Company funding.
•Maturing Bank Loans
As further described in Note 20 to the Consolidated Financial Statements
on page 169, CGMHI has a series of committed and uncommitted third-
party bank facilities that it uses in the ordinary course of business.
•Interest and Preferred Dividends
Represents interest on the Company’s debt and dividends on its preferred
stock.
•Other
At December 31, 2008, this category included miscellaneous payables and
potential payments under letters of credit, legal settlements and structured
notes.
In addition, a series of funding and risk-management benchmarks and
monitoring tools are established for the parent, broker-dealer and bank
entities, as further described in the following sections below.
102