Citibank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 109
Download and view the complete annual report
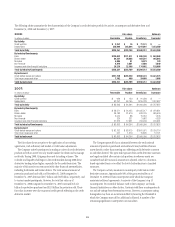
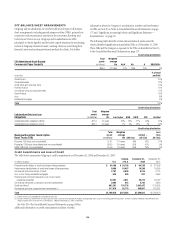
Please find page 109 of the 2008 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Liquidity Ratios
A series of standard corporate-wide liquidity ratios has been established to
monitor the structural elements of Citigroup’s liquidity. As discussed on page
102, for the Parent and CGMHI, ratios are established for liquid assets
against short-term obligations. For bank entities, key liquidity ratios include
cash capital (defined as core deposits, long-term debt, and capital compared
with illiquid assets), liquid assets against liquidity gaps, core deposits to
loans, and deposits to loans. Several measures exist to review potential
concentrations of funding by individual name, product, industry, or
geography. Triggers for management discussion, which may result in other
actions, have been established against these ratios. In addition, each
individual major operating subsidiary or country establishes targets against
these ratios and may monitor other ratios as approved in its funding and
liquidity plan.
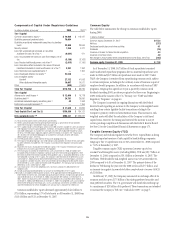
For CGMHI and Bank Entities, one of the key structural liquidity
measures is the cash capital ratio. Cash capital is a broader measure of the
ability to fund the structurally illiquid portion of the Company’s balance
sheet than traditional measures such as deposits to loans or core deposits to
loans. The ratio measures the ability to fund illiquid assets with structurally
long-term funding over one year. At December 31, 2008, both CGMHI and
the aggregate Bank Entities had an excess of structural long-term funding as
compared with their illiquid assets.
Market Triggers
Market triggers are internal or external market or economic factors that may
imply a change to market liquidity or Citigroup’s access to the markets.
Citigroup market triggers are monitored on a weekly basis by the Treasurer
and the head of Risk Architecture and are presented to the FinALCO.
Appropriate market triggers are also established and monitored for each
major operating subsidiary and/or country as part of the funding and
liquidity plans. Local triggers are reviewed with the local country or business
ALCO and independent risk management.
Stress Testing
Simulated liquidity stress testing is periodically performed for each major
operating subsidiary and/or country. A variety of firm-specific and market-
related scenarios are used at the consolidated level and in individual
countries. These scenarios include assumptions about significant changes in
key funding sources, credit ratings, contingent uses of funding, and political
and economic conditions in certain countries. The results of stress tests of
individual countries and operating subsidiaries are reviewed to ensure that
each individual major operating subsidiary or country is either a self-funded
or net provider of liquidity. In addition, a Contingency Funding Plan is
prepared on a periodic basis for Citigroup. The plan includes detailed
policies, procedures, roles and responsibilities, and the results of corporate
stress tests. The product of these stress tests is a series of alternatives that can
be used by the Treasurer in a liquidity event.
During 2008, Citigroup increased the frequency, duration, and severity of
certain stress testing, particularly related to the interconnection of
idiosyncratic and systemic risk. In addition, in conformity with
recommendations made by the Credit Risk Management Policy Group III,
Citigroup instituted a 30-day maximum cash flow for some of its key
operating entities.
CGMHI monitors liquidity by tracking asset levels, collateral and funding
availability to maintain flexibility to meet its financial commitments. As a
policy, CGMHI attempts to maintain sufficient capital and funding sources in
order to have the capacity to finance itself on a fully collateralized basis in
the event that its access to uncollateralized financing is temporarily
impaired. This is documented in CGMHI’s Contingency Funding Plan. This
plan is reviewed periodically to keep the funding options current and in line
with market conditions. The management of this plan includes an analysis
used to determine CGMHI’s ability to withstand varying levels of stress,
including rating downgrades, which could impact its liquidation horizons
and required margins. CGMHI maintains liquidity reserves of cash and
available loan value of unencumbered securities in excess of its outstanding
short-term uncollateralized liabilities. This is monitored on a daily basis.
CGMHI also ensures that long-term illiquid assets are funded with long-term
liabilities.
103