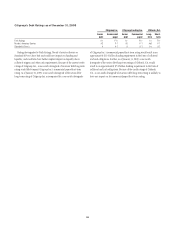
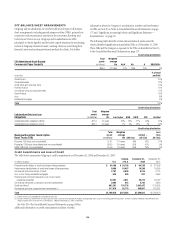
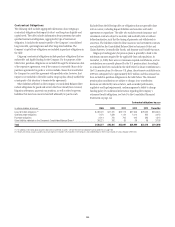
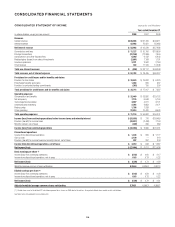
Citibank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 116
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 116 of the 2008 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Managed Net Credit Losses—Net credit losses adjusted for the effect of
credit card securitizations. See Managed Loans.
Market-Related Value of Plan Assets—A balance used to calculate the
expected return on pension-plan assets. Market-related value can be either
fair value or a calculated value that recognizes changes in fair value in a
systematic and rational manner over not more than five years.
Minority Interest—When a parent owns a majority (but less than 100%) of
a subsidiary’s stock, the Consolidated Financial Statements must reflect the
minority’s interest in the subsidiary. The minority interest as shown in the
Consolidated Statement of Income is equal to the minority’s proportionate
share of the subsidiary’s net income and, as included in Other Liabilities on
the Consolidated Balance Sheet, is equal to the minority’s proportionate
share of the subsidiary’s net assets.
Mortgage Servicing Rights (MSRs)—An intangible asset representing
servicing rights retained in the securitization of mortgage loans.
Net Credit Losses—Gross credit losses (write-offs) less gross credit
recoveries.
Net Credit Loss Ratio—Annualized net credit losses divided by average
loans outstanding.
Net Credit Margin—Revenues less net credit losses.
Net Excess Spread Revenue—Net cash flows from our credit card
securitization activities that are returned to the Company, less the
amortization of previously recorded revenue (i.e., residual interest) related to
prior periods’ securitizations. The net cash flows include collections of
interest income and fee revenue in excess of the interest paid to securitization
trust investors, reduced by net credit losses, servicing fees, and other costs
related to the securitized receivables.
Net Interest Revenue (NIR)—Interest revenue less interest expense.
Net Interest Margin—Interest revenue less interest expense divided by
average interest-earning assets.
Non-Qualified Plan—A retirement plan that is not subject to certain
Internal Revenue Code requirements and subsequent regulations.
Contributions to non-qualified plans do not receive tax-favored treatment;
the employer’s tax deduction is taken when the benefits are paid to
participants.
Notional Amount—The principal balance of a derivative contract used as a
reference to calculate the amount of interest or other payments.
On-Balance-Sheet Loans—Loans originated or purchased by the
Company that reside on the balance sheet at the date of the balance sheet.
Other Real Estate Owned (OREO)—The carrying value of all property
acquired by foreclosure or other legal proceedings when the Company has
taken possession of the collateral.
Projected Benefit Obligation (PBO)—The actuarial present value of all
pension benefits accrued for employee service rendered prior to the
calculation date, including an allowance for future salary increases if the
pension benefit is based on future compensation levels.
Purchase Sales—Customers’ credit card purchase sales plus cash
advances.
Qualified Plan—A retirement plan that satisfies certain requirements of the
Internal Revenue Code and provides benefits on a tax-deferred basis.
Contributions to qualified plans are tax deductible.
Qualifying SPE (QSPE)—A Special Purpose Entity that is very limited in its
activities and in the types of assets it can hold. It is a passive entity and may
not engage in active decision making. QSPE status allows the seller to
remove assets transferred to the QSPE from its books, achieving sale
accounting. QSPEs are not consolidated by the seller or the investors in the
QSPE.
Return on Assets—Annualized income divided by average assets.
Return on Common Equity—Annualized income less preferred stock
dividends, divided by average common equity.
Securities Purchased Under Agreements to Resell (Reverse Repo
Agreements)—An agreement between a seller and a buyer, generally of
government or agency securities, whereby the buyer agrees to purchase the
securities and the seller agrees to repurchase them at an agreed-upon price
at a future date.
Securities Sold Under Agreements to Repurchase (Repurchase
Agreements)—An agreement between a seller and a buyer, generally of
government or agency securities, whereby the seller agrees to repurchase the
securities at an agreed-upon price at a future date.
Securitizations—A process by which a legal entity issues to investors
certain securities which pay a return based on the principal and interest cash
flows from a pool of loans or other financial assets.
Significant Unconsolidated VIE—An entity where the Company has any
variable interest, including those where the likelihood of loss, or the notional
amount of exposure, is small. Variable interests are ownership interests, debt
securities, contractual arrangements or other pecuniary interests in an entity
that absorbs the VIE’s expected losses and/or returns.
Special Purpose Entity (SPE)—An entity in the form of a trust or other
legal vehicle, designed to fulfill a specific limited need of the company that
organized it (such as a transfer of risk or desired tax treatment).
Standby Letter of Credit—An obligation issued by a bank on behalf of a
bank customer to a third party where the bank promises to pay the third
party, contingent upon the failure by the bank’s customer to perform under
the terms of the underlying contract with the beneficiary, or it obligates the
bank to guarantee or stand as a surety for the benefit of the third party to the
extent permitted by law or regulation.
110