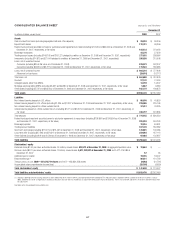
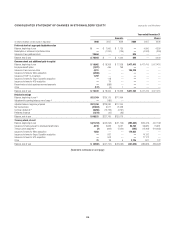
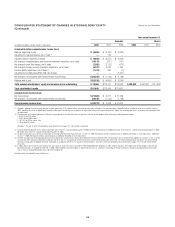
Citibank 2008 Annual Report Download - page 115
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 115 of the 2008 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Accumulated Benefit Obligation (ABO)—The actuarial present value of
benefits (vested and unvested) attributed to employee services rendered up to
the calculation date.
Adjusted Average Assets—Each year’s fourth quarter adjusted average of
total GAAP assets (net of allowance for loan losses) less goodwill; certain
other intangible assets; certain credit-enhancing interest-only strips;
investments in subsidiaries or associated companies that the Federal Reserve
determines should be deducted from Tier 1 Capital; deferred tax assets that
are dependent upon future taxable income; and certain equity investments
that are subject to a deduction from Tier 1 Capital.
APB 23 Benefit—In accordance with paragraph 31(a) of SFAS No. 109,
“Accounting for Income Taxes” (SFAS 109), a deferred tax liability is not
recognized for the excess of the amount for financial reporting over the tax
basis of an investment in a foreign subsidiary unless it becomes apparent
that the temporary difference will reverse in the foreseeable future.
Assets Under Management (AUMs)—Assets held by Citigroup in a
fiduciary capacity for clients. These assets are not included on Citigroup’s
balance sheet.
Basel II—A new set of risk-based regulatory capital standards for
internationally active banking organizations, published June 26, 2004
(subsequently amended in November 2005) by the Basel Committee on
Banking Supervision, which consists of central banks and bank supervisors
from 13 countries and is organized under the auspices of the Bank for
International Settlements (“BIS”).
Cash-Basis Formula—A formula, within a defined benefit plan, that
defines the ultimate benefit as a hypothetical account balance based on
annual benefit credits and interest earnings.
Cash-Basis Loans—Loans in which the borrower has fallen behind in
interest payments are considered impaired and are classified as
non-performing or non-accrual assets. In situations where the lender
reasonably expects that only a portion of the principal and interest owed
ultimately will be collected, all payments are credited directly to the
outstanding principal.
Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs)—security issued by a trust,
which is backed by a pool of bonds, loans, or other assets, including
residential or commercial mortgage-backed securities and other asset-
backed securities.
Credit Default Swap—An agreement between two parties whereby one
party pays the other a fixed coupon over a specified term. The other party
makes no payment unless a specified credit event such as a default occurs, at
which time a payment is made and the swap terminates.
Deferred Tax Asset—An asset attributable to deductible temporary
differences and carryforwards. A deferred tax asset is measured using the
applicable enacted tax rate and provisions of the enacted tax law.
Deferred Tax Liability—A liability attributable to taxable temporary
differences. A deferred tax liability is measured using the applicable enacted
tax rate and provisions of the enacted tax law.
Defined Benefit Plan—A retirement plan under which the benefits paid
are based on a specific formula. The formula is usually a function of age,
service and compensation. A non-contributory plan does not require
employee contributions.
Defined Contribution Plan—A retirement plan that provides an individual
account for each participant and specifies how contributions to that account
are to be determined, instead of specifying the amount of benefits the
participant will receive. The benefits a participant will receive depend solely
on the amount contributed to the participant’s account, the return on
investments of those contributions, and forfeitures of other participants’
benefits that may be allocated to such participant’s account.
Derivative—A contract or agreement whose value is derived from changes
in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, prices of securities or commodities,
or financial or commodity indices.
Federal Funds—Non-interest-bearing deposits held by member banks at
the Federal Reserve Bank.
Foregone Interest—Interest on cash-basis loans that would have been
earned at the original contractual rate if the loans were on accrual status.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)—Accounting rules
and conventions defining acceptable practices in preparing financial
statements in the United States of America. The Financial Accounting
Standards Board (FASB), an independent, self-regulatory organization, is the
primary source of accounting rules.
Interest-Only (or IO) Strip—A residual interest in securitization trusts
representing the remaining value of expected net cash flows to the Company
after payments to third-party investors and net credit losses.
Leverage Ratio—The Leverage Ratio is calculated by dividing Tier 1
Capital by leverage assets. Leverage assets are defined as each year’s fourth
quarter adjusted average of total assets, net of goodwill, intangibles and
certain other items as required by the Federal Reserve.
Managed Average Yield—Gross managed interest revenue earned,
divided by average managed loans.
Managed Basis—Managed basis presentation includes results from both
on-balance-sheet loans and off-balance-sheet loans, and excludes the
impact of card securitization activity. Managed basis disclosures assume that
securitized loans have not been sold and present the result of the securitized
loans in the same manner as the Company’s owned loans.
Managed Loans—Includes loans classified as Loans on the balance sheet
plus loans held-for-sale that are included in other assets plus securitized
receivables. These are primarily credit card receivables.
109