Citibank 2015 Annual Report Download - page 85
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 85 of the 2015 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.67
CREDIT RISK
OVERVIEW
Credit risk is the potential for financial loss resulting from the failure of a
borrower or counterparty to honor its financial or contractual obligations.
Credit risk arises in many of Citigroup’s business activities, including:
• wholesale and retail lending;
• capital markets derivative transactions;
• structured finance; and
• repurchase and reverse repurchase transactions.
Credit risk also arises from settlement and clearing activities, when Citi
transfers an asset in advance of receiving its counter-value or advances funds
to settle a transaction on behalf of a client. Concentration risk, within credit
risk, is the risk associated with having credit exposure concentrated within a
specific client, industry, region or other category.
Credit risk is one of the most significant risks Citi faces as an institution.
As a result, Citi has a well-established framework in place for managing
credit risk across all businesses. This includes a defined risk appetite,
credit limits and credit policies, both at the business level as well as at the
company-wide level. Citi’s credit risk management also includes processes
and policies with respect to problem recognition, including “watch lists,”
portfolio review, updated risk ratings and classification triggers.
With respect to Citi’s settlement and clearing activities, intra-day client
usage of lines is closely monitored against limits, as well as against “normal”
usage patterns. To the extent a problem develops, Citi typically moves
the client to a secured (collateralized) operating model. Generally, Citi’s
intra-day settlement and clearing lines are uncommitted and cancellable
at any time.
To manage concentration of risk within credit risk, Citi has in place
a concentration management framework consisting of industry limits,
obligor limits and single-name triggers. In addition, the independent
Risk organization reviews concentration of risk across Citi’s regions and
businesses to assist in managing this type of risk.
Credit exposures are generally reported in notional terms for accrual
loans, reflecting the value at which the loans as well as loan and other off-
balance sheet commitments are carried on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Credit exposure arising from capital markets activities is generally expressed
as the current mark-to-market, net of margin, reflecting the net value owed
to Citi by a given counterparty.
The credit risk associated with these credit exposures is a function of
the creditworthiness of the obligor, as well as the terms and conditions of
the specific obligation. Citi assesses the credit risk associated with its credit
exposures on a regular basis through its loan loss reserve process (see
“Significant Accounting Policies and Significant Estimates” below and Notes
1 and 16 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), as well as through
regular stress testing at the company, business, geography and product levels.
These stress-testing processes typically estimate potential incremental credit
costs that would occur as a result of either downgrades in the credit quality or
defaults of the obligors or counterparties.
For additional information on Citi’s credit risk management, see Note 15
to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
CONSUMER CREDIT
North America Consumer Mortgage Lending
Overview
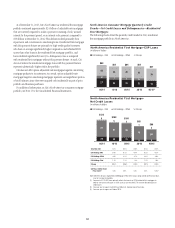
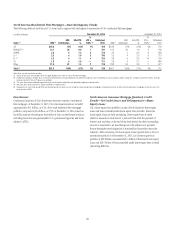
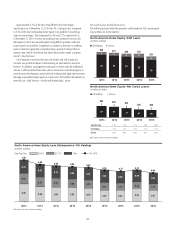
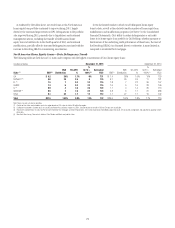
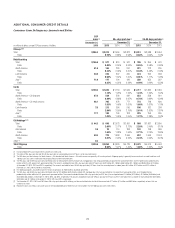
Citi’s North America consumer mortgage portfolio consists of both
residential first mortgages and home equity loans. At December 31, 2015,
Citi’s North America consumer mortgage portfolio was $79.7 billion
(compared to $95.9 billion at December 31, 2014), of which the residential
first mortgage portfolio was $56.9 billion (compared to $67.8 billion at
December 31, 2014), and the home equity loan portfolio was $22.8 billion
(compared to $28.1 billion at December 31, 2014). The decline during the
year was primarily attributed to $14.7 billion of North America consumer
mortgages sold or transferred to held-for-sale, including $6.6 billion of
CitiFinancial consumer mortgages ($5.4 billion of residential first mortgages
and $1.2 billion of home equity loans) transferred to held-for-sale and
classified as Other assets in the fourth quarter of 2015. At December 31, 2015,
$18.7 billion of residential first mortgages were recorded in Citi Holdings,
with the remaining $38.2 billion recorded in Citicorp. At December 31, 2015,
$19.1 billion of home equity loans was recorded in Citi Holdings, with the
remaining $3.6 billion recorded in Citicorp.
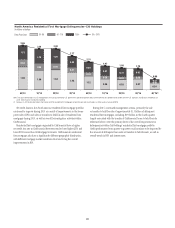
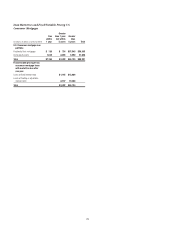
Citi’s residential first mortgage portfolio included $3.4 billion of loans
with Federal Housing Administration (FHA) insurance or Department
of Veterans Affairs (VA) guarantees at December 31, 2015, compared to
$5.2 billion at December 31, 2014. The decline during the year was primarily
due to mortgage loans with FHA insurance sold or transferred to held-for-
sale. Citi’s FHA/VA portfolio consists of loans to low-to-moderate-income
borrowers with lower FICO (Fair Isaac Corporation) scores and generally
higher loan-to-value ratios (LTVs). Credit losses on FHA loans are borne
by the sponsoring governmental agency, provided that the insurance terms
have not been rescinded as a result of an origination defect. With respect
to VA loans, the VA establishes a loan-level loss cap, beyond which Citi is
liable for loss. While FHA and VA loans have high delinquency rates, given
the insurance and guarantees, respectively, Citi has experienced negligible
credit losses on these loans.