Citibank 2015 Annual Report Download - page 115
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 115 of the 2015 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.97
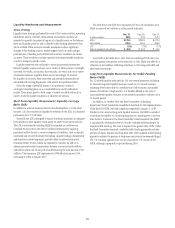
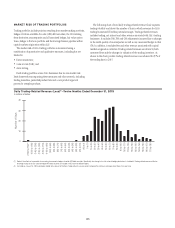
MARKET RISK
OVERVIEW
Market risk is the potential for losses arising from changes in the value of
Citi’s assets and liabilities resulting from changes in market variables such
as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, equity prices, commodity prices and
credit spreads, as well as their implied volatilities.
Each business is required to establish, with approval from Citi’s market
risk management, a market risk limit framework for identified risk factors
that clearly defines approved risk profiles and is within the parameters
of Citi’s overall risk appetite. These limits are monitored by the Risk
organization, Citi’s country and business Asset and Liability Committees and
the Citigroup Asset and Liability Committee. In all cases, the businesses are
ultimately responsible for the market risks taken and for remaining within
their defined limits.
Market risk emanates from both Citi’s trading and non-trading portfolios.
Trading portfolios comprise all assets and liabilities marked-to-market, with
results reflected in earnings. Non-trading portfolios include all other assets
and liabilities.
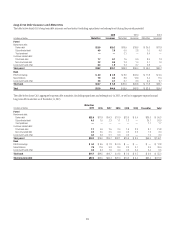
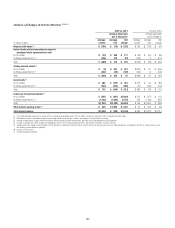
MARKET RISK OF NON-TRADING PORTFOLIOS
Market risk from non-trading portfolios stems from the potential impact of
changes in interest rates and foreign exchange rates on Citi’s net interest
revenues, the changes in Accumulated other comprehensive income
(loss) (AOCI) from its investment portfolios and capital invested in
foreign currencies.
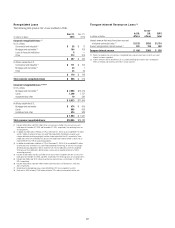
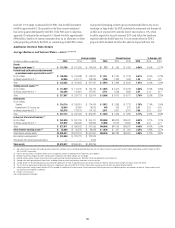
Net Interest Revenue at Risk
Net interest revenue, for interest rate exposure purposes, is the difference
between the yield earned on the non-trading portfolio assets (including
customer loans) and the rate paid on the liabilities (including customer
deposits or company borrowings). Net interest revenue is affected by changes
in the level of interest rates, as well as the amounts of assets and liabilities,
and the timing of repricing of assets and liabilities to reflect market rates.
Citi’s principal measure of risk to net interest revenue is interest rate
exposure (IRE). IRE measures the change in expected net interest revenue
in each currency resulting solely from unanticipated changes in forward
interest rates.
Citi’s estimated IRE incorporates various assumptions including
prepayment rates on loans, customer behavior, and the impact of pricing
decisions. For example, in rising interest rate scenarios, portions of the
deposit portfolio may be assumed to experience rate increases that are less
than the change in market interest rates. In declining interest rate scenarios,
it is assumed that mortgage portfolios experience higher prepayment rates.
IRE assumes that businesses and/or Citi Treasury make no additional
changes in balances or positioning in response to the unanticipated
rate changes.
In order to manage changes in interest rates effectively, Citi may modify
pricing on new customer loans and deposits, purchase fixed rate securities,
issue debt that is either fixed or floating or enter into derivative transactions
that have the opposite risk exposures. Citi regularly assesses the viability of
these and other strategies to reduce its interest rate risks and implements
such strategies when it believes those actions are prudent.
Citi manages interest rate risk as a consolidated company-wide position.
Citi’s client-facing businesses create interest-rate sensitive positions,
including loans and deposits, as part of their ongoing activities. Citi Treasury
aggregates these risk positions and manages them centrally. Operating within
established limits, Citi Treasury makes positioning decisions and uses tools,
such as Citi’s investment securities portfolio, company-issued debt, and
interest rate derivatives, to target the desired risk profile. Changes in Citi’s
interest rate risk position reflect the accumulated changes in all non-trading
assets and liabilities, with potentially large and offsetting impacts, as well as
Citi Treasury’s positioning decisions.
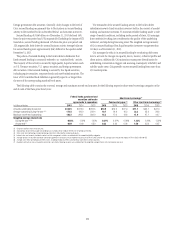
Citigroup employs additional measurements, including stress testing the
impact of non-linear interest rate movements on the value of the balance
sheet; the analysis of portfolio duration and volatility, particularly as they
relate to mortgage loans and mortgage-backed securities; and the potential
impact of the change in the spread between different market indices.
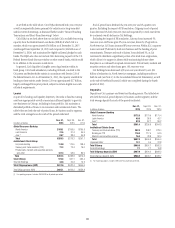
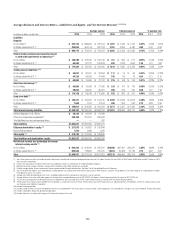
Interest Rate Risk of Investment Portfolios—Impact
on AOCI
Citi also measures the potential impacts of changes in interest rates on the
value of its AOCI, which can in turn impact Citi’s Common Equity Tier 1
Capital ratio. Citi’s goal is to benefit from an increase in the market level of
interest rates, while limiting the impact of changes in AOCI on its regulatory
capital position.
AOCI at risk is managed as part of the company-wide interest rate
risk position. AOCI at risk considers potential changes in AOCI (and the
corresponding impact on the Common Equity Tier 1 Capital ratio) relative to
Citi’s capital generation capacity.