Citibank 2015 Annual Report Download - page 259
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 259 of the 2015 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332
 |
 |
241
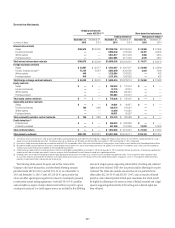
For asset/liability management hedging, fixed-rate long-term debt is
recorded at amortized cost under GAAP. However, by designating an interest
rate swap contract as a hedging instrument and electing to apply ASC 815
fair value hedge accounting, the carrying value of the debt is adjusted for
changes in the benchmark interest rate, with such changes in value recorded
in current earnings. The related interest-rate swap also is recorded on the
balance sheet at fair value, with any changes in fair value also reflected in
earnings. Thus, any ineffectiveness resulting from the hedging relationship is
captured in current earnings.
Alternatively, for management hedges that do not meet the ASC 815
hedging criteria, the derivative is recorded at fair value on the balance sheet,
with the associated changes in fair value recorded in earnings, while the
debt continues to be carried at amortized cost. Therefore, current earnings
are affected only by the interest rate shifts and other factors that cause a
change in the swap’s value. This type of hedge is undertaken when hedging
requirements cannot be achieved or management decides not to apply ASC
815 hedge accounting.
Another alternative is to elect to carry the debt at fair value under the
fair value option. Once the irrevocable election is made upon issuance of
the debt, the full change in fair value of the debt is reported in earnings.
The related interest rate swap, with changes in fair value, is also reflected in
earnings, which provides a natural offset to the debt’s fair value change. To
the extent the two offsets are not exactly equal because the full change in the
fair value of the debt includes risks not offset by the interest rate swap, the
difference is captured in current earnings.
The key requirements to achieve ASC 815 hedge accounting are
documentation of a hedging strategy and specific hedge relationships at
hedge inception and substantiating hedge effectiveness on an ongoing basis.
A derivative must be highly effective in accomplishing the hedge objective of
offsetting either changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedged item
for the risk being hedged. Any ineffectiveness in the hedge relationship is
recognized in current earnings. The assessment of effectiveness may exclude
changes in the value of the hedged item that are unrelated to the risks being
hedged. Similarly, the assessment of effectiveness may exclude changes
in the fair value of a derivative related to time value that, if excluded, are
recognized in current earnings.
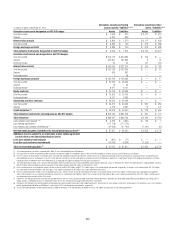
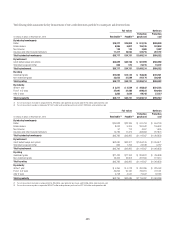
Fair Value Hedges
Hedging of Benchmark Interest Rate Risk
Citigroup hedges exposure to changes in the fair value of outstanding
fixed-rate issued debt. These hedges are designated as fair value hedges
of the benchmark interest rate risk associated with the currency of the
hedged liability. The fixed cash flows of the hedged items are converted to
benchmark variable-rate cash flows by entering into receive-fixed, pay-
variable interest rate swaps. These fair value hedge relationships use either
regression or dollar-offset ratio analysis to assess whether the hedging
relationships are highly effective at inception and on an ongoing basis.
Citigroup also hedges exposure to changes in the fair value of fixed-rate
assets due to changes in benchmark interest rates, including available-
for-sale debt securities and loans. The hedging instruments used are
receive-variable, pay-fixed interest rate swaps. These fair value hedging
relationships use either regression or dollar-offset ratio analysis to assess
whether the hedging relationships are highly effective at inception and on
an ongoing basis.
