Citibank 2014 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2014 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.65
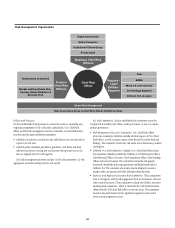
Citi May Incur Significant Losses If Its Risk Management
Models, Processes or Strategies Are Ineffective.
Citi employs a broad and diversified set of risk management and mitigation
processes and strategies, including the use of various risk models, in
analyzing and monitoring the various risks Citi assumes in conducting
its activities, such as credit, market and operational risks (for additional
information regarding these areas of risk as well as risk management at Citi,
see “Managing Global Risk” below). For example, Citi uses models as part of
its various stress testing initiatives across the firm. Management of these risks
is made even more challenging within a global financial institution such as
Citi, particularly given the complex, diverse and rapidly changing financial
markets and conditions in which Citi operates.
These models, processes and strategies are inherently limited because
they involve techniques, including the use of historical data in some
circumstances, and judgments that cannot anticipate every economic
and financial outcome in the markets in which Citi operates nor can they
anticipate the specifics and timing of such outcomes. Citi could incur
significant losses if its risk management models, processes or strategies are
ineffective in properly anticipating or managing these risks.
Citi’s Performance and the Performance of Its Individual
Businesses Could Be Negatively Impacted If Citi Is Not Able
to Hire and Retain Qualified Employees for Any Reason.
Citi’s performance and the performance of its individual businesses is
largely dependent on the talents and efforts of highly skilled employees.
Specifically, Citi’s continued ability to compete in its businesses, to manage
its businesses effectively and to continue to execute its overall global strategy
depends on its ability to attract new employees and to retain and motivate its
existing employees. Citi’s ability to attract and retain employees depends on
numerous factors, including its culture, compensation, the management and
leadership of the company as well as its individual businesses, Citi’s presence
in the particular market or region at issue and the professional opportunities
it offers.
The banking industry has and may continue to experience more stringent
regulation of employee compensation, including limitations relating to
incentive-based compensation, clawback requirements and special taxation.
Moreover, given its continued focus on the emerging markets, Citi is often
competing for qualified employees in these markets with entities that have a
significantly greater presence in the region or are not subject to significant
regulatory restrictions on the structure of incentive compensation. If Citi
is unable to continue to attract and retain qualified employees for any
reason, Citi’s performance, including its competitive position, the successful
execution of its overall strategy and its results of operations could be
negatively impacted.
Incorrect Assumptions or Estimates in Citi’s Financial
Statements Could Cause Significant Unexpected Losses
in the Future, and Changes to Financial Accounting and
Reporting Standards or Interpretations Could Have a
Material Impact on How Citi Records and Reports Its
Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
Citi is required to use certain assumptions and estimates in preparing its
financial statements under U.S. GAAP, including determining credit loss
reserves, reserves related to litigation and regulatory exposures, valuation of
DTAs and the fair values of certain assets and liabilities, among other items.
If Citi’s assumptions or estimates underlying its financial statements are
incorrect or differ from actual future events, Citi could experience unexpected
losses, some of which could be significant.
Moreover, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is currently
reviewing, or has proposed or issued, changes to several financial accounting
and reporting standards that govern key aspects of Citi’s financial statements
or interpretations thereof, including those areas where Citi is required to
make assumptions or estimates. For example, the FASB has proposed a new
accounting model intended to require earlier recognition of credit losses
on financial instruments. The proposed accounting model would require
that lifetime “expected credit losses” on financial assets not recorded at fair
value through net income, such as loans and held-to-maturity securities, be
recorded at inception of the financial asset, replacing the multiple existing
impairment models under U.S. GAAP which generally require that a loss be
“incurred” before it is recognized. For additional information on this and
other proposed changes, see Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Changes to financial accounting or reporting standards or interpretations,
whether promulgated or required by the FASB or other regulators, could
present operational challenges and could require Citi to change certain of
the assumptions or estimates it previously used in preparing its financial
statements, which could negatively impact how it records and reports its
financial condition and results of operations generally and/or with respect
to particular businesses. In addition, the FASB is seeking to converge U.S.
GAAP with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to the extent
IFRS provides an improvement to accounting standards. Any transition to
IFRS could further have a material impact on how Citi records and reports
its financial results. For additional information on the key areas for which
assumptions and estimates are used in preparing Citi’s financial statements,
see “Significant Accounting Policies and Significant Estimates” below and
Note 28 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.