Citibank 2014 Annual Report Download - page 110
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 110 of the 2014 Citibank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327
 |
 |
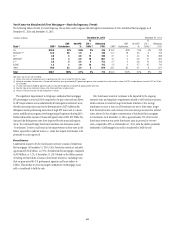
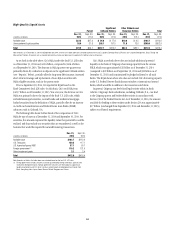
93
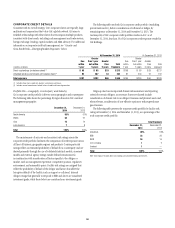
MARKET RISK
Market risk encompasses funding and liquidity risk and price risk, each
of which arises in the normal course of business of a global financial
intermediary such as Citi.
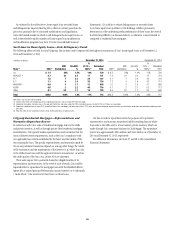
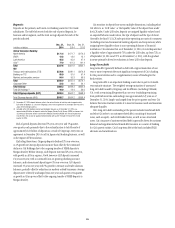
Market Risk Management
Each business is required to establish, with approval from Citi’s market risk
management, a market risk limit framework for identified risk factors that
clearly defines approved risk profiles and is within the parameters of Citi’s
overall risk tolerance. These limits are monitored by independent market
risk, Citi’s country and business Asset and Liability Committees and the
Citigroup Asset and Liability Committee. In all cases, the businesses are
ultimately responsible for the market risks taken and for remaining within
their defined limits.
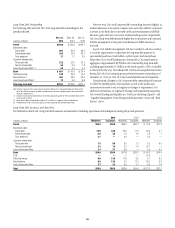
Funding and Liquidity Risk
Adequate liquidity and sources of funding are essential to Citi’s businesses.
Funding and liquidity risks arise from several factors, many of which Citi
cannot control, such as disruptions in the financial markets, changes in key
funding sources, credit spreads, changes in Citi’s credit ratings and political
and economic conditions in certain countries. For additional information,
see “Risk Factors” above.
Overview
Citi’s funding and liquidity objectives are to maintain adequate liquidity
to (i) fund its existing asset base; (ii) grow its core businesses in Citicorp;
(iii) maintain sufficient liquidity, structured appropriately, so that it can
operate under a wide variety of market conditions, including market
disruptions for both short- and long-term periods; and (iv) satisfy regulatory
requirements. Citigroup’s primary liquidity objectives are established by
entity, and in aggregate, across three major categories:
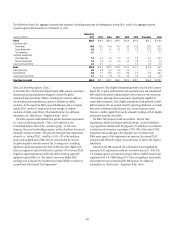
• the parent entity, which includes the parent holding company (Citigroup)
and Citi’s broker-dealer subsidiaries that are consolidated into Citigroup
(collectively referred to in this section as “parent”);
• Citi’s significant Citibank entities, which consist of Citibank, N.A.
units domiciled in the U.S., Western Europe, Hong Kong, Japan and
Singapore (collectively referred to in this section as “significant Citibank
entities”); and
• other Citibank and Banamex entities.
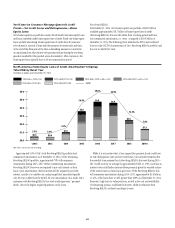
At an aggregate level, Citigroup’s goal is to maintain sufficient funding
in amount and tenor to fully fund customer assets and to provide an
appropriate amount of cash and high quality liquid assets (as discussed
further below), even in times of stress. The liquidity framework provides that
entities be self-sufficient or net providers of liquidity, including in conditions
established under their designated stress tests.
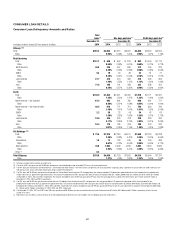
Citi’s primary sources of funding include (i) deposits via Citi’s bank
subsidiaries, which are Citi’s most stable and lowest cost source of long-
term funding, (ii) long-term debt (primarily senior and subordinated
debt) primarily issued at the parent and certain bank subsidiaries, and
(iii) stockholders’ equity. These sources may be supplemented by short-term
borrowings, primarily in the form of secured funding transactions.
As referenced above, Citigroup works to ensure that the structural tenor of
these funding sources is sufficiently long in relation to the tenor of its asset
base. The goal of Citi’s asset/liability management is to ensure that there is
excess tenor in the liability structure so as to provide excess liquidity after
funding the assets. The excess liquidity resulting from a longer-term tenor
profile can effectively offset potential decreases in liquidity that may occur
under stress. This excess funding is held in the form of high-quality liquid
assets (HQLA), as set forth in the table below.
