Capital One 2010 Annual Report Download - page 99
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 99 of the 2010 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
79
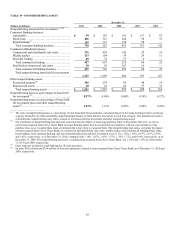
Table 37: Interest Rate Sensitivity Analysis
December 31,
2010 2009
Impact to projected base-line net interest income:
+ 200 basis points(1) ...................................................................... (0.7)% (0.4)%
- 50 basis points(1) ........................................................................ (0.2) (0.1)
Impact to economic value of equity:
+ 200 basis points(2) ...................................................................... (3.8)% (3.2)%
- 50 basis points(2) ........................................................................ 0.1 0.3
________________________
(1) These sensitivities include our net interest income and mortgage servicing rights valuation change (net of hedges). For net interest income, the
rate scenarios are based on a hypothetical gradual increase in interest rates of 200 basis points and a hypothetical gradual decrease of 50 basis
points to forward rates over the next 9 months. For the mortgage servicing rights valuation change (net of hedges), the rate scenarios are based
on a hypothetical instantaneous parallel rate shock of plus 200 basis points and minus 50 basis points to spot rates.
(2) Based on a hypothetical instantaneous parallel shift in the level of interest rates of plus 200 basis points and minus 50 basis points to spot rates.
The interest rate risk models that we use in deriving these measures incorporate contractual information, internally-developed
assumptions and proprietary modeling methodologies, which project borrower and deposit behavior patterns in certain interest rate
environments. Other market inputs, such as interest rates, market prices and interest rate volatility, are also critical components of our
interest rate risk measures. We regularly evaluate, update and enhance these assumptions, models and analytical tools as we believe
appropriate to reflect our best assessment of the market environment and the expected behavior patterns of our existing assets and
liabilities.
There are inherent limitations in any methodology used to estimate the exposure to changes in market interest rates. The above
sensitivity analyses contemplate only certain movements in interest rates and are performed at a particular point in time based on the
existing balance sheet, and do not incorporate other factors that may have a significant effect, most notably future business activities
and strategic actions that management may take to manage interest rate risk. Actual earnings and economic value of equity could
differ from the above sensitivity analyses.
Foreign Exchange Risk
We are exposed to changes in foreign exchange rates, which may impact the earnings of our foreign operations. Our asset/liability
management policy requires that we use derivatives to hedge material foreign currency denominated transactions to limit our earnings
exposure to foreign exchange risk. The estimated reduction in our 12-month earnings due to adverse foreign exchange rate movements
corresponding to a 95% probability was less than 2% as of December 31, 2010 and 2009. The precision of this estimate is limited due
to the inherent uncertainty of the underlying forecast assumptions.
Derivative Instruments
Derivatives are one of the primary tools we use in managing interest rate and foreign exchange risk. We execute our derivative
contracts in both over-the-counter and exchange-traded derivative markets. Although the majority of our derivatives are interest rate
swaps, we also use a variety of other derivative instruments, including caps, floors, options, futures and forward contracts, to manage
our interest rate and foreign currency risk. The outstanding notional amount of our derivative contracts totaled $50.8 billion as of
December 31, 2010, compared with $59.2 billion as of December 31, 2009. See “Note 11—Derivative Instruments and Hedging
Activities” for additional information on our derivatives activity.