Capital One 2012 Annual Report Download - page 230
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 230 of the 2012 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
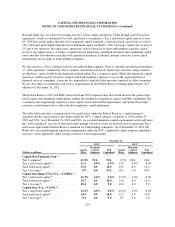
CAPITAL ONE FINANCIAL CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
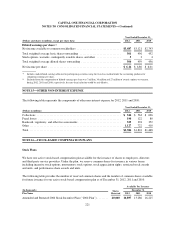
NOTE 11—DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
Use of Derivatives
We manage our asset/liability position and market risk exposure in accordance with prescribed risk management
policies and limits established by our Asset Liability Management Committee and approved by our Board of
Directors. Our primary market risk stems from the impact on our earnings and economic value of equity from
changes in interest rates, and to a lesser extent, changes in foreign exchange rates. We manage our interest rate
sensitivity through several approaches, which include, but are not limited to, changing the maturity and re-pricing
characteristics of various balance sheet categories and by entering into interest rate derivatives. Derivatives are
also utilized to manage our exposure to changes in foreign exchange rates. Derivative instruments may be
privately negotiated contracts, which are often referred to as over-the-counter (“OTC”) derivatives, or they may
be listed and traded on an exchange. We execute our derivative contracts in both the OTC and exchange-traded
derivative markets. In addition to interest rate swaps, we use a variety of other derivative instruments, including
caps, floors, options, futures and forward contracts, to manage our interest rate and foreign currency risk. On a
regular basis, we enter into customer derivative transactions. We engage in these transactions as a service to our
commercial banking customers to facilitate their risk management objectives. We typically offset the market risk
exposure to our customer-accommodation derivatives through derivative transactions with other counterparties.
Accounting for Derivatives
We account for derivatives pursuant to the accounting standards for derivatives and hedging activities. The
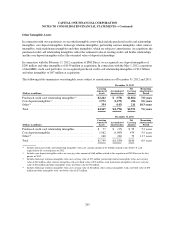
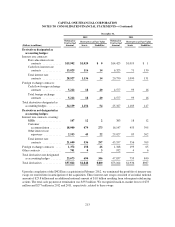
outstanding notional amount of our derivative contracts totaled $57.8 billion as of December 31, 2012, compared
with $73.2 billion as of December 31, 2011. The decrease was due primarily to the termination of hedges
associated with the ING Direct acquisition. The notional amount provides an indication of the volume of our
derivatives activity and is used as the basis on which interest and other payments are determined; however, it is
generally not the amount exchanged. Derivatives are recorded at fair value in our consolidated balance sheets.
The fair value of a derivative represents our estimate of the amount at which a derivative could be exchanged in
an orderly transaction between market participants. We report derivatives in a gain position, or derivative assets,
in our consolidated balance sheets as a component of other assets. We report derivatives in a loss position, or
derivative liabilities, in our consolidated balance sheets as a component of other liabilities. We report derivative
asset and liability amounts on a gross basis based on individual contracts, which does not take into consideration
the effects of master counterparty netting agreements or collateral netting. The fair value of derivative assets and
derivative liabilities reported in our consolidated balance sheets was $1.8 billion and $400 million, respectively,
as of December 31, 2012, compared with $1.9 billion and $987 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2011.
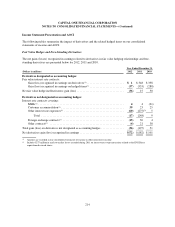
Our derivatives are designated as either qualifying accounting hedges or free-standing derivatives. Free-standing
derivatives consist of customer-accommodation derivatives and economic hedges that we enter into for risk
management purposes that are not linked to specific assets or liabilities or to forecasted transactions and,
therefore, do not qualify for hedge accounting. Qualifying accounting hedges are designated as fair value hedges,
cash flow hedges or net investment hedges.
•Fair Value Hedges: We designate derivatives as fair value hedges to manage our exposure to changes in the
fair value of certain financial assets and liabilities, which fluctuate in value as a result of movements in
interest rates. Changes in the fair value of derivatives designated as fair value hedges are recorded in
earnings together with offsetting changes in the fair value of the hedged item and any resulting
ineffectiveness. Our fair value hedges consist of interest rate swaps that are intended to modify our exposure
to interest rate risk on various fixed rate senior notes, subordinated notes, securitization debt, and brokered
211