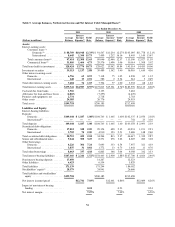
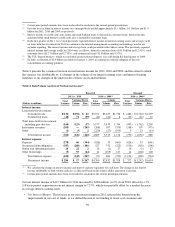
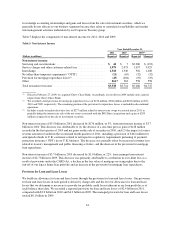
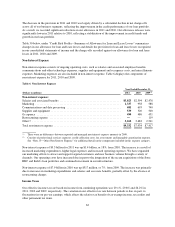
Capital One 2011 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2011 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.International reporting unit being at the low end of this range. As such, none of our reporting units was at risk of
failing step one of the impairment test. Accordingly, the goodwill for each of our reporting units was considered
not impaired. Therefore, the second step of impairment testing was not required.
As part of the annual goodwill impairment test, we assessed our market capitalization based on the average
market price relative to the aggregate fair value of our reporting units and determined that any excess fair value
in our reporting units at that time could be attributed to a reasonable control premium compared to historical
control premiums seen in the industry. Continued market volatility and uncertainty regarding overall economic
conditions have led to a decline in market capitalization in recent years resulting in significantly higher control
premiums than what had been seen historically. We will continue to regularly monitor our market capitalization
in 2012, overall economic conditions and other events or circumstances that may result in an impairment of
goodwill in the future.
Intangible assets with definite useful lives are amortized over their estimated lives and evaluated for potential
impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances suggest that an asset’s or asset group’s carrying value
may not be fully recoverable. An impairment loss, generally calculated as the difference between the estimated
fair value and the carrying value of an asset or asset group, is recognized if the sum of the estimated
undiscounted cash flows relating to the asset or asset group is less than the corresponding carrying value. We did
not recognize impairment on our other intangible assets in 2011, 2010 or 2009.
We provide additional information on the nature of and accounting for goodwill and intangible assets, including
the process and methodology used to conduct goodwill impairment testing, in “Note 8—Goodwill and Other
Intangible Assets.”
Fair Value
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly
transaction between market participants on the measurement date (also referred to as an exit price). The fair value
accounting guidance provides a three-level fair value hierarchy for classifying financial instruments. This
hierarchy is based on whether the inputs to the valuation techniques used to measure fair value are observable or
unobservable. Fair value measurement of a financial asset or liability is assigned to a level based on the lowest
level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. The three levels of the fair value
hierarchy are described below:
Level 1: Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Observable market-based inputs, other than quoted prices in active markets for identical
assets or liabilities.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs.
The degree of management judgment involved in determining the fair value of a financial instrument is
dependent upon the availability of quoted prices in active markets or observable market parameters. When
quoted prices and observable data in active markets are not fully available, management judgment is necessary to
estimate fair value. Changes in market conditions, such as reduced liquidity in the capital markets or changes in
secondary market activities, may reduce the availability and reliability of quoted prices or observable data used
to determine fair value.
We have developed policies and procedures to determine when markets for our financial assets and liabilities are
inactive if the level and volume of activity has declined significantly relative to normal conditions. If markets are
determined to be inactive, it may be appropriate to adjust price quotes received. When significant adjustments are
required to price quotes or inputs, it may be appropriate to utilize an estimate based primarily on unobservable
inputs.
52