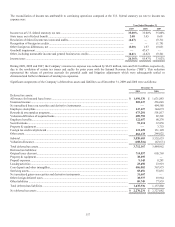
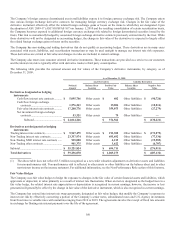
Capital One 2009 Annual Report Download - page 174
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 174 of the 2009 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report. 161
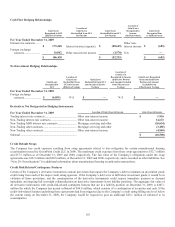
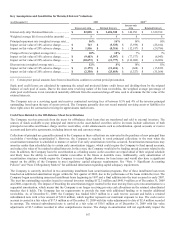
During 2009, the Company entered into interest rate swap agreements, also designated as fair value hedges that modify the
Company’s exposure to interest rate risk by effectively converting a portion of the Company’s brokered CD liabilities from fixed rate
to variable rates with maturities ranging from 2010 to 2018. The agreements involve the receipt of fixed rate amounts in exchange for
floating rate interest payments over the life of the agreement.
The Company has entered into forward exchange contracts to hedge foreign currency denominated investments against fluctuations in
exchange rates. The purpose of the Company’s foreign currency hedging activities is to protect the Company from the risk of adverse
effects of movements in exchange rates.
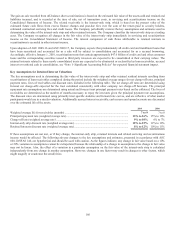
Cash Flow Hedges
The Company uses cash flow hedges to hedge the exposure to variability in the cash flows of a forecasted transaction. Changes in fair
value of derivatives designated as cash flow hedges are recognized in other comprehensive income, a separate component of
stockholders’ equity. The Company has entered into interest rate swap agreements, designated as cash flow hedges, that effectively
modify the Company’s exposure to interest rate risk by converting floating rate debt to a fixed rate debt with maturities ranging from
2010 to 2013. The agreements involve the receipt of floating rate amounts in exchange for fixed rate interest payments over the life of
the agreement.
The Company has also entered into interest rate swap agreements, designated as cash flow hedges, that effectively modify the
Company’s exposure to interest rate risk by converting floating rate assets to fixed rate assets, with maturities in 2013. The agreements
involve the receipt of fixed rate amounts in exchange for floating rate interest payments over the life of the agreements.
The Company has entered into forward exchange contracts to reduce the Company’s sensitivity to foreign currency exchange rate
changes on its foreign currency denominated loans. The forward rate agreements allow the Company to “lock-in” functional currency
equivalent cash flows associated with the foreign currency denominated loans.
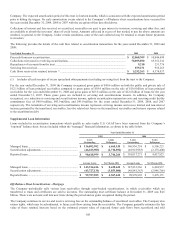
At December 31, 2009, the Company expects to reclassify $25.8 million of net losses, after tax, on derivative instruments from
accumulated other comprehensive income to earnings during the next 12 months terminated swaps are amortized and as interest
payments and receipts on derivative instruments occur. This amount could change in future periods if the Company decides to
terminate additional swaps in the context of managing its overall market risk profile.
Hedge of Net Investment in Foreign Operations
The Company uses forward exchange contracts to protect the value of its investment in its foreign subsidiaries. Realized and
unrealized foreign currency gains and losses from these hedges are not included in the income statement, but are shown in the
translation adjustments in other comprehensive income. The purpose of these hedges is to protect against adverse movements in
exchange rates.
Trading Interest Rate Contracts
The Company enters into customer-oriented derivative financial instruments, including interest rate swaps, options, caps, floors, and
foreign exchange contracts. These customer-oriented positions may be matched with offsetting positions to minimize risk to the
Company.
These derivatives do not qualify as accounting hedges and are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value with changes in value
included in current earnings in non-interest income.
Non-Trading Interest Rate Contracts
The Company uses interest rate swaps to manage interest rate sensitivity related to the Company’s non-mortgage securitization
programs. The Company enters into interest rate swaps with its securitization trust and essentially offsets the derivative with separate
interest rate swaps with third parties. The Company is exposed to higher credit risk related to interest rate swaps with the trust, and has
charged a higher rate to offset this risk. The trust is unable to post collateral because of its QSPE status. At December 31, 2009, the
Company had a $22.3 million valuation allowance on the derivative receivable from the trust, representing counterparty credit risk.
Upon consolidation of the trust on January 1, 2010 due to the adoption of AU 2009-17 (ASC 810/SFAS 167), the interest rate swap
agreements between the Company and its credit card master trust will be considered intercompany agreements and any related
receivables and payables are eliminated in consolidation. On December 31, 2009, the interest rate swaps with third parties were
terminated and replaced with similar agreements at current fixed interest rates. The replacement interest rate swaps will be designated
as cash flow hedges converting floating rate debt of the trust to fixed rate debt in connection with the consolidation of the trust, and
the corresponding debt securities issued to third parties. See “Note 1- Significant Accounting Policies” for additional information.