Capital One 2009 Annual Report Download - page 173
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 173 of the 2009 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
160
The Company’s foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities expose it to foreign currency exchange risk. The Company enters
into various foreign exchange derivative contracts for managing foreign currency exchange risk. Changes in the fair value of the
derivative instrument effectively offset the related foreign exchange gains or losses on the items to which they are designated. Upon
the adoption of ASU 2009-17 (ASC 810/SFAS 167) on January 1, 2010 and the resulting consolidation of certain securitization trusts,
the Company becomes exposed to additional foreign currency exchange risk related to foreign denominated securities issued by the
trusts. That risk is economically hedged by associated foreign exchange derivative contracts previously entered into by the trust. While
those derivatives will not be designated as accounting hedges, the change in fair value of the derivatives is expected to largely offset
the related foreign exchange gains or losses on the securities.
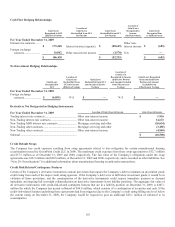
The Company has non-trading and trading derivatives that do not qualify as accounting hedges. These derivatives are in many cases
associated with assets, liabilities, and securitization transactions or may be used outright to manage our interest rate risk exposures.
These derivatives are carried at fair value and changes in value are included in current earnings.
The Company also enters into customer oriented derivative instruments. These transactions are provided as a service to our customers
and the interest rate risk is typically offset with derivative trades to third party counterparties.
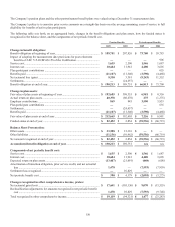
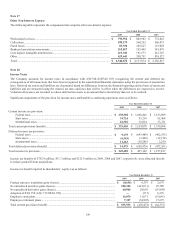
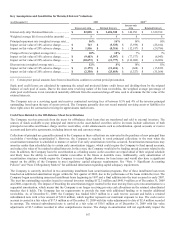
The following table provides the notional amount and fair values of the Company’s derivative instruments, by category, as of
December 31, 2009:
As of December 31, 2009
Asset Derivatives Liability Derivatives
Notional
Amount Balance Sheet
Location Positive Fair
Value Balance Sheet
Location
Negative Fair
Value
Derivatives designated as hedging
instruments
Cash flow interest rate contracts ..........
.
$ 5,095,786 Other assets $ 402 Other liabilities $ (90,726)
Cash flow foreign exchange
contracts ..........................................
.
1,576,363 Other assets 15,006 Other liabilities (12,216)
Fair value interest rate contracts ..........
.
17,288,776 Other assets 359,075 Other liabilities (27,279)
Net investment foreign exchange
contracts ..........................................
.
53,321 Other assets 79 Other liabilities —
Subtotal ......................................
.
$ 24,014,246 $ 374,562 $ (130,221)
Derivatives not designated as hedging
instruments
Trading interest rate contracts .......................
.
$ 9,967,475 Other assets $ 193,382 Other liabilities $ (173,279)
N
on-Trading interest rate contracts ...............
.
23,337,974 Other assets 493,492 Other liabilities (77,336)
N
on-Trading MSR interest rate contracts .....
.
935,000 Other assets 4,215 Other liabilities (19,589)
N
on-Trading other contracts .........................
.
981,375 Other assets 3,622 Other liabilities (6,707)
Subtotal .........................................................
.
$ 35,221,824 $ 694,711 $ (276,911)
Total derivatives $ 59,236,070 $ 1,069,273 $ (407,132)
(1) The above table does not reflect $3.5 million recognized as a net credit valuation adjustment on derivative assets and liabilities
for non-performance risk. Non-performance risk is reflected in other assets or other liabilities on the balance sheet and in other
non-interest income on the income statement. For additional information, see the Non-Performance Risk section of this footnote.
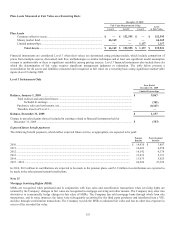
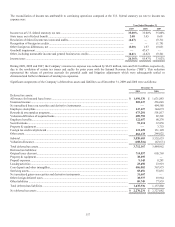
Fair Value Hedges
The Company uses fair value hedges to hedge the exposure to changes in the fair value of certain financial assets and liabilities, which
appreciate or depreciate in value primarily as a result of interest rate fluctuations. When an item is designated as the hedged item in a
fair value hedge, the related interest rate appreciation or depreciation is recognized in current earnings; however, the income or loss
generated will generally be offset by the change in fair value of the derivative instrument, which is also recognized in current earnings.
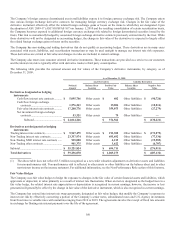
The Company has entered into interest rate swap agreements, designated as fair value hedges, that modify the Company’s exposure to
interest rate risk by effectively converting a portion of the Company’s senior notes, subordinated notes and U.S. Agency investments
from fixed rates to variable rates with maturities ranging from 2010 to 2019. The agreements involve the receipt of fixed rate amounts
in exchange for floating rate interest payments over the life of the agreement.