PNC Bank 2011 Annual Report Download - page 186
Download and view the complete annual report
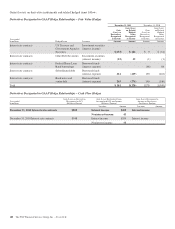
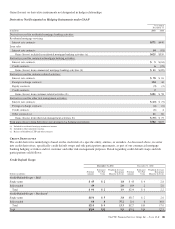
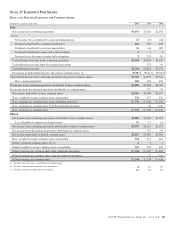
Please find page 186 of the 2011 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Net Investment Hedges
We enter into foreign currency forward contracts to hedge
non-U.S. Dollar (USD) net investments in foreign subsidiaries
against adverse changes in foreign exchange rates. We assess
whether the hedging relationship is highly effective in
achieving offsetting changes in the value of the hedge and
hedged item by qualitatively verifying the critical terms of the
hedge and hedged item match at the inception of the hedging
relationship and on an ongoing basis. There were no
components of derivative gains or losses excluded from the
assessment of the hedge effectiveness.
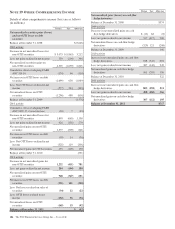
At December 31, 2011, there was no net investment hedge
ineffectiveness and the loss recognized in Accumulated other
comprehensive income was less than $1 million to PNC’s
results of operations.
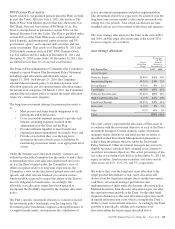
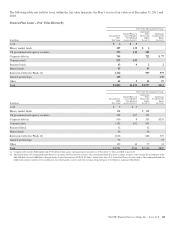
Further detail regarding the notional amounts, fair values and
gains and losses recognized related to derivatives used in fair
value and cash flow hedge strategies is presented in the tables
that follow.
D
ERIVATIVES
N
OT
D
ESIGNATED IN
H
EDGE
R
ELATIONSHIPS
We also enter into derivatives that are not designated as
accounting hedges under GAAP.
The majority of these derivatives are used to manage risk
related to residential and commercial mortgage banking
activities and are considered economic hedges. Although these
derivatives are used to hedge risk, they are not designated as
accounting hedges because the contracts they are hedging are
typically also carried at fair value on the balance sheet,
resulting in symmetrical accounting treatment for both the
hedging instrument and the hedged item.
Our residential mortgage banking activities consist of
originating, selling and servicing mortgage loans. Residential
mortgage loans that will be sold in the secondary market, and
the related loan commitments, which are considered
derivatives, are accounted for at fair value. Changes in the fair
value of the loans and commitments due to interest rate risk
are hedged with forward loan sale contracts as well as US
Treasury and Eurodollar futures and options. Gains and losses
on the loans and commitments held for sale and the
derivatives used to economically hedge them are included in
residential mortgage noninterest income on the Consolidated
Income Statement.
We typically retain the servicing rights related to residential
mortgage loans that we sell. Residential mortgage servicing
rights are accounted for at fair value with changes in fair value
influenced primarily by changes in interest rates. Derivatives
used to hedge the fair value of residential mortgage servicing
rights include interest rate futures, swaps, options (including
caps, floors, and swaptions), and forward contracts to
purchase mortgage-backed securities. Gains and losses on
residential mortgage servicing rights and the related
derivatives used for hedging are included in Residential
mortgage noninterest income.
Certain commercial mortgage loans are also sold into the
secondary market as part of our commercial mortgage banking
activities and the loans, and the related loan commitments,
which are considered derivatives, are accounted for at fair
value. Derivatives used to economically hedge these loans and
commitments from changes in fair value due to interest rate
risk and credit risk include forward loan sale contracts,
interest rate swaps, and credit default swaps. Gains and losses
on the commitments, loans and derivatives are included in
Other noninterest income.
The residential and commercial loan commitments associated
with loans to be sold which are accounted for as derivatives
are valued based on the estimated fair value of the underlying
loan and the probability that the loan will fund within the
terms of the commitment. The fair value also takes into
account the fair value of the embedded servicing right.
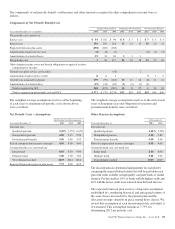
We offer derivatives to our customers in connection with their
risk management needs. These derivatives primarily consist of
interest rate swaps, interest rate caps, floors, swaptions,
foreign exchange contracts, and equity contracts. We
primarily manage our market risk exposure from customer
transactions by entering into a variety of hedging transactions
with third-party dealers. Gains and losses on customer-related
derivatives are included in Other noninterest income.
The derivatives portfolio also includes derivatives used for
other risk management activities. These derivatives are
entered into based on stated risk management objectives.
This segment of the portfolio includes credit default swaps
(CDS) used to mitigate the risk of economic loss on a portion
of our loan exposure. We also sell loss protection to mitigate
the net premium cost and the impact of mark-to-market
accounting on CDS purchases to hedge the loan portfolio. The
fair values of these derivatives typically are based on related
credit spreads. Gains and losses on the derivatives entered into
for other risk management are included in Other noninterest
income.
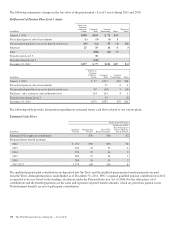
Included in the customer, mortgage banking risk management,
and other risk management portfolios are written interest-rate
caps and floors entered into with customers and for risk
management purposes. We receive an upfront premium from
the counterparty and are obligated to make payments to the
counterparty if the underlying market interest rate rises above
or falls below a certain level designated in the contract. At
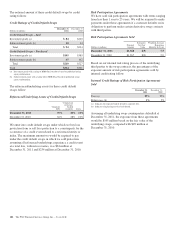
December 31, 2011, the fair value of the written caps and
floors liability on our Consolidated Balance Sheet was $6
million compared with $15 million at December 31, 2010. Our
ultimate obligation under written options is based on future
market conditions and is only quantifiable at settlement.
The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. – Form 10-K 177