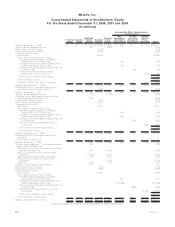
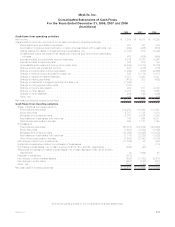
MetLife 2008 Annual Report Download - page 137
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 137 of the 2008 MetLife annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.policyholder benefits and claims. Additionally, the Company may elect to carry an entire contract on the balance sheet at estimated fair
value, with changes in estimated fair value recognized in the current period in net investment gains (losses) or in policyholder benefits and
claims if that contract contains an embedded derivative that requires bifurcation. There is a risk that embedded derivatives requiring
bifurcation may not be identified and reported at estimated fair value in the consolidated financial statements and that their related changes
in estimated fair value could materially affect reported net income.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with an original or remaining maturity of three months or less at the date
of purchase to be cash equivalents.
Property, Equipment, Leasehold Improvements and Computer Software
Property, equipment and leasehold improvements, which are included in other assets, are stated at cost, less accumulated depre-
ciation and amortization. Depreciation is determined using either the straight-line or sum-of-the-years-digits method over the estimated
useful lives of the assets, as appropriate. The estimated life for company occupied real estate property is generally 40 years. Estimated
lives generally range from five to ten years for leasehold improvements and three to seven years for all other property and equipment. The
cost basis of the property, equipment and leasehold improvements was $1.8 billion and $1.6 billion at December 31, 2008 and 2007,
respectively. Accumulated depreciation and amortization of property, equipment and leasehold improvements was $926 million and
$810 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Related depreciation and amortization expense was $150 million, $132 million
and $125 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Computer software, which is included in other assets, is stated at cost, less accumulated amortization. Purchased software costs, as
well as certain internal and external costs incurred to develop internal-use computer software during the application development stage,
are capitalized. Such costs are amortized generally over a four-year period using the straight-line method. The cost basis of computer
software was $1.5 billion and $1.3 billion at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Accumulated amortization of capitalized software
was $1,002 million and $858 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Related amortization expense was $153 million,
$121 million and $109 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Deferred Policy Acquisition Costs and Value of Business Acquired
The Company incurs significant costs in connection with acquiring new and renewal insurance business. Costs that vary with and relate
to the production of new business are deferred as DAC. Such costs consist principally of commissions and agency and policy issuance
expenses. VOBA is an intangible asset that reflects the estimated fair value of in-force contracts in a life insurance company acquisition and
represents the portion of the purchase price that is allocated to the value of the right to receive future cash flows from the business in-force
at the acquisition date. VOBA is based on actuarially determined projections, by each block of business, of future policy and contract
charges, premiums, mortality and morbidity, separate account performance, surrenders, operating expenses, investment returns and other
factors. Actual experience on the purchased business may vary from these projections. The recovery of DAC and VOBA is dependent upon
the future profitability of the related business. DAC and VOBA are aggregated in the financial statements for reporting purposes.
DAC for property and casualty insurance contracts, which is primarily composed of commissions and certain underwriting expenses, is
amortized on a pro rata basis over the applicable contract term or reinsurance treaty.
DAC and VOBA on life insurance or investment-type contracts are amortized in proportion to gross premiums, gross margins or gross
profits, depending on the type of contract as described below.
The Company amortizes DAC and VOBA related to non-participating and non-dividend-paying traditional contracts (term insurance,
non-participating whole life insurance, non-medical health insurance, and traditional group life insurance) over the entire premium paying
period in proportion to the present value of actual historic and expected future gross premiums. The present value of expected premiums is
based upon the premium requirement of each policy and assumptions for mortality, morbidity, persistency, and investment returns at policy
issuance, or policy acquisition, as it relates to VOBA, that include provisions for adverse deviation and are consistent with the assumptions
used to calculate future policyholder benefit liabilities. These assumptions are not revised after policy issuance or acquisition unless the
DAC or VOBA balance is deemed to be unrecoverable from future expected profits. Absent a premium deficiency, variability in amortization
after policy issuance or acquisition is caused only by variability in premium volumes.
The Company amortizes DAC and VOBA related to participating, dividend-paying traditional contracts over the estimated lives of the
contracts in proportion to actual and expected future gross margins. The amortization includes interest based on rates in effect at inception
or acquisition of the contracts. The future gross margins are dependent principally on investment returns, policyholder dividend scales,
mortality, persistency, expenses to administer the business, creditworthiness of reinsurance counterparties, and certain economic
variables, such as inflation. For participating contracts (dividend paying traditional contracts within the closed block) future gross margins
are also dependent upon changes in the policyholder dividend obligation. Of these factors, the Company anticipates that investment
returns, expenses, persistency, and other factor changes and policyholder dividend scales are reasonably likely to impact significantly the
rate of DAC and VOBA amortization. Each reporting period, the Company updates the estimated gross margins with the actual gross
margins for that period. When the actual gross margins change from previously estimated gross margins, the cumulative DAC and VOBA
amortization is re- estimated and adjusted by a cumulative charge or credit to current operations. When actual gross margins exceed those
previously estimated, the DAC and VOBA amortization will increase, resulting in a current period charge to earnings. The opposite result
occurs when the actual gross margins are below the previously estimated gross margins. Each reporting period, the Company also
updates the actual amount of business in-force, which impacts expected future gross margins. When expected future gross margins are
below those previously estimated, the DAC and VOBA amortization will increase, resulting in a current period charge to earnings. The
opposite result occurs when the expected future gross margins are above the previously estimated expected future gross margins. Total
DAC and VOBA amortization during a particular period may increase or decrease depending upon the relative size of the amortization
F-14 MetLife, Inc.
MetLife, Inc.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)