MetLife 2012 Annual Report Download - page 74
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 74 of the 2012 MetLife annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Hedging Activities. We use derivative contracts primarily to hedge a wide range of risks including interest rate risk, foreign currency exchange rate
risk, and equity market risk. Derivative hedges are designed to reduce risk on an economic basis while considering their impact on accounting results
and GAAP and Statutory capital. The construction of our derivative hedge programs vary depending on the type of risk being hedged. Some hedge
programs are asset or liability specific while others are portfolio hedges that reduce risk related to a group of liabilities or assets. Our use of derivatives
by major hedge programs is as follows:
‰Risks Related to Living Guarantee Benefits — We use a wide range of derivative contracts to hedge the risk associated with variable annuity living
guarantee benefits. These hedges include equity and interest rate futures, interest rate swaps, currency futures/forwards, equity indexed options
and interest rate option contracts and equity variance swaps.
‰Minimum Interest Rate Guarantees — For certain liability contracts, we provide the contractholder a guaranteed minimum interest rate. These
contracts include certain fixed annuities and other insurance liabilities. We purchase interest rate floors to reduce risk associated with these liability
guarantees.
‰Reinvestment Risk in Long Duration Liability Contracts — Derivatives are used to hedge interest rate risk related to certain long duration liability
contracts, such as deferred annuities. Hedges include zero coupon interest rate swaps and swaptions.
‰Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk — We use currency swaps, forwards and options to hedge foreign currency exchange rate risk. These
hedges primarily swap foreign currency denominated bonds, investments in foreign subsidiaries or equity market exposures to U.S. dollars.
‰General ALM Hedging Strategies — In the ordinary course of managing our asset/liability risks, we use interest rate futures, interest rate swaps,
interest rate caps, interest rate floors and inflation swaps. These hedges are designed to reduce interest rate risk or inflation risk related to the
existing assets or liabilities or related to expected future cash flows.
Risk Measurement: Sensitivity Analysis
We measure market risk related to our market sensitive assets and liabilities based on changes in interest rates, equity market prices and foreign
currency exchange rates utilizing a sensitivity analysis. This analysis estimates the potential changes in estimated fair value based on a hypothetical 10%
change (increase or decrease) in interest rates, equity market prices and foreign currency exchange rates. We believe that a 10% change (increase or
decrease) in these market rates and prices is reasonably possible in the near-term. In performing the analysis summarized below, we use market rates
at December 31, 2012. The sensitivity analysis separately calculates each of our market risk exposures (interest rate, equity market and foreign currency
exchange rate) relating to our trading and non-trading assets and liabilities. We modeled the impact of changes in market rates and prices on the
estimated fair values of our market sensitive assets and liabilities as follows:
‰the net present values of its interest rate sensitive exposures resulting from a 10% change (increase or decrease) in interest rates;
‰the U.S. dollar equivalent estimated fair values of our foreign currency exposures due to a 10% change (increase or decrease) in foreign currency
exchange rates; and
‰the estimated fair value of its equity positions due to a 10% change (increase or decrease) in equity market prices.
The sensitivity analysis is an estimate and should not be viewed as predictive of our future financial performance. We cannot ensure that our actual
losses in any particular period will not exceed the amounts indicated in the table below. Limitations related to this sensitivity analysis include:
‰the market risk information is limited by the assumptions and parameters established in creating the related sensitivity analysis, including the
impact of prepayment rates on mortgage loans;
‰for the derivatives that qualify as hedges, the impact on reported earnings may be materially different from the change in market values;
‰the analysis excludes liabilities pursuant to insurance contracts and real estate holdings; and
‰the model assumes that the composition of assets and liabilities remains unchanged throughout the period.
Accordingly, we use such models as tools and not as substitutes for the experience and judgment of our management. Based on our analysis of the
impact of a 10% change (increase or decrease) in market rates and prices, we have determined that such a change could have a material adverse
effect on the estimated fair value of certain assets and liabilities from interest rate, foreign currency exchange rate and equity market exposures.
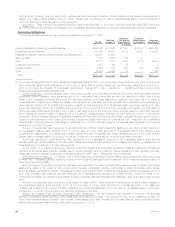
The table below illustrates the potential loss in estimated fair value for each market risk exposure of our market sensitive assets and liabilities at
December 31, 2012:
December 31, 2012
(In millions)
Non-trading:
Interest rate risk ........................................................................... $5,996
Foreign currency exchange rate risk ........................................................... $6,553
Equity market risk ......................................................................... $ 319
Trading:
Interest rate risk ........................................................................... $ 5
Foreign currency exchange rate risk ........................................................... $ 19
68 MetLife, Inc.