Sallie Mae 2005 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2005 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.56
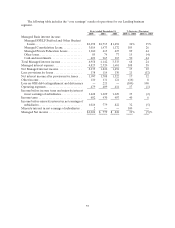
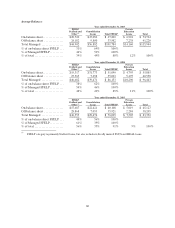
supplemented by our direct-to-consumer Private Education Loans channel. The Private Education Loan
portfolio grew by 43 percent in 2005 to $16.4 billion and now represents 13 percent of our Managed
student loan portfolio, up from 11 percent in 2004.
Private Education Loans consist of two general types: those that meet the needs of borrowers at
higher education schools and other Title IV eligible schools, and those that are used to meet the needs of
students in alternative learning programs such as career training, distance learning and lifelong learning
programs. Unlike FFELP loans, Private Education Loans are subject to the full credit risk of the borrower.
We manage this additional risk through clearly defined loan underwriting standards and a combination of
higher interest rates and loan origination fees that compensate us for the higher risk. As a result, we earn
higher spreads on Private Education Loans than on FFELP loans. Private Education Loans will continue
to be an important driver of future earnings growth as the demand for post-secondary education grows and
costs increase much faster than increases in federal loan limits.
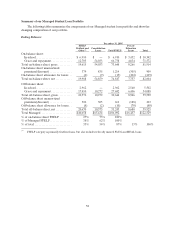
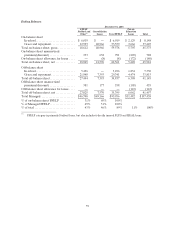
We also originate lesser quantities of mortgage and consumer loans with the intent of immediately
selling the majority of the mortgage loans. Mortgage and consumer loan originations and the mortgage
loan portfolio we hold were nine percent and one percent, respectively, of total loan originations and total
loans outstanding as of and for the year ended December 31, 2005.
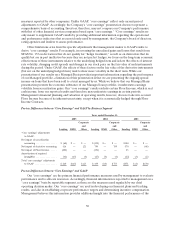
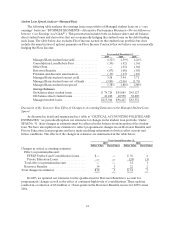
Student Loan Spread
An important performance measure closely monitored by management is the student loan spread.
The student loan spread is the difference between the income earned on the student loan assets and the
interest paid on the debt funding those assets. A number of factors can affect the overall student loan
spread such as:
•the mix of student loans in the portfolio, with Consolidation Loans having the lowest spread and
Private Education Loans having the highest spread;
•the premiums paid, borrower fees charged and capitalized costs incurred to acquire student loans
which impact the spread through subsequent amortization;
•the type and level of Borrower Benefits programs;
•the level of Floor Income; and when considering the “core earnings” managed spread, the amount
of Floor Income-eligible loans that have been hedged through Floor Income Contracts; and
•funding and hedging costs.
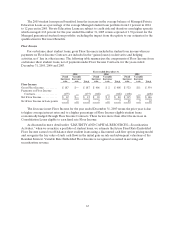
The student loan spread is highly susceptible to liquidity, funding and interest rate risk. These risks
are discussed separately at “LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES” and in the “RISK FACTORS”
discussion at the front of the document.