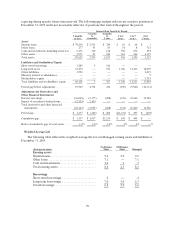
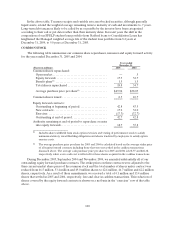
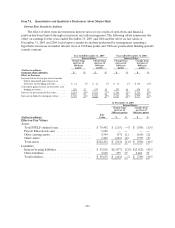
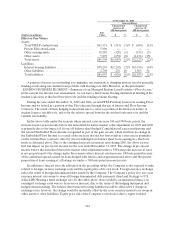
Sallie Mae 2005 Annual Report Download - page 104
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 104 of the 2005 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.94
Market and Interest Rate Risk
Market and interest rate risk is the risk of loss from adverse changes in market prices, interest rates,
and/or foreign currency exchange rates of our financial instruments. Our primary market risk is from
changes in interest rates and interest spreads. We have an active interest rate risk management program
that is designed to reduce our exposure to changes in interest rates and maintain consistent earning
spreads in all interest rate environments. We use derivative instruments extensively to hedge our interest
rate exposure, but there still is a risk that we are not hedging all potential interest rate exposures or that
the hedges do not perform as designed. We measure interest rate risk by calculating the variability of net
interest income in future periods under various interest rate scenarios using projected balances for interest
earning assets, interest-bearing liabilities and derivatives used to hedge interest rate risk. Many
assumptions are utilized by management to calculate the impact that changes in interest rates may have on
net interest income, the more significant of which are related to student loan volumes and pricing, the
timing of cash flows from our student loan portfolio, particularly the impact of Floor Income and the rate
of student loan consolidations, basis risk, credit spreads and the maturity of our debt and derivatives. (See
also “Interest Rate Risk Management.”)
Even though we believe our derivatives are economic hedges, changes in interest rates can cause
volatility in our earnings for the market value of our derivatives that do not qualify for hedge accounting
treatment under SFAS No. 133. Under SFAS No. 133, these changes in derivative market values are
recorded through earnings with no consideration for the corresponding change in the fair value of the
hedged item. As a result, our earnings are highly susceptible to changes in interest rates caused by these
one-sided marks-to-market. Changes in interest rates can also have a material effect on the amount of
Floor Income earned in our student loan portfolio and the valuation of our Retained Interest asset. Our
earnings can also be materially affected by changes in our estimate of the rate at which loans may prepay in
our portfolios as measured by the CPR. The value of the Retained Interests on FFELP Stafford
securitizations is particularly affected by the level of Consolidation Loan activity. We face a number of
other challenges and risks that can materially affect our future results such as changes in:
•applicable laws and regulations, which may change the volume, average term, effective yields and
refinancing options of student loans under the FFELP or provide advantages to competing FFELP
and non-FFELP loan providers;
•demand and competition for education financing;
•financing preferences of students and their families;
•borrower default rates on Private Education Loans;
•continued access to the capital markets for funding at favorable spreads particularly for our non-
federally insured Private Education Loan portfolio; and
•our operating execution and efficiencies, including errors, omissions, and effectiveness of internal
control.
Our foreign currency exchange rate exposure is the result of foreign denominated liabilities issued by
the Company. Cross-currency interest rate swaps are used to lock-in the exchange rate for the term of the
liability.
We are also subject to market risk relative to our equity forward contracts that allow us to repurchase
our common stock in the future from a third party at the market price at the time of entering the contract.
Should the market value of our stock fall below certain predetermined levels, the counterparty to the
contract has a right to terminate the contract and settle all or a portion at the original contract price. We
are required to mark our equity forwards to market, so decreases in our stock price could result in material
losses.