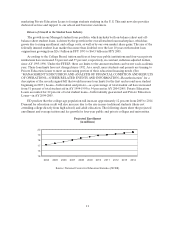
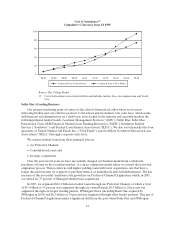
Sallie Mae 2005 Annual Report Download - page 12
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 12 of the 2005 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.2
This report contains forward-looking statements and information that are based on management’s
current expectations as of the date of this document. When used in this report, the words “anticipate,”
“believe,” “estimate,” “intend” and “expect” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-
looking statements. These forward-looking statements are subject to risks, uncertainties, assumptions and
other factors that may cause the actual results to be materially different from those reflected in such
forward-looking statements. These factors include, among others, changes in the terms of student loans
and the educational credit marketplace arising from the implementation of applicable laws and regulations
and from changes in these laws and regulations, which may reduce the volume, average term and costs of
yields on student loans under the Federal Family Education Loan Program (“FFELP”) or result in loans
being originated or refinanced under non-FFELP programs or may affect the terms upon which banks and
others agree to sell FFELP loans to SLM Corporation, more commonly known as Sallie Mae, and its
subsidiaries (collectively, “the Company”). In addition, a larger than expected increase in third party
consolidations of our FFELP loans could materially adversely affect our results of operations. The
Company could also be affected by changes in the demand for educational financing or in financing
preferences of lenders, educational institutions, students and their families; incorrect estimates or
assumptions by management in connection with the preparation of our consolidated financial statements;
changes in the composition of our Managed FFELP and Private Education Loan portfolios; a significant
decrease in our common stock price, which may result in counterparties terminating equity forward
positions with us, which, in turn, could have a materially dilutive effect on our common stock; changes in
the general interest rate environment and in the securitization markets for education loans, which may
increase the costs or limit the availability of financings necessary to initiate, purchase or carry education
loans; losses from loan defaults; changes in prepayment rates and credit spreads; and changes in the
demand for debt management services and new laws or changes in existing laws that govern debt
management services.
GLOSSARY
Listed below are definitions of key terms that are used throughout this document. See also
APPENDIX A, “FEDERAL FAMILY EDUCATION LOAN PROGRAM,” for a further discussion of
the FFELP.
Borrower Benefits—Borrower Benefits are financial incentives offered to borrowers who qualify
based on pre-determined qualifying factors, which are generally tied directly to making on-time monthly
payments. The impact of Borrower Benefits is dependent on the estimate of the number of borrowers who
will eventually qualify for these benefits and the amount of the financial benefit offered to the borrower.
We occasionally change Borrower Benefits programs in both amount and qualification factors. These
programmatic changes must be reflected in the estimate of the Borrower Benefits discount.
Consolidation Loans—Under both the FFELP and the William D. Ford Federal Direct Student Loan
Program (“FDLP”), borrowers with eligible student loans may consolidate them into one note with one
lender and convert the variable interest rates on the loans being consolidated into a fixed rate for the life
of the loan. The new note is considered a Consolidation Loan. Typically a borrower can consolidate his
student loans only once unless the borrower has another eligible loan to consolidate with the existing
Consolidation Loan. FFELP Consolidation Loan borrowers can reconsolidate their FFELP Consolidation
Loan into a FDLP Consolidation Loan under certain conditions. The borrower rate on a Consolidation
Loan is fixed for the term of the loan and is set by the weighted-average interest rate of the loans being
consolidated, rounded up to the nearest 1/8th of a percent, not to exceed 8.25 percent. In low interest rate
environments, Consolidation Loans provide an attractive refinancing opportunity to certain borrowers
because they allow borrowers to consolidate variable rate loans into a long-term fixed rate loan. Holders of
Consolidation Loans are eligible to earn interest under the Special Allowance Payment (“SAP”) formula
(see definition below).