Sallie Mae 2005 Annual Report Download - page 136
Download and view the complete annual report
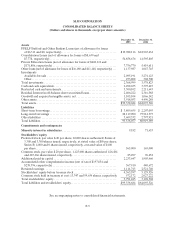
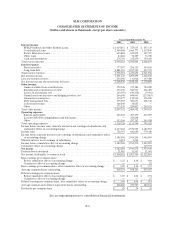
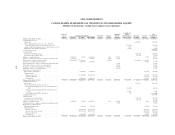
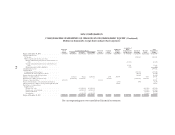
Please find page 136 of the 2005 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SLM CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts, unless otherwise stated)
F-14
2. Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
investment in order to allow for an anticipated recovery in market value. If, based on the analysis, it is
determined that the impairment is other than temporary, the investment is written down to fair value and a
loss is recognized through earnings. Securities classified as trading are accounted for at fair market value
with unrealized gains and losses included in investment income. Securities that the Company has the intent
and ability to hold to maturity are classified as held-to-maturity and are accounted for at amortized cost.
The Company also has insurance-related investments and investments in leveraged leases, primarily with
U.S. commercial airlines, which are accounted for at amortized cost.
Interest Expense
Interest expense is based upon contractual interest rates adjusted for the amortization of debt
issuance costs and premiums and the accretion of discounts. The Company’s interest expense may also be
adjusted for net payments/receipts related to interest rate and foreign currency swap agreements and
interest rate futures contracts that qualify as hedges under GAAP. Interest expense also includes the
amortization of deferred gains and losses on closed hedge transactions that qualified as cash flow hedges.
Amortization of debt issue costs, premiums, discounts and terminated hedge basis adjustments are
recognized using the effective interest rate method.
Securitization Accounting
To meet the sale criteria of SFAS No. 140, the Company’s securitizations use a two-step structure with
a QSPE that legally isolates the transferred assets from the Company, even in the event of bankruptcy.
Transactions receiving sale treatment are also structured to ensure that the holders of the beneficial
interests issued by the QSPE are not constrained from pledging or exchanging their interests, and that the
Company does not maintain effective control over the transferred assets. If these criteria are not met, then
the transaction is accounted for as an on-balance sheet secured borrowing. In all cases, irrespective of
whether they qualify as sales under SFAS No. 140, the Company’s securitizations are structured such that
they are legally sales of assets that isolate the transferred assets from the Company.
The Company assesses the financial structure of each securitization to determine whether the trust or
other securitization vehicle meets the sale criteria as defined in SFAS No. 140 and accounts for the
transaction accordingly. To be a QSPE, the trust must meet all of the following conditions:
•It is demonstrably distinct from the Company and cannot be unilaterally dissolved by the Company
and at least 10 percent of the fair value of its interests is held by independent third parties.
•The activities in which the trust can participate are significantly limited. These activities are entirely
specified up-front in the legal documents creating the QSPE.
•There are limits to the assets the QSPE can hold; specifically, it can hold only financial assets
transferred to it that are passive in nature, passive derivative instruments pertaining to the
beneficial interests held by independent third parties, servicing rights, temporary investments
pending distribution to security holders and cash.
•It can only dispose of its assets in automatic response to the occurrence of an event specified in the
applicable legal documents and must be outside the control of the Company.