Sallie Mae 2009 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
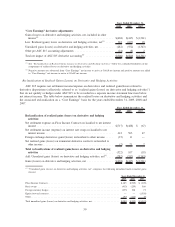
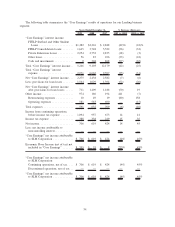
Please find page 50 of the 2009 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.2) Derivative Accounting: “Core Earnings” exclude periodic unrealized gains and losses that are
caused primarily by the one-sided mark-to-market derivative valuations prescribed by ASC 815 on derivatives
that do not qualify for “hedge treatment” under GAAP. These unrealized gains and losses occur in our Lending
operating segment. In our “Core Earnings” presentation, we recognize the economic effect of these hedges,
which generally results in any cash paid or received being recognized ratably as an expense or revenue over
the hedged item’s life.
ASC 815 requires that changes in the fair value of derivative instruments be recognized currently in
earnings unless specific hedge accounting criteria, as specified by ASC 815, are met. We believe that our
derivatives are effective economic hedges, and as such, are a critical element of our interest rate risk
management strategy. However, some of our derivatives, primarily Floor Income Contracts and certain basis
swaps, do not qualify for “hedge treatment” as defined by ASC 815, and the stand-alone derivative must be
marked-to-market in the income statement with no consideration for the corresponding change in fair value of
the hedged item. The gains and losses described in “Gains (losses) on derivative and hedging activities, net”
are primarily caused by interest rate and foreign currency exchange rate volatility and changing credit spreads
during the period, as well as the volume and term of derivatives not receiving hedge treatment.
Our Floor Income Contracts are written options that must meet more stringent requirements than other
hedging relationships to achieve hedge effectiveness under ASC 815. Specifically, our Floor Income Contracts
do not qualify for hedge accounting treatment because the pay down of principal of the student loans
underlying the Floor Income embedded in those student loans does not exactly match the change in the
notional amount of our written Floor Income Contracts. Under ASC 815, the upfront payment is deemed a
liability and changes in fair value are recorded through income throughout the life of the contract. The change
in the value of Floor Income Contracts is primarily caused by changing interest rates that cause the amount of
Floor Income earned on the underlying student loans and paid to the counterparties to vary. This is
economically offset by the change in value of the student loan portfolio, including our Retained Interests,
earning Floor Income but that offsetting change in value is not recognized under ASC 815. We believe the
Floor Income Contracts are economic hedges because they effectively fix the amount of Floor Income earned
over the contract period, thus eliminating the timing and uncertainty that changes in interest rates can have on
Floor Income for that period. Prior to ASC 815, we accounted for Floor Income Contracts as hedges and
amortized the upfront cash compensation ratably over the lives of the contracts.
Basis swaps are used to convert floating rate debt from one floating interest rate index to another to better
match the interest rate characteristics of the assets financed by that debt. We primarily use basis swaps to
change the index of our floating rate debt to better match the cash flows of our student loan assets that are
primarily indexed to a commercial paper, Prime or Treasury bill index. In addition, we use basis swaps to
convert debt indexed to the Consumer Price Index to three-month month LIBOR debt. ASC 815 requires that
when using basis swaps, the change in the cash flows of the hedge effectively offset both the change in the
cash flows of the asset and the change in the cash flows of the liability. Our basis swaps hedge variable
interest rate risk; however, they generally do not meet this effectiveness test because the index of the swap
does not exactly match the index of the hedged assets as required by ASC 815. Additionally, some of our
FFELP loans can earn at either a variable or a fixed interest rate depending on market interest rates. We also
have basis swaps that do not meet the ASC 815 effectiveness test that economically hedge off-balance sheet
instruments. As a result, under GAAP, these swaps are recorded at fair value with changes in fair value
reflected currently in the income statement.
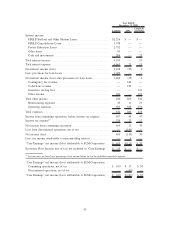
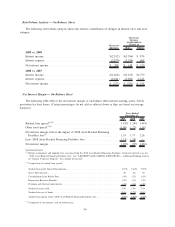
The table below quantifies the adjustments for derivative accounting under ASC 815 on our net income
for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 when compared with the accounting principles
employed in all years prior to the ASC 815 implementation.
49