Sallie Mae 2009 Annual Report Download - page 111
Download and view the complete annual report
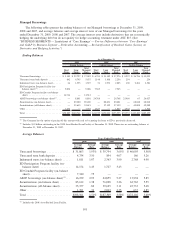
Please find page 111 of the 2009 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.the sources and uses of liquidity see the “LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES” section of this
Form 10-K.
Credit Risk Management
The Company’s Chief Credit Officer reports, on a regular basis, to the Board regarding the Company’s
asset quality. In addition, during 2009, the Chief Credit Officer commenced reporting, on a regular basis, to
the Audit Committee of the Board regarding asset quality.
Private credit is managed within a credit risk infrastructure which includes (i) a well-defined underwriting
and collection policy framework; (ii) an ongoing monitoring and review process of portfolio segments and
trends; (iii) assignment and management of credit authorities and responsibilities; and (iv) establishment of an
allowance that covers estimated losses based upon portfolio and economic analysis.
Private Education Loans are underwritten and priced according to the risk profile of the borrower,
generally determined by a custom credit scoring system and the Company’s proprietary underwriting process.
Additionally, for borrowers who do not meet our lending requirements or who desire more favorable terms, we
generally require credit-worthy cosigners. The Company bears the full risk of loss of these loans.
Probable losses for Private Education Loans are based upon statistical analysis of inherent losses over
specific periods of time and are estimated using sophisticated portfolio modeling, credit scoring and decision
support tools to project credit losses. Potential credit losses are considered in our risk-based pricing model.
The performance of the Private Education Loan portfolio may be affected by borrowers who fail to complete
their education and by the economy. A prolonged economic downturn may have an adverse effect on our
credit performance. This is taken into account when establishing allowances to cover estimated losses.
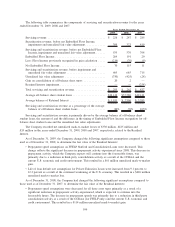
We have credit risk exposure to the various counterparties with whom we have entered into derivative
contracts. We review the credit strength of these companies on an ongoing basis. Our credit policies place
limits on the amount of exposure we may take with any one counterparty and, in most cases, require collateral
to secure the position. The credit risk associated with derivatives is measured based on the replacement cost
should the counterparties with contracts in a gain position to the Company fail to perform under the terms of
the contract.
Credit risk in our investment portfolio is minimized by only investing in paper with highly rated issuers.
Additionally, limits per issuer are determined by our internal credit and investment guidelines to limit our
exposure to any one issuer. We also have credit risk with several higher education institutions related to
academic facilities loans secured by real estate.
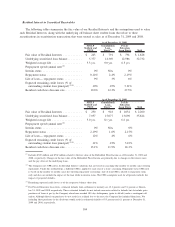
Market and Interest Rate Risk Management
We measure interest rate risk by calculating the variability of net interest income in future periods under
various interest rate scenarios using projected balances for interest-earning assets, interest-bearing liabilities
and derivatives used to hedge interest rate risk. Many assumptions are utilized by management to calculate the
impact that changes in interest rates may have on net interest income, the more significant of which are related
to student loan volumes and pricing, the timing of cash flows from our student loan portfolio, particularly the
impact of Floor Income, and the rate of student loan consolidations, basis risk, credit spreads and the maturity
of our debt and derivatives.
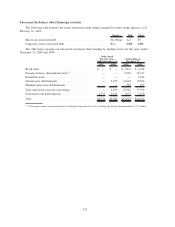
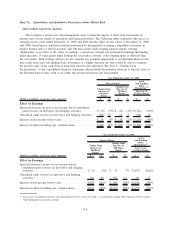
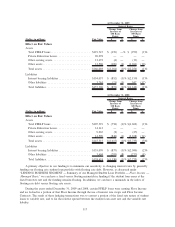
Asset and Liability Funding Gap
The tables below present our assets and liabilities (funding) arranged by underlying indices as of
December 31, 2009. In the following GAAP presentation, the funding gap only includes derivatives that
qualify as effective ASC 815 hedges (those derivatives which are reflected in net interest margin, as opposed
to those reflected in the “gains/(losses) on derivatives and hedging activities, net” line on the consolidated
statements of income). The difference between the asset and the funding is the funding gap for the specified
index. This represents our exposure to interest rate risk in the form of basis risk and repricing risk, which is
110