SunTrust 2013 Annual Report Download - page 185
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 185 of the 2013 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, continued
169
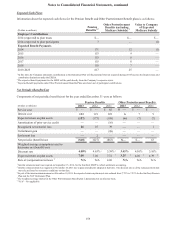
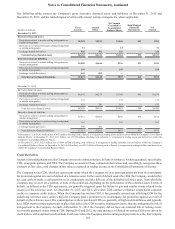
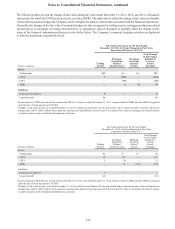
excluded from the Company's assessments of hedge effectiveness. Ineffectiveness gains on the Agreements of $1 million and
$2 million were recognized in trading income during the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively, and related to
changes in market dividends.
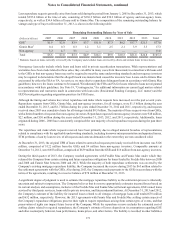
During 2012, the Company and the Coke Counterparty accelerated the termination of the Agreements, and the Company sold
in the market or to the Coke Counterparty 59 million of its 60 million shares of Coke and contributed the remaining 1 million
shares to the SunTrust Foundation for a net gain of $1.9 billion, which is net of a $305 million loss related to the derivative
contract termination of the Agreements. Upon approval by the Board to terminate the Agreements and sell and donate the Coke
shares, the Agreements no longer qualified as cash flow hedges. Thus, subsequent changes in value of the Agreements until
termination totaled $60 million and were recognized in net securities gains in the Consolidated Statements of Income. Amounts
recognized in AOCI in the Consolidated Statements of Shareholders' Equity during the period the Agreements qualified as cash
flow hedges totaled $365 million in losses. These amounts remained in AOCI until the sale of the Coke shares, at which time
the amounts were reclassified to net securities gains in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
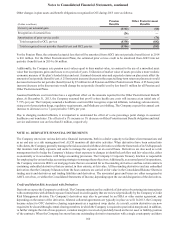
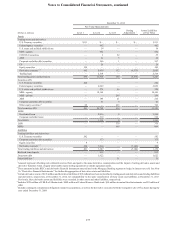
Fair Value Hedges
The Company enters into interest rate swap agreements as part of the Company’s risk management objectives for hedging its
exposure to changes in fair value due to changes in interest rates. These hedging arrangements convert Company-issued fixed
rate long-term debt to floating rates. Consistent with this objective, the Company reflects the accrued contractual interest on the
hedged item and the related swaps as part of current period interest. There were no components of derivative gains or losses
excluded in the Company’s assessment of hedge effectiveness related to the fair value hedges.
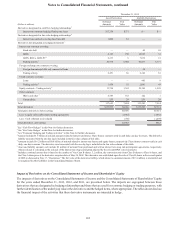
Economic Hedging and Trading Activities
In addition to designated hedging relationships, the Company also enters into derivatives as an end user as a risk management
tool to economically hedge risks associated with certain non-derivative and derivative instruments, along with entering into
derivatives in a trading capacity with its clients.
The primary risks that the Company economically hedges are interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, and credit risk. Economic
hedging objectives are accomplished by entering into offsetting derivatives either on an individual basis or collectively on a
macro basis and generally accomplish the Company’s goal of mitigating the targeted risk. To the extent that specific derivatives
are associated with specific hedged items, the notional amounts, fair values, and gains/(losses) on the derivatives are illustrated
in the tables in this footnote.
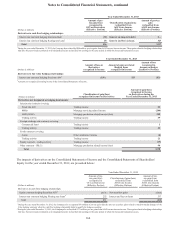
• The Company utilizes interest rate derivatives to mitigate exposures from various instruments.
The Company is subject to interest rate risk on its fixed rate debt. As market interest rates move, the fair
value of the Company’s debt is affected. To protect against this risk on certain debt issuances that the
Company has elected to carry at fair value, the Company has entered into pay variable-receive fixed interest
rate swaps that decrease in value in a rising rate environment and increase in value in a declining rate
environment.
The Company is exposed to risk on the returns of certain of its brokered deposits that are carried at fair
value. To hedge against this risk, the Company has entered into interest rate derivatives that mirror the risk
profile of the returns on these instruments.
The Company is exposed to interest rate risk associated with MSRs, which the Company hedges with a
combination of mortgage and interest rate derivatives, including forward and option contracts, futures, and
forward rate agreements.
The Company enters into mortgage and interest rate derivatives, including forward contracts, futures, and
option contracts to mitigate interest rate risk associated with IRLCs and mortgage LHFS.
• The Company is exposed to foreign exchange rate risk associated with certain commercial loans.
• The Company enters into CDS to hedge credit risk associated with certain loans held within its Wholesale Banking
segment. The Company accounts for these contracts as derivatives and, accordingly, recognizes these contracts at
fair value, with changes in fair value recognized in other noninterest income in the Consolidated Statements of
Income.
• Trading activity, as illustrated in the tables within this footnote, primarily includes interest rate swaps, equity
derivatives, CDS, futures, options, foreign currency contracts, and commodities. These derivatives are entered into
in a dealer capacity to facilitate client transactions or are utilized as a risk management tool by the Company as an