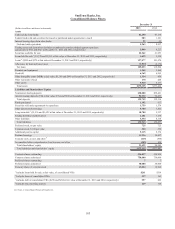
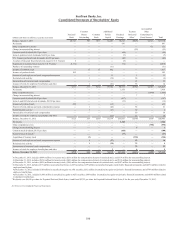
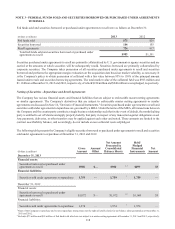
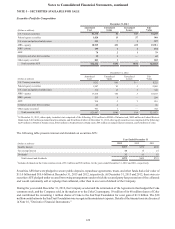
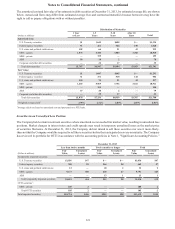
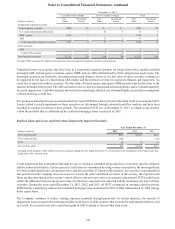
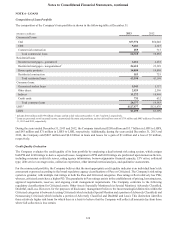
SunTrust 2013 Annual Report Download - page 131
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 131 of the 2013 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, continued
115
For designated hedging relationships, the Company performs retrospective and prospective effectiveness testing using
quantitative methods and does not assume perfect effectiveness through the matching of critical terms. Assessments of hedge
effectiveness and measurements of hedge ineffectiveness are performed at least quarterly for ongoing effectiveness. Changes
in the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective and that has been designated and qualifies as a fair value hedge are
recorded in current period earnings, along with the changes in the fair value of the hedged item that are attributable to the
hedged risk. The effective portion of the changes in the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective and that has been
designated and qualifies as a cash flow hedge are initially recorded in AOCI and reclassified to earnings in the same period
that the hedged item impacts earnings; any ineffective portion is recorded in current period earnings.
Hedge accounting ceases on transactions that are no longer deemed effective, or for which the derivative has been terminated
or de-designated. For discontinued fair value hedges where the hedged item remains outstanding, the hedged item would cease
to be remeasured at fair value attributable to changes in the hedged risk and any existing basis adjustment would be recognized
as an adjustment to earnings over the remaining life of the hedged item. For discontinued cash flow hedges, the unrealized
gains and losses recorded in AOCI would be reclassified to earnings in the period when the previously designated hedged
cash flows occur unless it was determined that transaction was probable to not occur, whereby any unrealized gains and losses
in AOCI would be immediately reclassified to earnings. For additional information on the Company’s derivative activities,
see Note 16, “Derivative Financial Instruments,” and Note 18, “Fair Value Election and Measurement.”
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company sponsors stock plans under which incentive and nonqualified stock options and restricted stock may be granted
periodically to certain employees. The Company accounts for stock-based compensation under the fair value recognition
provisions whereby the fair value of the award at grant date is expensed over the award’s vesting period. Additionally, the
Company estimates the number of awards for which it is probable that service will be rendered and adjusts compensation cost
accordingly. Estimated forfeitures are subsequently adjusted to reflect actual forfeitures. For additional information on the
Company’s stock-based employee compensation plans, see Note 15, “Employee Benefit Plans.”
Employee Benefits
Employee benefits expense includes the net periodic benefit costs associated with the pension, supplemental retirement, and
other postretirement benefit plans, as well as contributions under the defined contribution plan, the amortization of restricted
stock, stock option awards, and costs of other employee benefits. For additional information on the Company's employee
benefit plans, see Note 15, “Employee Benefit Plans.”
Foreign Currency Transactions
Foreign denominated assets and liabilities resulting from foreign currency transactions are valued using period end foreign
exchange rates and the associated interest income or expense is determined using approximate weighted average exchange
rates for the period. The Company may elect to enter into foreign currency derivatives to mitigate its exposure to changes in
foreign exchange rates. The derivative contracts are accounted for at fair value. Gains and losses resulting from such valuations
are included in noninterest income in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Fair Value
Certain assets and liabilities are measured at fair value on a recurring basis. Examples of these include derivative instruments,
AFS and trading securities, certain LHFI and LHFS, certain issuances of long-term debt, brokered deposits, and MSR assets.
Fair value is used on a non-recurring basis as a measurement basis either when assets are evaluated for impairment, the basis
of accounting is LOCOM, or for disclosure purposes. Examples of these non-recurring uses of fair value include certain LHFS
and LHFI, OREO, goodwill, intangible assets, certain cost or equity method investments and long-lived assets. Fair value is
defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between
market participants at the measurement date. Depending on the nature of the asset or liability, the Company uses various
valuation techniques and assumptions when estimating fair value.
The Company applies the following fair value hierarchy:
• Level 1 – Assets or liabilities valued using unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
that the Company can access at the measurement date, such as publicly-traded instruments or futures contracts.
• Level 2 – Assets and liabilities valued based on observable market data for similar instruments.