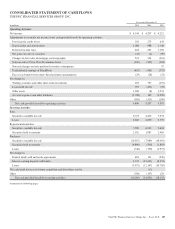
PNC Bank 2015 Annual Report Download - page 115
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 115 of the 2015 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Earning assets – Assets that generate income, which include:
federal funds sold; resale agreements; trading securities;
interest-earning deposits with banks; loans held for sale;
loans; investment securities; and certain other assets.
Effective duration – A measurement, expressed in years, that,
when multiplied by a change in interest rates, would
approximate the percentage change in value of on- and off-
balance sheet positions.
Efficiency – Noninterest expense divided by total revenue.
Enterprise risk management framework – An enterprise
process designed to identify potential risks that may affect
PNC, manage risk to be within our risk appetite and provide
reasonable assurance regarding achievement of our objectives.
Fair value – The price that would be received to sell an asset
or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between
market participants at the measurement date.
Fee income – When referring to the components of
Noninterest income, we use the term fee income to refer to the
following categories within Noninterest income: Asset
management; Consumer services; Corporate services;
Residential mortgage; and Service charges on deposits.
FICO score – A credit bureau-based industry standard score
created by Fair Isaac Co. which predicts the likelihood of
borrower default. We use FICO scores both in underwriting
and assessing credit risk in our consumer lending portfolio.
Lower FICO scores indicate likely higher risk of default,
while higher FICO scores indicate likely lower risk of default.
FICO scores are updated on a periodic basis.
Foreign exchange contracts – Contracts that provide for the
future receipt and delivery of foreign currency at previously
agreed-upon terms.
Funds transfer pricing – A management accounting
methodology designed to recognize the net interest income
effects of sources and uses of funds provided by the assets and
liabilities of a business segment. Assets receive a funding
charge and liabilities and capital receive a funding credit
based on a transfer pricing methodology that incorporates
product repricing characteristics, tenor and other factors.
Futures and forward contracts – Contracts in which the buyer
agrees to purchase and the seller agrees to deliver a specific
financial instrument at a predetermined price or yield. May be
settled either in cash or by delivery of the underlying financial
instrument.
GAAP – Accounting principles generally accepted in the
United States of America.
Home price index (HPI) – A broad measure of the movement
of single-family house prices in the U.S.
Impaired loans – Loans are determined to be impaired when,
based on current information and events, it is probable that all
contractually required payments will not be collected.
Impaired loans include commercial nonperforming loans and
consumer and commercial TDRs, regardless of nonperforming
status. Excluded from impaired loans are nonperforming
leases, loans held for sale, loans accounted for under the fair
value option, smaller balance homogenous type loans and
purchased impaired loans.
Interest rate floors and caps – Interest rate protection
instruments that involve payment from the protection seller to
the protection buyer of an interest differential, which
represents the difference between a short-term rate (e.g., three-
month LIBOR) and an agreed-upon rate (the strike rate)
applied to a notional principal amount.
Interest rate swap contracts – Contracts that are entered into
primarily as an asset/liability management strategy to reduce
interest rate risk. Interest rate swap contracts are exchanges of
interest rate payments, such as fixed-rate payments for
floating-rate payments, based on notional principal amounts.
Intrinsic value – The difference between the price, if any,
required to be paid for stock issued pursuant to an equity
compensation arrangement and the fair market value of the
underlying stock.
Leverage ratio – Tier 1 capital divided by average quarterly
adjusted total assets.
LIBOR – Acronym for London InterBank Offered Rate.
LIBOR is the average interest rate charged when banks in the
London wholesale money market (or interbank market)
borrow unsecured funds from each other. LIBOR rates are
used as a benchmark for interest rates on a global basis.
PNC’s product set includes loans priced using LIBOR as a
benchmark.
Loan-to-value ratio (LTV) – A calculation of a loan’s
collateral coverage that is used both in underwriting and
assessing credit risk in our lending portfolio. LTV is the sum
total of loan obligations secured by collateral divided by the
market value of that same collateral. Market values of the
collateral are based on an independent valuation of the
collateral. For example, a LTV of less than 90% is better
secured and has less credit risk than a LTV of greater than or
equal to 90%.
Loss given default (LGD) –An estimate of loss, net of
recovery based on collateral type, collateral value, loan
The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. – Form 10-K 97