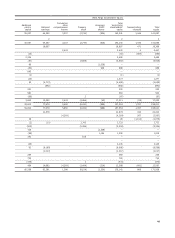
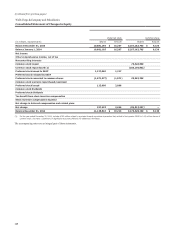
Wells Fargo 2014 Annual Report Download - page 147
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 147 of the 2014 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.account assets, loans, MSRs or other liabilities (including
liabilities for mortgage repurchase losses) and are accounted for
as described herein.
Mortgage Servicing Rights (MSRs)
We recognize the rights to service mortgage loans for others, or
MSRs, as assets whether we purchase the MSRs or the MSRs
result from a sale or securitization of loans we originate (asset
transfers). We initially record all of our MSRs at fair value.
Subsequently, residential loan MSRs are carried at fair value. All
of our MSRs related to our commercial mortgage loans are
subsequently measured at LOCOM. The valuation and sensitivity
of MSRs is discussed further in Note 8 (Securitizations and
Variable Interest Entities), Note 9 (Mortgage Banking Activities)
and Note 17 (Fair Values of Assets and Liabilities).
For MSRs carried at fair value, changes in fair value are
reported in noninterest income in the period in which the
change occurs. MSRs subsequently measured at LOCOM are
amortized in proportion to, and over the period of, estimated net
servicing income. The amortization of MSRs is reported in
noninterest income, analyzed monthly and adjusted to reflect
changes in prepayment speeds, as well as other factors.
MSRs accounted for at LOCOM are periodically evaluated
for impairment based on the fair value of those assets. For
purposes of impairment evaluation and measurement, we
stratify MSRs based on the predominant risk characteristics of
the underlying loans, including investor and product type. If, by
individual stratum, the carrying amount of these MSRs exceeds
fair value, a valuation allowance is established. The valuation
reserve is adjusted as the fair value changes.
Premises and Equipment
Premises and equipment are carried at cost less accumulated
depreciation and amortization. Capital leases, where we are the
lessee, are included in premises and equipment at the capitalized
amount less accumulated amortization.
We primarily use the straight-line method of depreciation
and amortization. Estimated useful lives range up to 40 years for
buildings, up to 10 years for furniture and equipment, and the
shorter of the estimated useful life (up to 8 years) or the lease
term for leasehold improvements. We amortize capitalized
leased assets on a straight-line basis over the lives of the
respective leases.
Goodwill and Identifiable Intangible Assets
Goodwill is recorded in business combinations under the
purchase method of accounting when the purchase price is
higher than the fair value of net assets, including identifiable
intangible assets.
We assess goodwill for impairment at a reporting unit level
on an annual basis or more frequently in certain circumstances.
We have determined that our reporting units are one level below
the operating segments. We have the option of performing a
qualitative assessment of goodwill. We may also elect to bypass
the qualitative test and proceed directly to a quantitative test.
We initially perform a qualitative assessment of goodwill to test
for impairment. If, based on our qualitative review, we conclude
that more likely than not a reporting unit’s fair value is less than
its carrying amount, then we complete quantitative steps as
described below to determine if there is goodwill impairment. If
we conclude that a reporting unit’s fair value is not less than its
carrying amount, quantitative tests are not required. We assess
goodwill for impairment on a reporting unit level and apply
various quantitative valuation methodologies when required to
compare the estimated fair value to the carrying value of each
reporting unit. Valuation methodologies include discounted cash
flow and earnings multiple approaches. If the fair value is less
than the carrying amount, an additional test is required to
measure the amount of impairment. We recognize impairment
losses as a charge to noninterest expense (unless related to
discontinued operations) and an adjustment to the carrying
value of the goodwill asset. Subsequent reversals of goodwill
impairment are prohibited.
We amortize core deposit and other customer relationship
intangibles on an accelerated basis over useful lives not
exceeding 10 years. We review such intangibles for impairment
whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their
carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Impairment is
indicated if the sum of undiscounted estimated future net cash
flows is less than the carrying value of the asset. Impairment is
permanently recognized by writing down the asset to the extent
that the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value.
Operating Lease Assets
Operating lease rental income for leased assets is recognized in
other income on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Related
depreciation expense is recorded on a straight-line basis over the
estimated useful life, considering the estimated residual value of
the leased asset. The useful life may be adjusted to the term of
the lease depending on our plans for the asset after the lease
term. On a periodic basis, leased assets are reviewed for
impairment. Impairment loss is recognized if the carrying
amount of leased assets exceeds fair value and is not recoverable.
The carrying amount of leased assets is not recoverable if it
exceeds the sum of the undiscounted cash flows expected to
result from the lease payments and the estimated residual value
upon the eventual disposition of the equipment.
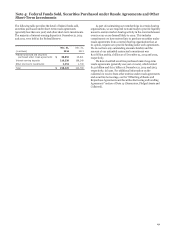
Liability for Mortgage Loan Repurchase Losses
In connection with our sales and securitization of residential
mortgage loans to various parties, we establish a mortgage
repurchase liability, initially at fair value, related to various
representations and warranties that reflect management’s
estimate of losses for loans for which we could have a repurchase
obligation, whether or not we currently service those loans,
based on a combination of factors. Such factors include default
expectations, expected investor repurchase demands (influenced
by current and expected mortgage loan file requests and
mortgage insurance rescission notices, as well as estimated
levels of origination defects) and appeals success rates (where
the investor rescinds the demand based on a cure of the defect or
acknowledges that the loan satisfies the investor’s applicable
representations and warranties), reimbursement by
correspondent and other third party originators, and projected
loss severity. We continually update our mortgage repurchase
liability estimate during the life of the loans.
The liability for mortgage loan repurchase losses is included
in other liabilities. For additional information on our repurchase
liability, see Note 9 (Mortgage Banking Activities).
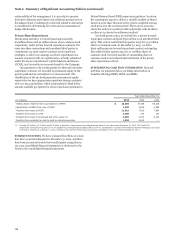
Pension Accounting
We account for our defined benefit pension plans using an
actuarial model. Two principal assumptions in determining net
periodic pension cost are the discount rate and the expected long
term rate of return on plan assets.
A discount rate is used to estimate the present value of our
future pension benefit obligations. We use a consistent
methodology to determine the discount rate based upon the
yields on multiple portfolios of bonds with maturity dates that
closely match the estimated timing and amounts of the expected
145