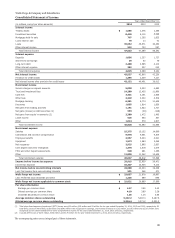
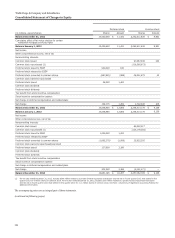
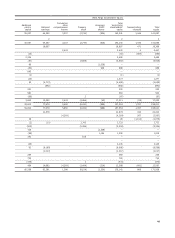
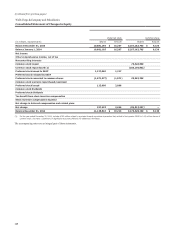
Wells Fargo 2014 Annual Report Download - page 129
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 129 of the 2014 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.become more challenging and we might not attain our goal of
selling an average of eight products to each customer.
Our ability to attract and retain qualified team
members is critical to the success of our business and
failure to do so could adversely affect our business
performance, competitive position and future
prospects. The success of Wells Fargo is heavily dependent on
the talents and efforts of our team members, and in many areas
of our business, including the commercial banking, brokerage,
investment advisory, and capital markets businesses, the
competition for highly qualified personnel is intense. In order to
attract and retain highly qualified team members, we must
provide competitive compensation. As a large financial
institution we may be subject to limitations on compensation by
our regulators that may adversely affect our ability to attract and
retain these qualified team members. Some of our competitors
may not be subject to these same compensation limitations,
which may further negatively affect our ability to attract and
retain highly qualified team members.
RISKS RELATED TO OUR FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Changes in accounting policies or accounting
standards, and changes in how accounting standards
are interpreted or applied, could materially affect how
we report our financial results and condition. Our
accounting policies are fundamental to determining and
understanding our financial results and condition. As described
below, some of these policies require use of estimates and
assumptions that may affect the value of our assets or liabilities
and financial results. Any changes in our accounting policies
could materially affect our financial statements.
From time to time the FASB and the SEC change the
financial accounting and reporting standards that govern the
preparation of our external financial statements. In addition,
accounting standard setters and those who interpret the
accounting standards (such as the FASB, SEC, banking
regulators and our outside auditors) may change or even reverse
their previous interpretations or positions on how these
standards should be applied. Changes in financial accounting
and reporting standards and changes in current interpretations
may be beyond our control, can be hard to predict and could
materially affect how we report our financial results and
condition. We may be required to apply a new or revised
standard retroactively or apply an existing standard differently,
also retroactively, in each case potentially resulting in our
restating prior period financial statements in material amounts.
Our financial statements are based in part on
assumptions and estimates which, if wrong, could
cause unexpected losses in the future, and our financial
statements depend on our internal controls over
financial reporting. Pursuant to U.S. GAAP, we are required
to use certain assumptions and estimates in preparing our
financial statements, including in determining credit loss
reserves, reserves for mortgage repurchases, reserves related to
litigation and the fair value of certain assets and liabilities,
among other items. Several of our accounting policies are critical
because they require management to make difficult, subjective
and complex judgments about matters that are inherently
uncertain and because it is likely that materially different
amounts would be reported under different conditions or using
different assumptions. For a description of these policies, refer
to the “Critical Accounting Policies” section in this Report. If
assumptions or estimates underlying our financial statements
are incorrect, we may experience material losses.
Certain of our financial instruments, including trading
assets and liabilities, investment securities, certain loans, MSRs,
private equity investments, structured notes and certain
repurchase and resale agreements, among other items, require a
determination of their fair value in order to prepare our financial
statements. Where quoted market prices are not available, we
may make fair value determinations based on internally
developed models or other means which ultimately rely to some
degree on management judgment, and there is no assurance that
our models will capture or appropriately reflect all relevant
inputs required to accurately determine fair value. Some of these
and other assets and liabilities may have no direct observable
price levels, making their valuation particularly subjective, being
based on significant estimation and judgment. In addition,
sudden illiquidity in markets or declines in prices of certain
loans and securities may make it more difficult to value certain
balance sheet items, which may lead to the possibility that such
valuations will be subject to further change or adjustment and
could lead to declines in our earnings.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Sarbanes-Oxley) requires
our management to evaluate the Company’s disclosure controls
and procedures and its internal control over financial reporting
and requires our auditors to issue a report on our internal
control over financial reporting. We are required to disclose, in
our annual report on Form 10-K, the existence of any “material
weaknesses” in our internal controls. We cannot assure that we
will not identify one or more material weaknesses as of the end
of any given quarter or year, nor can we predict the effect on our
stock price of disclosure of a material weakness. Sarbanes-Oxley
also limits the types of non-audit services our outside auditors
may provide to us in order to preserve their independence from
us. If our auditors were found not to be “independent” of us
under SEC rules, we could be required to engage new auditors
and re-file financial statements and audit reports with the SEC.
We could be out of compliance with SEC rules until new
financial statements and audit reports were filed, limiting our
ability to raise capital and resulting in other adverse
consequences.
RISKS RELATED TO ACQUISITIONS
Acquisitions could reduce our stock price upon
announcement and reduce our earnings if we overpay
or have difficulty integrating them. We regularly explore
opportunities to acquire companies in the financial services
industry. We cannot predict the frequency, size or timing of our
acquisitions, and we typically do not comment publicly on a
possible acquisition until we have signed a definitive agreement.
When we do announce an acquisition, our stock price may fall
depending on the size of the acquisition, the type of business to
be acquired, the purchase price, and the potential dilution to
existing stockholders or our earnings per share if we issue
common stock in connection with the acquisition.
We generally must receive federal regulatory approvals
before we can acquire a bank, bank holding company or certain
other financial services businesses depending on the size of the
financial services business to be acquired. In deciding whether to
approve a proposed acquisition, federal bank regulators will
consider, among other factors, the effect of the acquisition on
competition and the risk to the stability of the U.S. banking or
financial system, our financial condition and future prospects
including current and projected capital ratios and levels, the
competence, experience, and integrity of management and
127