Wells Fargo 2014 Annual Report Download - page 146
Download and view the complete annual report
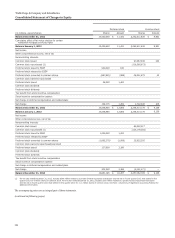
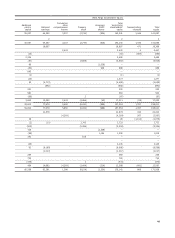
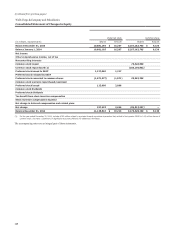
Please find page 146 of the 2014 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Note 1: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
have been written down to their net realizable value prior to
foreclosure. Any further reduction to their net realizable value is
recorded with a charge to the allowance for credit losses at
foreclosure. We allow up to 90 days after foreclosure to finalize
determination of net realizable value. Thereafter, changes in net
realizable value are recorded to noninterest expense. The net
realizable value of these assets is reviewed and updated
periodically depending on the type of property. See the
discussion earlier in this Note about classification changes for
certain government-guaranteed loan foreclosures that resulted
from our adoption of ASU 2014-14 this year.
ALLOWANCE FOR CREDIT LOSSES (ACL) The allowance for
credit losses is management’s estimate of credit losses inherent
in the loan portfolio, including unfunded credit commitments, at
the balance sheet date. We have an established process to
determine the appropriateness of the allowance for credit losses
that assesses the losses inherent in our portfolio and related
unfunded credit commitments. We develop and document our
allowance methodology at the portfolio segment level -
commercial loan portfolio and consumer loan portfolio. While
we attribute portions of the allowance to our respective
commercial and consumer portfolio segments, the entire
allowance is available to absorb credit losses inherent in the total
loan portfolio and unfunded credit commitments.
Our process involves procedures to appropriately consider
the unique risk characteristics of our commercial and consumer
loan portfolio segments. For each portfolio segment, losses are
estimated collectively for groups of loans with similar
characteristics, individually or pooled for impaired loans or, for
PCI loans, based on the changes in cash flows expected to be
collected.
Our allowance levels are influenced by loan volumes, loan
grade migration or delinquency status, historic loss experience
and other conditions influencing loss expectations, such as
economic conditions.
COMMERCIAL PORTFOLIO SEGMENT ACL METHODOLOGY
Generally, commercial loans are assessed for estimated losses by
grading each loan using various risk factors as identified through
periodic reviews. Our estimation approach for the commercial
portfolio reflects the estimated probability of default in
accordance with the borrower’s financial strength, and the
severity of loss in the event of default, considering the quality of
any underlying collateral. Probability of default and severity at
the time of default are statistically derived through historical
observations of default and losses after default within each credit
risk rating. These estimates are adjusted as appropriate based on
additional analysis of long-term average loss experience
compared to previously forecasted losses, external loss data or
other risks identified from current economic conditions and
credit quality trends. The estimated probability of default and
severity at the time of default are applied to loan equivalent
exposures to estimate losses for unfunded credit commitments.
The allowance also includes an amount for the estimated
impairment on nonaccrual commercial loans and commercial
loans modified in a TDR, whether on accrual or nonaccrual
status.
CONSUMER PORTFOLIO SEGMENT ACL METHODOLOGY
For consumer loans that are not identified as a TDR, we
determine the allowance predominantly on a collective basis
utilizing forecasted losses to represent our best estimate of
inherent loss. We pool loans, generally by product types with
similar risk characteristics, such as residential real estate
mortgages and credit cards. As appropriate and to achieve
greater accuracy, we may further stratify selected portfolios by
sub-product, origination channel, vintage, loss type, geographic
location and other predictive characteristics. Models designed
for each pool are utilized to develop the loss estimates. We use
assumptions for these pools in our forecast models, such as
historic delinquency and default, loss severity, home price
trends, unemployment trends, and other key economic variables
that may influence the frequency and severity of losses in the
pool.
In determining the appropriate allowance attributable to
our residential mortgage portfolio, we take into consideration
portfolios determined to be at elevated risk, such as junior lien
mortgages behind delinquent first lien mortgages and junior lien
lines of credit subject to near term significant payment increases.
We incorporate the default rates and high severity of loss for
these higher risk portfolios, including the impact of our
established loan modification programs. When modifications
occur or are probable to occur, our allowance considers the
impact of these modifications, taking into consideration the
associated credit cost, including re-defaults of modified loans
and projected loss severity. Accordingly, the loss content
associated with the effects of existing and probable loan
modifications and higher risk portfolios has been captured in our
allowance methodology.
We separately estimate impairment for consumer loans that
have been modified in a TDR (including trial modifications),
whether on accrual or nonaccrual status.
OTHER ACL MATTERS The allowance for credit losses for both
portfolio segments includes an amount for imprecision or
uncertainty that may change from period to period. This amount
represents management’s judgment of risks inherent in the
processes and assumptions used in establishing the allowance.
This imprecision considers economic environmental factors,
modeling assumptions and performance, process risk, and other
subjective factors, including industry trends and emerging risk
assessments.
Securitizations and Beneficial Interests
In certain asset securitization transactions that meet the
applicable criteria to be accounted for as a sale, assets are sold to
an entity referred to as an SPE, which then issues beneficial
interests in the form of senior and subordinated interests
collateralized by the assets. In some cases, we may retain
beneficial interests issued by the entity. Additionally, from time
to time, we may also re-securitize certain assets in a new
securitization transaction.
The assets and liabilities transferred to an SPE are excluded
from our consolidated balance sheet if the transfer qualifies as a
sale and we are not required to consolidate the SPE.
For transfers of financial assets recorded as sales, we
recognize and initially measure at fair value all assets obtained
(including beneficial interests) and liabilities incurred. We
record a gain or loss in noninterest income for the difference
between the carrying amount and the fair value of the assets
sold. Fair values are based on quoted market prices, quoted
market prices for similar assets, or if market prices are not
available, then the fair value is estimated using discounted cash
flow analyses with assumptions for credit losses, prepayments
and discount rates that are corroborated by and verified against
market observable data, where possible. Retained interests and
liabilities incurred from securitizations with off-balance sheet
entities, including SPEs and VIEs, where we are not the primary
beneficiary, are classified as investment securities, trading
144