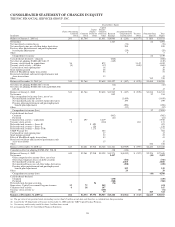
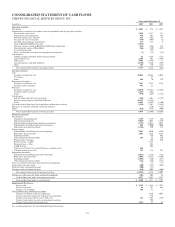
PNC Bank 2009 Annual Report Download - page 88
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 88 of the 2009 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Risk-weighted assets - Computed by the assignment of
specific risk-weights (as defined by the Board of Governors of
the Federal Reserve System) to assets and off-balance sheet
instruments.
Securitization - The process of legally transforming financial
assets into securities.
Servicing rights - An intangible asset or liability created by an
obligation to service assets for others. Typical servicing rights
include the right to receive a fee for collecting and forwarding
payments on loans and related taxes and insurance premiums
held in escrow.
Swaptions - Contracts that grant the purchaser, for a premium
payment, the right, but not the obligation, to enter into an
interest rate swap agreement during a specified period or at a
specified date in the future.
Taxable-equivalent interest - The interest income earned on
certain assets is completely or partially exempt from Federal
income tax. As such, these tax-exempt instruments typically
yield lower returns than taxable investments. To provide more
meaningful comparisons of yields and margins for all interest-
earning assets, we use interest income on a taxable-equivalent
basis in calculating average yields and net interest margins by
increasing the interest income earned on tax-exempt assets to
make it fully equivalent to interest income earned on other
taxable investments. This adjustment is not permitted under
GAAP on the Consolidated Income Statement.
Tier 1 common capital - Tier 1 risk-based capital, less
preferred equity, less trust preferred capital securities, and less
noncontrolling interests.
Tier 1 common capital ratio - Tier 1 common capital divided
by period-end risk-weighted assets.
Tier 1 risk-based capital - Total shareholders’ equity, plus
trust preferred capital securities, plus certain noncontrolling
interests that are held by others; less goodwill and certain
other intangible assets (net of eligible deferred taxes relating
to taxable and nontaxable combinations), less equity
investments in nonfinancial companies less ineligible
servicing assets and less net unrealized holding losses on
available for sale equity securities. Net unrealized holding
gains on available for sale equity securities, net unrealized
holding gains (losses) on available for sale debt securities and
net unrealized holding gains (losses) on cash flow hedge
derivatives are excluded from total shareholders’ equity for
Tier 1 risk-based capital purposes.
Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio - Tier 1 risk-based capital
divided by period-end risk-weighted assets.
Total equity – Total shareholders’ equity plus noncontrolling
interests.
Total return swap - A non-traditional swap where one party
agrees to pay the other the “total return” of a defined
underlying asset (e.g., a loan), usually in return for receiving a
stream of LIBOR-based cash flows. The total returns of the
asset, including interest and any default shortfall, are passed
through to the counterparty. The counterparty is therefore
assuming the credit and economic risk of the underlying asset.
Total risk-based capital - Tier 1 risk-based capital plus
qualifying subordinated debt and trust preferred securities,
other noncontrolling interest not qualified as Tier 1, eligible
gains on available for sale equity securities and the allowance
for loan and lease losses, subject to certain limitations.
Total risk-based capital ratio - Total risk-based capital divided
by period-end risk-weighted assets.
Transaction deposits - The sum of money market and interest-
bearing demand deposits and demand and other noninterest-
bearing deposits.
Troubled debt restructuring – A restructuring of debt whereby
the lender for economic or legal reasons related to the
borrower’s financial difficulties grants a concession to the
borrower that it would not otherwise consider.
Value-at-risk (VaR) - A statistically-based measure of risk
which describes the amount of potential loss which may be
incurred due to severe and adverse market movements. The
measure is of the maximum loss which should not be
exceeded on 99 out of 100 days.
Watchlist - A list of criticized loans, credit exposure or other
assets compiled for internal monitoring purposes. We define
criticized exposure for this purpose as exposure with an
internal risk rating of other assets especially mentioned,
substandard, doubtful or loss.
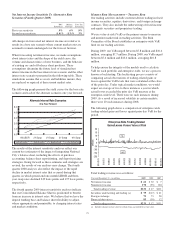
Yield curve - A graph showing the relationship between the
yields on financial instruments or market indices of the same
credit quality with different maturities. For example, a
“normal” or “positive” yield curve exists when long-term
bonds have higher yields than short-term bonds. A “flat” yield
curve exists when yields are the same for short-term and long-
term bonds. A “steep” yield curve exists when yields on long-
term bonds are significantly higher than on short-term bonds.
An “inverted” or “negative” yield curve exists when short-
term bonds have higher yields than long-term bonds.
84