PNC Bank 2009 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
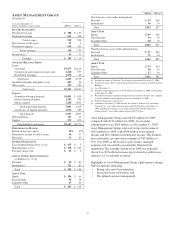
Please find page 69 of the 2009 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.nonqualified supplemental retirement plans for certain
employees. See Note 15 Employee Benefit Plans in the Notes
To Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 of this Report
for additional information.
R
ISK
M
ANAGEMENT
We encounter risk as part of the normal course of our business
and we design risk management processes to help manage
these risks. This Risk Management section describes our risk
management philosophy, principles, governance and various
aspects of our corporate-level risk management program. We
also provide an overview of 2009 enterprise-wide risk,
followed by an analysis of our primary areas of risk: credit,
operational, liquidity, and market. The discussion of market
risk is further subdivided into interest rate, trading, and equity
and other investment risk areas. Our use of financial
derivatives as part of our overall asset and liability risk
management process is also addressed within the Risk
Management section of this Item 7. In appropriate places
within this section, historical performance is also addressed.
Risk Management Philosophy
PNC’s risk management philosophy is to manage to an overall
moderate level of risk to capture opportunities and optimize
shareholder value. We dynamically set our strategies and
make distinct risk taking decisions with consideration for the
impact to our aggregate risk profile. While, due to the
National City acquisition and the overall state of the economy,
our enterprise risk profile does not currently meet our desired
moderate risk level, we are making progress in returning to
that level.
Risk Management Principles
• Designed to only take risks consistent with our
strategy and within our capability to manage,
• Limit risk-taking by a set of boundaries,
• Practice disciplined capital and liquidity
management,
• Help ensure that risks and earnings volatility are
appropriately understood, measured and rewarded,
• Avoid excessive concentrations, and
• Help support external stakeholder confidence in
PNC.
We support risk management through a governance structure
involving the Board, senior management and a corporate risk
management organization.
Although our Board as a whole is responsible generally for
oversight of risk management, committees of the Board
provide oversight to specific areas of risk with respect to the
level of risk and risk management structure.
We use management level risk committees to help ensure that
business decisions are executed within our desired risk profile.
The Executive Committee (EC), consisting of senior
management executives, provides oversight for the
establishment and implementation of new comprehensive risk
management initiatives, reviews enterprise level risk profiles
and discusses key risk issues.
Corporate-Level Risk Management Program
The corporate risk management organization has the following
key roles:
• Facilitate the identification, assessment and
monitoring of risk across PNC,
• Provide support and oversight to the businesses,
• Help identify and implement risk management best
practices, as appropriate, and
• Work with the lines of business to shape and define
PNC’s business risk limits.
Risk Measurement
We conduct risk measurement activities specific to each area
of risk. The primary vehicle for aggregation of enterprise-wide
risk is a comprehensive risk management methodology that is
based on economic capital. This primary risk aggregation
measure is supplemented with secondary measures of risk to
arrive at an estimate of enterprise-wide risk. The economic
capital framework is a measure of potential losses above and
beyond expected losses. Potential one year losses are
capitalized to a level commensurate with a financial institution
with an A rating by the credit rating agencies. Economic
capital incorporates risk associated with potential credit losses
(Credit Risk), fluctuations of the estimated market value of
financial instruments (Market Risk), failure of people,
processes or systems (Operational Risk), and losses associated
with declining volumes, margins and/or fees, and the fixed
cost structure of the business. We estimate credit and market
risks at pool and exposure levels while we estimate the
remaining risk types at an institution or business segment
level. We routinely compare the output of our economic
capital model with industry benchmarks.
Risk Control Strategies
Risk management is not about eliminating risks, but about
identifying and accepting risks and then working to effectively
manage them so as to optimize shareholder value.
We centrally manage policy development and exception
approval and oversight through corporate-level risk
management. Some of these policies express our risk appetite
through limits to the acceptable level of risk. We are in excess
of certain limits and are progressively managing to bring our
risks within policy. We are also reviewing and revising certain
policies to better reflect our larger and more complex
organization. Corporate risk management is authorized to take
action to either prevent or mitigate unapproved exceptions to
policies and is responsible for monitoring compliance with
risk management policies. The Corporate Audit function
performs an independent assessment of the internal control
environment. Corporate Audit plays a critical role in risk
65