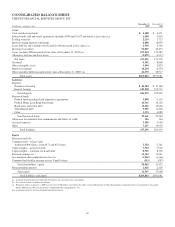
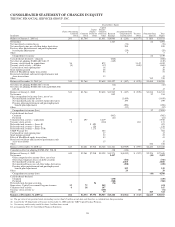
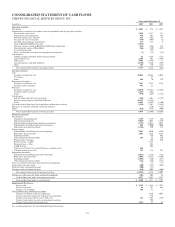
PNC Bank 2009 Annual Report Download - page 86
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 86 of the 2009 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Derivatives - Financial contracts whose value is derived from
publicly traded securities, interest rates, currency exchange
rates or market indices. Derivatives cover a wide assortment
of financial contracts, including but not limited to forward
contracts, futures, options and swaps.
Duration of equity - An estimate of the rate sensitivity of our
economic value of equity. A negative duration of equity is
associated with asset sensitivity (i.e., positioned for rising
interest rates), while a positive value implies liability
sensitivity (i.e., positioned for declining interest rates). For
example, if the duration of equity is +1.5 years, the economic
value of equity declines by 1.5% for each 100 basis point
increase in interest rates.
Earning assets - Assets that generate income, which include:
Federal funds sold; resale agreements; trading securities;
interest-earning deposits with banks; other short-term
investments; loans held for sale; loans; investment securities;
and certain other assets.
Economic capital - Represents the amount of resources that a
business segment should hold to guard against potentially
large losses that could cause insolvency. It is based on a
measurement of economic risk, as opposed to risk as defined
by regulatory bodies. The economic capital measurement
process involves converting a risk distribution to the capital
that is required to support the risk, consistent with our target
credit rating. As such, economic risk serves as a “common
currency” of risk that allows us to compare different risks on a
similar basis.
Effective duration - A measurement, expressed in years, that,
when multiplied by a change in interest rates, would
approximate the percentage change in value of on- and off-
balance sheet positions.
Efficiency - Noninterest expense divided by the sum of net
interest income (GAAP basis) and noninterest income.
Fair value - The price that would be received to sell an asset or
the price that would be paid to transfer a liability on the
measurement date using the principal or most advantageous
market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction
between willing market participants.
Foreign exchange contracts - Contracts that provide for the
future receipt and delivery of foreign currency at previously
agreed-upon terms.
Funds transfer pricing - A management accounting
methodology designed to recognize the net interest income
effects of sources and uses of funds provided by the assets and
liabilities of a business segment. We assign these balances
LIBOR-based funding rates at origination that represent the
interest cost for us to raise/invest funds with similar maturity
and repricing structures.
Futures and forward contracts - Contracts in which the buyer
agrees to purchase and the seller agrees to deliver a specific
financial instrument at a predetermined price or yield. May be
settled either in cash or by delivery of the underlying financial
instrument.
GAAP - Accounting principles generally accepted in the
United States of America.
Interest rate floors and caps - Interest rate protection
instruments that involve payment from the protection seller to
the protection buyer of an interest differential, which
represents the difference between a short-term rate (e.g., three-
month LIBOR) and an agreed-upon rate (the strike rate)
applied to a notional principal amount.
Interest rate swap contracts - Contracts that are entered into
primarily as an asset/liability management strategy to reduce
interest rate risk. Interest rate swap contracts are exchanges of
interest rate payments, such as fixed-rate payments for
floating-rate payments, based on notional principal amounts.
Intrinsic value - The amount by which the fair value of an
underlying stock exceeds the exercise price of an option on
that stock.
Investment securities - Collectively, securities available for
sale and securities held to maturity.
Leverage ratio - Tier 1 risk-based capital divided by adjusted
average total assets.
LIBOR - Acronym for London InterBank Offered Rate.
LIBOR is the average interest rate charged when banks in the
London wholesale money market (or interbank market)
borrow unsecured funds from each other. LIBOR rates are
used as a benchmark for interest rates on a global basis.
Net interest income from loans and deposits - A management
accounting assessment, using funds transfer pricing
methodology, of the net interest contribution from loans and
deposits.
Net interest margin - Annualized taxable-equivalent net
interest income divided by average earning assets.
Nonaccretable difference - Contractually required payments
receivable on a purchased impaired loan in excess of the cash
flows expected to be collected.
Nondiscretionary assets under administration - Assets we hold
for our customers/clients in a non-discretionary, custodial
capacity. We do not include these assets on our Consolidated
Balance Sheet.
Noninterest income to total revenue - Noninterest income
divided by the sum of net interest income (GAAP basis) and
noninterest income.
82