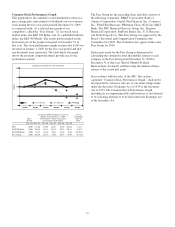
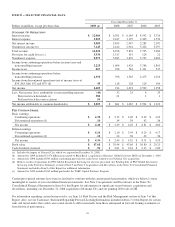
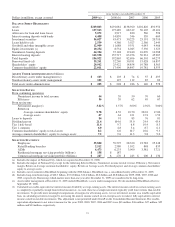
PNC Bank 2009 Annual Report Download - page 18
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 18 of the 2009 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.processing information. Each of our businesses consistently
must make significant technological investments to remain
competitive.
A failure to address adequately the competitive pressures we
face could make it harder for us to attract and retain customers
across our businesses. On the other hand, meeting these
competitive pressures could require us to incur significant
additional expenses or to accept risk beyond what we would
otherwise view as desirable under the circumstances. In
addition, in our interest sensitive businesses, pressures to
increase rates on deposits or decrease rates on loans could
reduce our net interest margin with a resulting negative impact
on our net interest income.
We grow our business in part by acquiring from time to
time other financial services companies, and these
acquisitions present us with a number of risks and
uncertainties related both to the acquisition transactions
themselves and to the integration of the acquired
businesses into PNC after closing.
Acquisitions of other financial services companies in general
present risks to PNC in addition to those presented by the
nature of the business acquired. We describe some of the
integration risks presented by our acquisition of National City
above. Many of these risks are common to some extent in
acquisition transactions.
In general, acquisitions may be substantially more expensive
to complete (including unanticipated costs incurred in
connection with the integration of the acquired company) and
the anticipated benefits (including anticipated cost savings and
strategic gains) may be significantly harder or take longer to
achieve than expected. In some cases, acquisitions involve our
entry into new businesses or new geographic or other markets,
and these situations also present risks resulting from our
inexperience in these new areas. As a regulated financial
institution, our pursuit of attractive acquisition opportunities
could be negatively impacted due to regulatory delays or other
regulatory issues. Regulatory and/or legal issues relating to the
pre-acquisition operations of an acquired business may cause
reputational harm to PNC following the acquisition and
integration of the acquired business into ours and may result
in additional future costs or regulatory limitations arising as a
result of those issues.
The performance of our asset management businesses may
be adversely affected by the relative performance of our
products compared with alternative investments as well as
by overall economic and market conditions.
Asset management revenue is primarily based on a percentage
of the value of assets under management and, in some cases,
performance fees, in most cases expressed as a percentage of
the returns realized on assets under management, and thus is
impacted by general changes in capital markets valuations as
well as by customer preferences and needs. In addition,
investment performance is an important factor influencing the
level of assets under management. Poor investment
performance could impair revenue and growth as existing
clients might withdraw funds in favor of better performing
products. Also, performance fees could be lower or
nonexistent. Additionally, the ability to attract funds from
existing and new clients might diminish. Overall economic
conditions may limit the amount that customers are able or
willing to invest.
The failure or negative performance of products of other
financial institutions could lead to a loss of confidence in
similar products offered by us without regard to the
performance of our products. Such a negative contagion could
lead to withdrawals, redemptions and liquidity issues in such
products and have a material adverse impact on our assets
under management and asset management revenues and
earnings.
The performance of our fund servicing business may be
adversely affected by changes in investor preferences, or
changes in existing or potential fund servicing clients or
alternative providers.
Fund servicing fees are primarily derived from the market
value of the assets and the number of shareholder accounts
that we administer for our clients. The performance of our
fund processing business is thus partially dependent on the
underlying performance of its fund clients and, in particular,
their ability to attract and retain customers. Changes in interest
rates or a sustained weakness, weakening or volatility in the
debt and equity markets could (in addition to affecting directly
the value of assets administered as discussed above) influence
an investor’s decision to invest or maintain an investment in a
particular mutual fund or other pooled investment product.
Other factors beyond our control may impact the ability of our
fund clients to attract or retain customers or customer funds,
including changes in preferences as to certain investment
styles. Further, to the extent that our fund clients’ businesses
are adversely affected by ongoing governmental investigations
into the practices of the mutual and hedge fund industries, our
fund processing business’ results also could be adversely
impacted. As a result of these types of factors, fluctuations
may occur in the level or value of assets for which we provide
processing services. In addition, this regulatory and business
environment is likely to continue to result in operating margin
pressure for our various services.
As a regulated financial services firm, we are subject to
numerous governmental regulations and to comprehensive
examination and supervision by regulators, which affects
our business as well as our competitive position.
PNC is a bank and financial holding company and is subject to
numerous governmental regulations involving both its
14