Telus 2011 Annual Report Download - page 175
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 175 of the 2011 Telus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
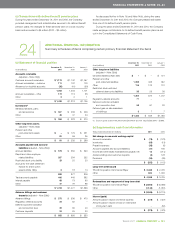
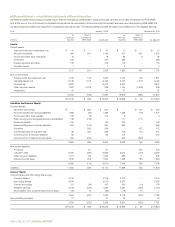
TELUS 2011 ANNUAL REPORT . 171
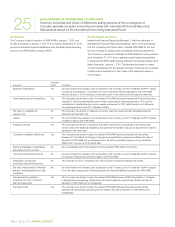
GLOSSARY
Mbps (megabits per second): A measurement of data transmission
speed for the amount of data transferred in a second between two
telecommunications points or within a network. Mbps is millions of bits
per second and Gbps (gigabits per second) is billions.
MDU (multiple dwelling unit): An apartment or condominium.
MMS (multimedia messaging service): Allows wireless customers
to send and receive messages that contain formatted text, graphics,
photographs, and audio and video clips.
MVNO (mobile virtual network operator): A mobile service operator
without licensed spectrum or network that leases wireless capacity from
other carriers to resell to end customers.
non-ILEC (non-incumbent local exchange carrier): The telecom-
munications operations of TELUS outside its traditional ILEC operating
territories, where TELUS competes with the incumbent telephone
company (e.g. Ontario, most of Quebec, etc.).
OTT (over-the-top): Content, services and applications in a video
environment where the delivery occurs through a medium other than
the main video delivery infrastructure.
PCS (personal communications services): Digital wireless voice, data
and text messaging services in the 1.9 GHz frequency range.
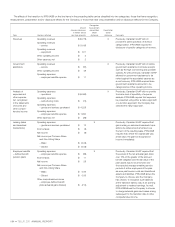
penetration: The degree, expressed as a percentage, to which a
product or service has been sold into or adopted by a base of potential
customers in a given geographic area or market segment.
POP: One person living in a populated area that is included in a
network’s coverage area.
postpaid: A conventional method of payment for service where a
subscriber is billed and pays for a significant portion of services and
usage in arrears, after consuming the services.
prepaid: A method of payment for wireless service that allows a
subscriber to prepay for a set amount of airtime and/or text messaging
in advance of actual usage.
PTT (Push to Talk): A two-way communication service that works like
a walkie-talkie using a button switch. With PTT, communication can only
travel in one direction at any given moment. PTT is provided by TELUS
through its Mike service using iDEN technology.
PVR (personal video recorder): An interactive TV set-top box that
records and plays back television programs.
roaming: A service offered by wireless network operators that allows
subscribers to use their mobile phones while in the service area of
another operator.
set-top box: A device that connects to a television and converts a signal
into content that is displayed by the television. In IP TV, a set-top box
allows two-way communications on the IP network.
SIM (subscriber identification module) card: A small electronic
chip used to identify a particular wireless subscriber on the network as
a legitimate user. Subscribers can switch between devices and carrier
networks by removing the SIM card and inserting it into another unlocked
mobile device. The SIM card can store personal information, phone
numbers, text messages and other data.
smartphone: An advanced mobile device that provides text messaging,
email, multimedia downloads and social networking functionality in
addition to voice. TELUS includes in this category iPhone, BlackBerry,
Android and other devices.
SMS (short messaging service): A wireless messaging service that
permits the transmission of a short text message from and/or to a digital
wireless device.
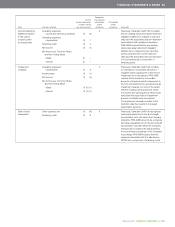
spectrum: The range of electromagnetic radio frequencies used in
the transmission of sound, data and video. The capacity of a wireless
network is in part a function of the amount of spectrum licensed and
utilized by the carrier.
tablet: A portable computer that includes a touchscreen interface with a
wireless and/or Wi-Fi connection. It combines the features and portability
of a smartphone with the power of a laptop.
VDSL2 (very high bit-rate digital subscriber line 2): Fibre-to-the-node
technology offering accelerated data download rates of up to 30 Mbps,
which enables four simultaneous video streams into a home. These rates
can be increased further by bonding multiple lines together.
VOD (video on demand): An interactive TV technology that allows
customers to access content at their convenience, allowing them to
view programming in real time or download and view it later. SVOD
(subscription VOD) provides customers with unlimited access to specific
subscribed programming.
VoIP (voice over Internet protocol): The transmission of voice signals
over the Internet or IP network.
Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity): The commercial name for networking
technology that allows any user with a Wi-Fi-enabled device to connect
to a wireless access point (e.g. hotspot).
WiMax: A standards-based wireless technology that provides high
throughput fixed broadband connections over long distances. The WiMax
standard also includes a mobile variation that can be used for cellular
service, but mobile WiMax has experienced very limited uptake globally.
For financial definitions, see Section 11 of
Management’s discussion and analysis in
this report.