Telus 2011 Annual Report Download - page 128
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 128 of the 2011 Telus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
124 . TELUS 2011 ANNUAL REPORT
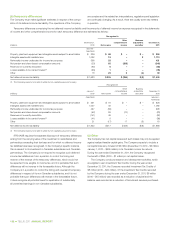
Net income and
comprehensive Capital
Years ended December 31 income expenditures
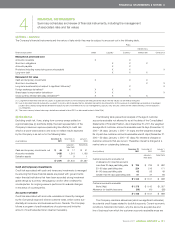
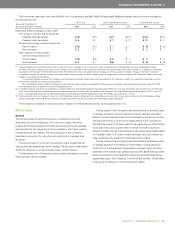
($ increase (decrease) in millions) 2 0 11 2010 2 0 11 2010
10% change in Cdn.$: U.S.$
exchange rate(1)
Canadian dollar appreciates $ 27 $ 20 $ß(23) $ß(17)
Canadian dollar depreciates $ß(27) $ß(20) $ 23 $ 17
(1)
These sensitivities are hypothetical and should be used with caution. Changes in net
income and comprehensive income generally cannot be extrapolated because the
relationship of the change in assumption to the change in net income and compre-
hen sive income may not be linear. In this table, the effect of a variation in the Canadian
dollar: U.S. dollar exchange rate on the amount of net income and comprehensive
income is calculated without changing any other analysis inputs; in reality, changes
in the Canadian dollar: U.S. dollar exchange rate may result in changes in another
factor (for example, increased strength of the Canadian dollar may result in more
favourable market interest rates), which might magnify or counteract the sensitivities.
The sensitivity analysis assumes that changes in exchange rates would be
realized by the Company; in reality, the competitive marketplace in which the Company
operates would impact this assumption. The sensitivity analysis is prepared based
on the simple average of the Canadian dollar: U.S. dollar exchange rate for the period.
In respect of U.S. dollar denominated inventory purchases, the current period’s
purchases have been included in the sensitivity analysis by assuming that all items
are sold in the period purchased. Similarly, this sensitivity analysis is based on the
assumption that all U.S. dollar denominated accounts receivable and accounts pay-
able arising in the period are collected and paid, respectively, in the period.
In respect of U.S. dollar denominated capital expenditures, the current period’s
expenditures have been included in the sensitivity analysis by assuming one-half
period’s straight-line depreciation and amortization in the year of acquisition and an
estimated useful life of ten years; no consideration has been made for U.S. dollar
denominated capital expenditures made in prior periods.
(e) Interest rate risk
Changes in market interest rates will cause fluctuations in the fair value
or future cash flows of temporary investments, short-term investments,
short-term obligations, long-term debt and/or cross currency interest
rate swap derivatives.
When the Company has temporary investments, they have short
maturities and fixed rates, thus their fair value will fluctuate with changes
in market interest rates; absent monetization prior to maturity, the related
future cash flows do not change due to changes in market interest rates.
If the balance of short-term investments includes debt instruments
and/or dividend-paying equity instruments, the Company could be
exposed to interest rate risks.
As short-term obligations arising from bilateral bank facilities, which
typically have variable interest rates, are rarely outstanding for periods
that exceed one calendar week, interest rate risk associated with this
item is not material.
Short-term borrowings arising from the sales of trade receivables to
an arm’s-length securitization trust are fixed-rate debt. Due to the short
maturities of these borrowings, interest rate risk associated with this item
is not material.
In respect of the Company’s currently outstanding long-term debt,
other than for commercial paper and amounts drawn on its credit
facilities (Note 20(b)), it is all fixed-rate debt. The fair value of fixed-rate
debt fluctuates with changes in market interest rates; absent early
redemption and/or foreign exchange rate fluctuations, the related future
cash flows do not change. Due to the short maturities of commercial
paper, its fair values are not materially affected by changes in market
interest rates but its cash flows representing interest payments may be
if the commercial paper is rolled over.
Amounts drawn on the Company’s short-term and long-term credit
facilities will be affected by changes in market interest rates in a manner
similar to commercial paper.
Similar to fixed-rate debt, the fair value of the Company’s cross
currency interest rate swap derivatives fluctuated with changes in market
interest rates as the interest rate swapped to was fixed; absent early
redemption, the related future cash flows would not have changed due
to changes in market interest rates.
(f) Other price risk
Provisions
The Company is exposed to other price risk arising from a written put
option provided for a non-controlling interest, as discussed further in
Note 16(e).
Short-term investments
If the balance of the short-term investments line item on the statement
of financial position includes equity instruments, the Company would be
exposed to equity price risks.
Long-term investments
The Company is exposed to equity price risks arising from investments
classified as available-for-sale. Such investments are held for strategic
rather than trading purposes.
Share-based compensation derivatives
The Company is exposed to other price risk arising from cash-settled
share-based compensation (appreciating Common Share and Non-Voting
Share prices increase both the expense and the potential cash outflow).
Cash-settled equity swap agreements have been entered into that estab-
lish a cap on the Company’s cost associated with its net-cash settled
share options (Note 13(b)) and fix the Company’s cost associated with
its restricted stock units (Note 13(c)).
(g) Market risk
Net income and other comprehensive income for the years ended
December 31, 2011 and 2010, could have varied if the Canadian dollar:
U.S. dollar exchange rates, market interest rates and the Company’s
Common Share and Non-Voting Share prices varied by reasonably pos-
sible amounts from their actual statement of financial position date values.
The sensitivity analysis of the Company’s exposure to currency risk
at the reporting date has been determined based upon a hypothetical
change taking place at the statement of financial position date (as con-
trasted with applying the hypothetical change to all relevant transactions
during the reported periods – see (d)). The U.S. dollar denominated
balances and derivative financial instrument notional amounts as at the
statement of financial position dates have been used in the calculations.
The sensitivity analysis of the Company’s exposure to interest rate
risk at the reporting date has been determined based upon a hypothetical
change taking place at the beginning of the relevant fiscal year and
being held constant through to the statement of financial position date.
The relevant statement of financial position date principal and notional
amounts have been used in the calculations.
The sensitivity analysis of the Company’s exposure to other price
risk arising from share-based compensation at the reporting date has
been determined based upon a hypothetical change taking place at the
relevant statement of financial position date. The relevant statement of
financial position date notional number of shares, including those in the
cash-settled equity swap agreements, has been used in the calculations.