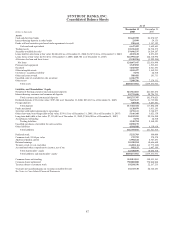
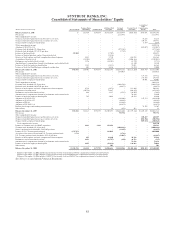
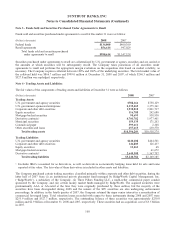
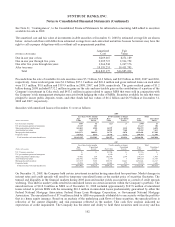
SunTrust 2008 Annual Report Download - page 108
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 108 of the 2008 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SUNTRUST BANKS, INC.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
activities, refer to Note 17, “Derivative Financial Instruments,” to the Consolidated Financial Statements, which includes
specific disclosures about credit derivatives per FSP FAS 133-1 and FIN 45-4 “Disclosures about Credit Derivatives and
Certain Guarantees”.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company sponsors stock plans under which incentive and nonqualified stock options, restricted stock, and performance
based restricted stock may be granted periodically to certain employees. The Company accounts for stock-based
compensation under the fair value recognition provisions of SFAS No. 123(R), “Share-Based Payment”. Effective January 1,
2006, the Company adopted SFAS No. 123(R), using the modified prospective application method. The modified prospective
application method was applied to new awards, to any outstanding liability awards, and to awards modified, repurchased, or
cancelled after January 1, 2006. For all awards granted prior to January 1, 2006, compensation cost has been recognized on
the portion of awards for which service has been rendered. Additionally, the Company estimates the number of awards for
which it is probable that service will be rendered and adjusts compensation cost accordingly. Estimated forfeitures are
subsequently adjusted to reflect actual forfeitures. The required disclosures related to the Company’s stock-based employee
compensation plan are included in Note 16, “Employee Benefit Plans,” to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Employee Benefits
Employee benefits expense includes the net periodic benefit costs associated with the pension, supplemental retirement, and
other postretirement benefit plans, as well as contributions under the defined contribution plan, the amortization of
performance and restricted stock, stock option awards, and costs of other employee benefits.
Foreign Currency Transactions
Foreign denominated assets and liabilities resulting from foreign currency transactions are valued using period end foreign
exchange rates and the associated interest income or expense is determined using approximate weighted average exchange
rates for the period. The Company may elect to enter into foreign currency derivatives to mitigate its exposure to changes in
foreign exchange rates. The derivative contracts are accounted for at fair value. Gains and losses resulting from such
valuations are included as noninterest income in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Fair Value
The Company measures or monitors many of its assets and liabilities on a fair value basis. Fair value is used on a recurring
basis for assets and liabilities that are elected to be accounted for under SFAS No. 159 as well as for certain assets and
liabilities in which fair value is the primary basis of accounting. Examples of these include derivative instruments, available
for sale and trading securities, loans held for sale, long-term debt, and certain residual interests from Company-sponsored
securitizations. Additionally, fair value is used on a non-recurring basis to evaluate assets for impairment or for disclosure
purposes. Examples of these non-recurring uses of fair value include certain loans held for sale accounted for on a lower of
cost or market basis, MSRs, goodwill, and long-lived assets. Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell
an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
Depending on the nature of the asset or liability, the Company uses various valuation techniques and assumptions when
-estimating fair value, which are in accordance with SFAS No. 157 and FSP FAS 157-3, “Determining the Fair Value of a
Financial Asset When the Market for that Asset is Not Active,” when applicable.
In accordance with SFAS No. 157, the Company applied the following fair value hierarchy:
Level 1 – Assets or liabilities for which the identical item is traded on an active exchange, such as publicly-traded
instruments or futures contracts.
Level 2 – Assets and liabilities valued based on observable market data for similar instruments.
Level 3 – Assets or liabilities for which significant valuation assumptions are not readily observable in the market;
instruments valued based on the best available data, some of which is internally developed, and considers risk premiums
that a market participant would require.
96