Capital One 2008 Annual Report Download - page 55
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 55 of the 2008 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report. 37
Variable Interest Entities
VIEs are entities defined in FIN 46(R), and are entities that have either a total equity investment that is insufficient to permit the entity
to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support or whose equity investors lack the characteristics of a
controlling financial interest (i.e., ability to make significant decisions through voting rights, right to receive the expected residual
returns of the entity, and obligation to absorb the expected losses of the entity). Investors that finance the VIE through debt or equity
interests, or other counterparties that provide other forms of support, such as guarantees, subordinated fee arrangements, or certain
types of derivative contracts, are variable interest holders in the entity. The variable interest holder, if any, that will absorb a majority
of the entitys expected losses, receive a majority of the entitys expected residual returns, or both, is deemed to be the primary
beneficiary and must consolidate the VIE. Consolidation under FIN 46(R) is based on expected losses and residual returns, which
consider various scenarios on a probability-weighted basis. Consolidation of a VIE is determined based primarily on variability
generated in scenarios that are considered most likely to occur, rather than based on scenarios that are considered more remote.
Certain variable interests may absorb significant amounts of losses or residual returns contractually, but if those scenarios are
considered very unlikely to occur, they may not lead to consolidation of the VIE.
All these facts and circumstances are taken into consideration when determining whether the Company has variable interest that would
deem it to be the primary beneficiary and require consolidation of the VIE or otherwise rise to the level where disclosure would
provide useful information to the users of the Companys financial statements. In some cases, it is qualitatively clear based on the
extent of the Companys involvement or the seniority of its investments that the Company is not the primary beneficiary of the VIE. In
other cases, a more detailed and quantitative analysis may be required to make such a determination.
Securitization Activities
The securitization of loans has been a significant source of liquidity for the Company. The Company typically uses QSPEs to
securitize its credit card loans. QSPEs are generally exempt from consolidation by the transferor of assets to the QSPE and any
investor or counterparty.
Recourse Exposure
The Company retains residual interests in the trusts as credit enhancements to support the credit quality of the receivables
transferred to the trust. The Companys retained residual interests are generally restricted or subordinated to investors interests
and their value is subject to substantial credit, repayment and interest rate risks on the transferred financial assets. The value of
the retained residual interests represents the Companys only exposure to loss resulting from its continuing involvement in the
trusts. The investors and the trusts have no recourse to the Companys assets if the off-balance sheet loans are not paid when
due. The Company has not provided any financial or other support during the periods presented that it was not previously
contractually required to provide. The Companys retained residual interests in the off-balance sheet securitizations are recorded
in accounts receivable from securitizations and are comprised of interest-only strips, retained senior tranches, retained
subordinated interests, cash collateral accounts, cash reserve accounts and unpaid interest and fees on the investors portion of
the transferred principal receivables. See Item 8 Financial Statements and Supplementary DataNotes to the Consolidated
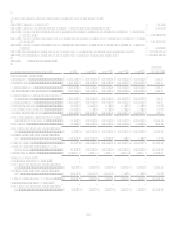
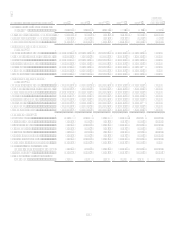
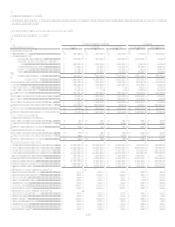
Financial StatementsNote 18 for quantitative information regarding retained interests.
Collections and Amortization
Collections of interest and fees received on securitized receivables are used to pay interest to investors, servicing and other fees,
and are available to absorb the investors share of credit losses. Amounts collected in excess of that needed to pay the above
amounts are remitted, in general, to the Company. Under certain conditions, some of the cash collected may be retained to
ensure future payments to investors. See Item 8 Financial Statements and Supplementary DataNotes to the Consolidated
Financial StatementsNote 18 for quantitative information regarding revenues, expenses and cash flows that arise from
securitization transactions.
Maturity terms of the existing securitizations vary from 2009 to 2025 and, for revolving securitizations, have accumulation
periods during which principal payments are aggregated to make payments to investors. As payments on the loans are
accumulated and are no longer reinvested in new loans, the Companys funding requirements for loans increase accordingly.
The Company believes that it has the ability to continue to utilize securitization arrangements as a source of liquidity; however,
a significant reduction, termination or change in sale accounting for the Companys off-balance sheet securitizations could
require the Company to draw down existing liquidity and/or to obtain additional funding through the issuance or recognition of
secured borrowings or unsecured debt, the raising of additional deposits or the slowing of asset growth to offset or to satisfy
liquidity needs.