Wells Fargo 2008 Annual Report Download - page 129
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 129 of the 2008 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
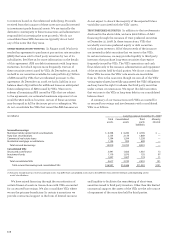
We issue standby letters of credit, which include
performance and financial guarantees, for customers in
connection with contracts between our customers and third
parties. Standby letters of credit are agreements where we
are obligated to make payment to a third party on behalf
of a customer in the event the customer fails to meet their
contractual obligations. We consider the credit risk in
standby letters of credit and commercial and similar letters
of credit in determining the allowance for credit losses.
As a securities lending agent, we loan client securities, on
a fully collateralized basis, to third party broker/dealers. We
indemnify our clients against broker default and, in certain
cases, against collateral losses. We support these guarantees
with collateral, generally in the form of cash or highly liquid
securities, that is marked to market daily. At December 31,
2008, there was $31.0 billion in collateral supporting the
$30.1 billion loaned.
We enter into other types of indemnification agreements
in the ordinary course of business under which we agree
to indemnify third parties against any damages, losses
and expenses incurred in connection with legal and other
proceedings arising from relationships or transactions with us.
These relationships or transactions include those arising from
service as a director or officer of the Company, underwriting
agreements relating to our securities, acquisition agreements
and various other business transactions or arrangements.
Because the extent of our obligations under these agreements
depends entirely upon the occurrence of future events,
our potential future liability under these agreements is
not determinable.
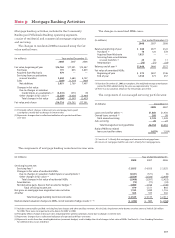
We provide liquidity facilities on all commercial paper
issued by the conduit we administer. We also provide liquidity
to certain off-balance sheet entities that hold securitized
fixed rate municipal bonds and consumer or commercial
assets that are partially funded with the issuance of money
market and other short-term notes. See Note 8 for additional
information on these arrangements.
Written put options are contracts that give the counterparty
the right to sell to us an underlying instrument held by the
counterparty at a specified price, and include options, floors,
caps and credit default swaps. These written put option
contracts generally permit net settlement. While these
derivative transactions expose us to risk in the event the
option is exercised, we manage this risk by entering into
offsetting trades or by taking short positions in the underlying
instrument. We offset substantially all put options written
to customers with purchased options. Additionally, for certain
of these contracts, we require the counterparty to pledge the
underlying instrument as collateral for the transaction. Our
ultimate obligation under written put options is based on
future market conditions and is only quantifiable at settlement.
See Note 8 for additional information regarding transactions
with VIEs and Note 16 for additional information regarding
written derivative contracts.
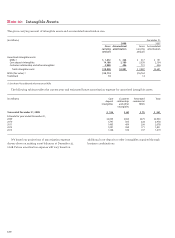
In certain loan sales or securitizations, we provide
recourse to the buyer whereby we are required to repurchase
loans at par value plus accrued interest on the occurrence of
certain credit-related events within a certain period of time.
The maximum risk of loss represents the outstanding principal
balance of the loans sold or securitized that are subject to
recourse provisions, but the likelihood of the repurchase
of the entire balance is remote and amounts paid can be
recovered in whole or in part from the sale of collateral.
In 2008 and in 2007, we did not repurchase a significant
amount of loans associated with these agreements.
We provide residual value guarantees as part of certain
leasing transactions of corporate assets, principally railcars.
The lessors in these leases are generally large financial
institutions or their leasing subsidiaries. These guarantees
protect the lessor from loss on sale of the related asset at the
end of the lease term. To the extent that a sale of the leased
assets results in proceeds less than a stated percent (generally
80% to 89%) of the asset’s cost less depreciation, we would be
required to reimburse the lessor under our guarantee.
In connection with certain brokerage, asset management,
insurance agency and other acquisitions we have made,
the terms of the acquisition agreements provide for deferred
payments or additional consideration, based on certain
performance targets.
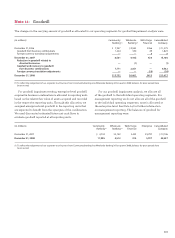
We have entered into various contingent performance
guarantees through credit risk participation arrangements.
Under these agreements, if a customer defaults on its
obligation to perform under certain credit agreements with
third parties, we will be required to make payments to the
third parties.
Wells Fargo is a Class B common shareholder of Visa Inc.
(Visa). Based on agreements previously executed among
Wells Fargo, Visa and its predecessors and certain member
banks of the Visa USA network, we may be required to
indemnify Visa with respect to certain covered litigation.
In conjunction with its initial public offering in March 2008,
Visa deposited $3 billion of the proceeds of the offering into
a litigation escrow account to be used to satisfy settlement
obligations with respect to prior litigation and to make
payments with respect to the future resolution of the covered
litigation. The extent of our future obligations, if any, under
these arrangements depends on the ultimate resolution of
the covered litigation. In October 2008, Visa entered into
an agreement in principle to settle with Discover Financial
Services (Discover). We had previously established a reserve
to reflect the fair value of our possible indemnification
obligation to Visa for the Discover litigation.