Sallie Mae 2007 Annual Report Download - page 171
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 171 of the 2007 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.10. Derivative Financial Instruments (Continued)
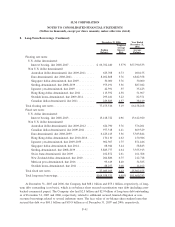
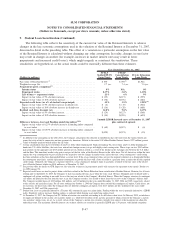
counterparties. As of December 31, 2007, the net positive exposure on these swaps is $1.7 billion. As
previously discussed, the Company’s corporate derivatives contain provisions which require collateral to be
posted on a regular basis for changes in market values. The on-balance sheet trusts’ derivatives are structured
such that swap counterparties are required to post collateral if their credit rating has been withdrawn or is
below a certain level. If the swap counterparty does not post the required collateral or is downgraded further,
the counterparty must find a suitable replacement counterparty or provide the trust with a letter of credit or a
guaranty from an entity that has the required credit ratings. In addition to the credit rating requirement, trusts
issued after November 2005 require the counterparty to post collateral due to a net positive exposure on cross-
currency interest rate swaps, irrespective of their counterparty rating. The trusts, however, are not required to
post collateral to the counterparty. As of December 31, 2007, counterparties have posted $310 million of
collateral due to a net positive exposure from changes in market value and have not posted any collateral
related to any credit rating downgrade as no downgrade triggers have been met. Ultimately, the Company’s
exposure related to a swap counterparty failing to make its required payments is limited to the trust assets
(primarily student loans and cash) which collateralize the outstanding bonds in the trust. Because the bonds
outstanding generally are at parity with the assets that collateralize the bonds, even in periods of great stress in
the foreign currency markets, the likelihood of a material loss is remote.
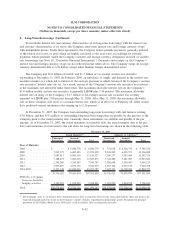
SFAS No. 133
Derivative instruments that are used as part of the Company’s interest rate and foreign currency risk
management strategy include interest rate swaps, basis swaps, cross-currency interest rate swaps, interest rate
futures contracts, and interest rate floor and cap contracts with indices that relate to the pricing of specific
balance sheet assets and liabilities including the Residual Interests from off-balance sheet securitizations. In
addition, the Company uses equity forward contracts based on the Company’s stock. The Company accounts
for its derivatives under SFAS No. 133 which requires that every derivative instrument, including certain
derivative instruments embedded in other contracts, be recorded in the balance sheet as either an asset or
liability measured at its fair value. As more fully described below, if certain criteria are met, derivative
instruments are classified and accounted for by the Company as either fair value or cash flow hedges. If these
criteria are not met, the derivative financial instruments are accounted for as trading.
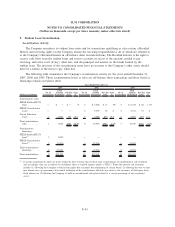
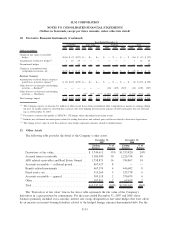
Fair Value Hedges
Fair value hedges are generally used by the Company to hedge the exposure to changes in fair value of a
recognized fixed rate asset or liability. The Company enters into interest rate swaps to convert fixed rate assets
into variable rate assets and fixed rate debt into variable rate debt. The Company also enters into cross-
currency interest rate swaps to convert foreign currency denominated fixed and floating debt to U.S. dollar
denominated variable debt. For fair value hedges, the Company generally considers all components of the
derivative’s gain and/or loss when assessing hedge effectiveness (in some cases the Company excludes time-
value components) and generally hedges changes in fair value due to interest rates or interest rates and foreign
currency exchange rates or the total change in fair value.
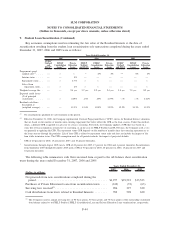
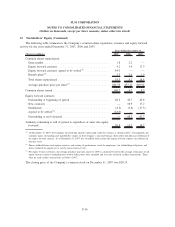
Cash Flow Hedges
Cash flow hedges are used by the Company to hedge the exposure to variability in cash flows for a
forecasted debt issuance and for exposure to variability in cash flows of floating rate debt. This strategy is
used primarily to minimize the exposure to volatility from future changes in interest rates. Gains and losses on
the effective portion of a qualifying hedge are accumulated in other comprehensive income and ineffectiveness
is recorded immediately to earnings. In the case of a forecasted debt issuance, gains and losses are reclassified
to earnings over the period which the stated hedged transaction impacts earnings. If the stated transaction is
F-50
SLM CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts, unless otherwise stated)