The Hartford 2014 Annual Report Download - page 103
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 103 of the 2014 The Hartford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
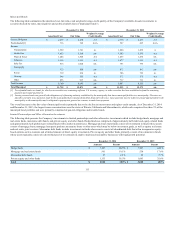
Credit risk is defined as the risk to earnings or capital due to uncertainty of an obligor’s or counterparty’s ability or willingness to meet its obligations in
accordance with contractually agreed upon terms. The majority of the Company’s credit risk is concentrated in its investment holdings but is also present in
reinsurance and insurance portfolios. Credit risk is comprised of three major factors: the risk of change in credit quality, or credit migration risk; the risk of
default; and the risk of a change in value of a financial instrument due to changes in credit spread that are unrelated to changes in obligor credit quality. A
decline in creditworthiness is typically associated with an increase in an investment’s credit spread, potentially resulting in an increase in other-than-
temporary impairments and an increased probability of a realized loss upon sale.
The objective of the Company’s enterprise credit risk management strategy is to identify, quantify, and manage credit risk on an aggregate portfolio basis and
to limit potential losses in accordance with an established credit risk management policy. The Company manages to its credit risk appetite by primarily
holding a diversified mix of investment grade issuers and counterparties across its investment, reinsurance, and insurance portfolios. Potential losses are also
limited within portfolios by diversifying across geographic regions, asset types, and sectors.
The Company manages credit risk exposure from its inception to its maturity or sale. Both the investment and reinsurance areas have formulated procedures
for counterparty approvals and authorizations. Although approval processes may vary by area and type of credit risk, approval processes establish minimum
levels of creditworthiness and financial stability. Credits considered for investment are subjected to prudent and conservative underwriting reviews. Within
the investment portfolio, private securities, such as commercial mortgages, and private placements, must be presented to their respective review committees
for approval.
Credit risks are managed on an on-going basis through the use of various processes and analyses. At the investment, reinsurance, and insurance product
levels, fundamental credit analyses are performed at the issuer/counterparty level on a regular basis. To provide a holistic review within the investment
portfolio, fundamental analyses are supported by credit ratings, assigned by nationally recognized rating agencies or internally assigned, and by quantitative
credit analyses. The Company utilizes a credit value at risk ("VaR") to measure default and migration risk on a monthly basis. Issuer and security level risk
measures are also utilized. In the event of deterioration in credit quality, the Company maintains watch lists of problem counterparties within the investment
and reinsurance portfolios. The watch lists are updated based on regular credit examinations and management reviews. The Company also performs quarterly
assessments of probable expected losses in the investment portfolio. The process is conducted on a sector basis and is intended to promptly assess and
identify potential problems in the portfolio and to recognize necessary impairments.
Credit risk policies at the enterprise and operation level ensure comprehensive and consistent approaches to quantifying, evaluating, and managing credit
risk under expected and stressed conditions. These policies define the scope of the risk, authorities, accountabilities, terms, and limits, and are regularly
reviewed and approved by senior management and ERM. Aggregate counterparty credit quality and exposure is monitored on a daily basis utilizing an
enterprise-wide credit exposure information system that contains data on issuers, ratings, exposures, and credit limits. Exposures are tracked on a current and
potential basis. Credit exposures are reported regularly to the ERCC and to the Finance, Investment and Risk Management Committee. Exposures are
aggregated by ultimate parent across investments, reinsurance receivables, insurance products with credit risk, and derivative counterparties. The credit
database and reporting system are available to all key credit practitioners in the enterprise.
The Company exercises various and differing methods to mitigate its credit risk exposure within its investment and reinsurance portfolios. Some of the
reasons for mitigating credit risk include financial instability or poor credit, avoidance of arbitration or litigation, future uncertainty, and exposure in excess
of risk tolerances. Credit risk within the investment portfolio is most commonly mitigated through asset sales or the use of derivative instruments.
Counterparty credit risk is mitigated through the practice of entering into contracts only with highly creditworthy institutions and through the practice of
holding and posting of collateral. In addition, transactions cleared through a central clearing house reduce risk due to their ability to require daily variation
margin, monitor the Company's ability to request additional collateral in the event of a counterparty downgrade, and be an independent valuation source.
Systemic credit risk is mitigated through the construction of high-quality, diverse portfolios that are subject to regular underwriting of credit risks. For further
discussion of the Company’s investment and derivative instruments, see MD&A - Enterprise Risk Management, Portfolio Risks and Risk Management and
Note 6 - Investments and Derivative Instruments of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. For further discussion on managing and mitigating credit
risk from the use of reinsurance via an enterprise security review process, see MD&A - Enterprise Risk Management, Insurance Risk Management,
Reinsurance as a Risk Management Strategy.
103