The Hartford 2014 Annual Report Download - page 101
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 101 of the 2014 The Hartford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
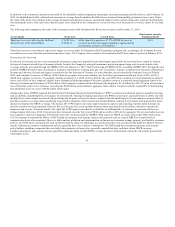
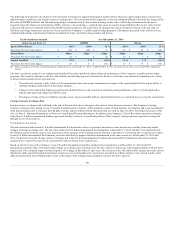
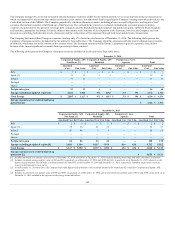
The following table presents our estimates of the potential instantaneous impacts from sudden market stresses related to equity market prices, interest rates,
implied market volatilities, and foreign currency exchange rates. The sensitivities below represent: (1) the net estimated difference between the change in the
fair value of GMWB liabilities and the underlying hedge instruments and (2) the estimated change in fair value of the hedge instruments for the macro
program, before the impacts of amortization of DAC, and taxes. As noted above, certain hedge assets are used to hedge liabilities that are not carried at fair
value and will not have a liability offset in the GAAP sensitivity analysis. All sensitivities are measured as of year end and are related to the fair value of
liabilities and hedge instruments in place as of year end for the Company’s variable annuity hedge programs. The impacts presented in the table below are
estimated individually and measured without consideration of any correlation among market risk factors.
Potential Net Fair Value Impact $ (19) $ (10) $ 8 $ 61 $ 22 $ (16)
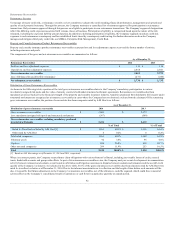
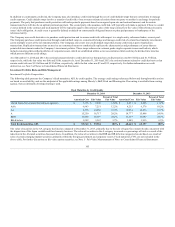
Potential Net Fair Value Impact $ (2) $ — $ (1) $ 14 $ 7 $ (7)
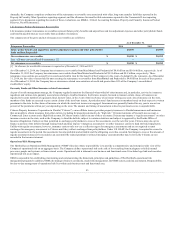
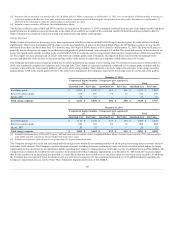
Potential Net Fair Value Impact $ 20 $ 4 $ (13) $ 74 $ 15 $ (76)
[1] These sensitivities are based on the following key market levels as of December 31, 2014: 1) S&P of 2059; 2) 10yr US swap rate of 2.34%; and 3) S&P 10yr volatility of
26.58%
The above sensitivity analysis is an estimate and should not be used to predict the future financial performance of the Company's variable annuity hedge
programs. The actual net changes in the fair value liability and the hedging assets illustrated in the above table may vary materially depending on a variety
of factors which include but are not limited to:
• The sensitivity analysis is only valid as of the measurement date and assumes instantaneous changes in the capital market factors and no ability to
rebalance hedge positions prior to the market changes;
• Changes to the underlying hedging program, policyholder behavior, and variation in underlying fund performance relative to the hedged index,
which could materially impact the liability; and
• The impact of elapsed time on liabilities or hedge assets, any non-parallel shifts in capital market factors, or correlated moves across the sensitivities.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
Foreign currency exchange risk is defined as the risk of financial loss due to changes in the relative value between currencies. The Company’s foreign
currency exchange risk is related to non-U.S. dollar denominated investments, which primarily consist of fixed maturity investments, and a yen denominated
fixed payout annuity that is reinsured from HLIKK, a former, indirect wholly-owned subsidiary that was sold on June 30, 2014. For further discussion of the
sale, see Note 2 - Business Dispositions of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. In addition, the Company’s Talcott Resolution operations formerly
issued non-U.S. dollar denominated funding agreement liability contracts. A significant portion of the Company’s foreign currency exposure is mitigated
through the use of derivatives.
Fixed Maturity Investments
The risk associated with the non-U.S. dollar denominated fixed maturities relates to potential decreases in value and income resulting from unfavorable
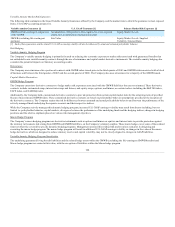
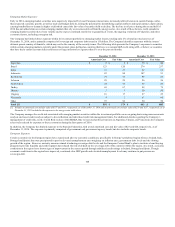
changes in foreign exchange rates. The fair value of the non-U.S. dollar denominated fixed maturities at December 31, 2014 and 2013 were approximately
$0.5 billion and $2.6 billion, respectively. Included in these amounts are $0.4 billion and $2.4 billion at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, related
to non-U.S. dollar denominated fixed maturity securities that directly support liabilities denominated in the same currencies. At December 31, 2014 and
2013, the derivatives used to hedge currency exchange risk related to the remaining non-U.S. dollar denominated fixed maturities had a total notional
amount of $137 and $194, respectively, and total fair value of $2 and $(13), respectively.
Based on the fair values of the Company’s non-U.S. dollar denominated securities and derivative instruments as of December 31, 2014 and 2013,
management estimates that a 10% unfavorable change in exchange rates would decrease the fair values by a before-tax total of approximately $38 and $165,
respectively. The estimated impact was based upon a 10% change in December 31 spot rates. The selection of the 10% unfavorable change was made only for
illustration of the potential hypothetical impact of such an event and should not be construed as a prediction of future market events. Actual results could
differ materially from those illustrated above due to the nature of the estimates and assumptions used in the above analysis.
101