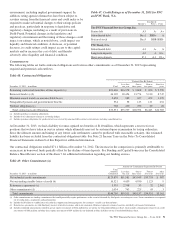
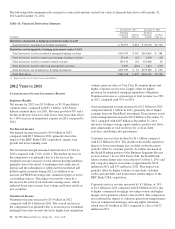
PNC Bank 2013 Annual Report Download - page 118
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 118 of the 2013 PNC Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Basis point – One hundredth of a percentage point.
Carrying value of purchased impaired loans – The net value
on the balance sheet which represents the recorded investment
less any valuation allowance.
Cash recoveries – Cash recoveries used in the context of
purchased impaired loans represent cash payments from
customers that exceeded the recorded investment of the
designated impaired loan.
Charge-off – Process of removing a loan or portion of a loan
from our balance sheet because it is considered uncollectible.
We also record a charge-off when a loan is transferred from
portfolio holdings to held for sale by reducing the loan
carrying amount to the fair value of the loan, if fair value is
less than carrying amount.
Combined loan-to-value ratio (CLTV) – This is the aggregate
principal balance(s) of the mortgages on a property divided by
its appraised value or purchase price.
Commercial mortgage banking activities – Includes
commercial mortgage servicing, originating commercial
mortgages for sale and related hedging activities. Commercial
mortgage banking activities revenue includes revenue derived
from commercial mortgage servicing (including net interest
income and noninterest income from loan servicing and
ancillary services, net of commercial mortgage servicing
rights amortization, and commercial mortgage servicing rights
valuations net of economic hedge), and revenue derived from
commercial mortgage loans intended for sale and related
hedges (including loan origination fees, net interest income,
valuation adjustments and gains or losses on sales).
Common shareholders’ equity to total assets – Common
shareholders’ equity divided by total assets. Common
shareholders’ equity equals total shareholders’ equity less the
liquidation value of preferred stock.
Core net interest income – Core net interest income is total net
interest income less purchase accounting accretion.
Credit derivatives – Contractual agreements, primarily credit
default swaps, that provide protection against a credit event of
one or more referenced credits. The nature of a credit event is
established by the protection buyer and protection seller at the
inception of a transaction, and such events include
bankruptcy, insolvency and failure to meet payment
obligations when due. The buyer of the credit derivative pays
a periodic fee in return for a payment by the protection seller
upon the occurrence, if any, of a credit event.
Credit spread – The difference in yield between debt issues of
similar maturity. The excess of yield attributable to credit
spread is often used as a measure of relative creditworthiness,
with a reduction in the credit spread reflecting an improvement
in the borrower’s perceived creditworthiness.
Credit valuation adjustment (CVA) – Represents an
adjustment to the fair value of our derivatives for our own and
counterparties’ non-performance risk.
Derivatives – Financial contracts whose value is derived from
changes in publicly traded securities, interest rates, currency
exchange rates or market indices. Derivatives cover a wide
assortment of financial contracts, including but not limited to
forward contracts, futures, options and swaps.
Duration of equity – An estimate of the rate sensitivity of our
economic value of equity. A negative duration of equity is
associated with asset sensitivity (i.e., positioned for rising
interest rates), while a positive value implies liability
sensitivity (i.e., positioned for declining interest rates). For
example, if the duration of equity is -1.5 years, the economic
value of equity increases by 1.5% for each 100 basis point
increase in interest rates.
Earning assets – Assets that generate income, which include:
federal funds sold; resale agreements; trading securities;
interest-earning deposits with banks; loans held for sale;
loans; investment securities; and certain other assets.
Effective duration – A measurement, expressed in years, that,
when multiplied by a change in interest rates, would
approximate the percentage change in value of on- and off-
balance sheet positions.
Efficiency – Noninterest expense divided by total revenue.
Enterprise risk management framework – An enterprise
process designed to identify potential risks that may affect
PNC, manage risk to be within our risk appetite and provide
reasonable assurance regarding achievement of our objectives.
Fair value – The price that would be received to sell an asset
or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between
market participants at the measurement date.
FICO score – A credit bureau-based industry standard score
created by Fair Isaac Co. which predicts the likelihood of
borrower default. We use FICO scores both in underwriting
and assessing credit risk in our consumer lending portfolio.
Lower FICO scores indicate likely higher risk of default,
while higher FICO scores indicate likely lower risk of default.
FICO scores are updated on a periodic basis.
Foreign exchange contracts – Contracts that provide for the
future receipt and delivery of foreign currency at previously
agreed-upon terms.
Funds transfer pricing – A management accounting
methodology designed to recognize the net interest income
100 The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. – Form 10-K