Reebok 2013 Annual Report Download - page 118
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 118 of the 2013 Reebok annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
adidas Group
/
2013 Annual Report
Group Management Report – Our Group
114
2013
Sustainability
/
02.10
/
Sustainable materials
One key goal of our Environmental Strategy is to reduce the overall
environmental impact of materials used in our products. We aim to find
materials that reduce waste or have less of an impact throughout their
whole life cycle. The adidas Group has various initiatives in place that
help to achieve its goal to increase the usage of recycled and sustainable
materials.
One example is our commitment to use 100% “sustainable cotton”
(Better Cotton, certified organic cotton or any other form of sustainably
produced cotton that is currently available or might be in future) in all
our products by 2018. More information about sustainable cotton can
be found on our website at :
//
WWW.ADIDAS-GROUP.COM/EN/SUSTAINABILITY/
PRODUCTS/MATERIALS.
Another initiative is the adidas brand’s sustainable product programme
“Better Place”, which creates sustainable products within the adidas
Sport Performance and Originals & Sport Style ranges. The product
creation process includes the utilisation of sustainable materials,
environmental design and innovative manufacturing techniques. The
first adidas “Better Place” products were introduced globally in 2009 in
response to increasing consumer demand for sustainable apparel and
footwear. These products have been a part of the adidas brand product
offering ever since.
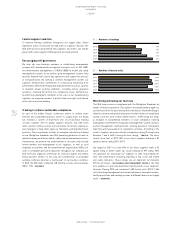
The number of adidas products that either reached or exceeded the
baseline “Better Place” criteria has grown continuously in recent years.
This growth is supported by ongoing innovation in the area of sustainable
product construction and manufacturing techniques, such as the
revolutionary DryDye technology or the low-waste initiative. DryDye is a
polyester fabric dyeing process that uses no water, 50% fewer chemicals
and 50% less energy than the traditional fabric dyeing process. The
low-waste initiative produces footwear and sports apparel with fewer
parts, recycled materials and maximum pattern efficiency, aiming to
reduce material waste.
Furthermore, at the adidas Group, we now increasingly use virtual
technologies to reduce the quantity of physical samples required to
design and sell new products. Virtualising processes saves energy and
materials, and reduces waste. As well as being innovative, virtualisation
is also quick and efficient. It helps us save resources and money by
reducing material waste, transportation and distribution costs. And with
fewer samples being transported by airfreight, we are also reducing our
carbon emissions.
In 2013, we focused on increasing the use of sustainable materials
such as recycled polyester, organic and Better Cotton and bio-based
materials in our products. These environmentally preferred materials
have replaced conventional materials in many of our footwear and
apparel products. In addition to increasing the use of environmentally
preferred materials, we strive to continuously increase the range of
more sustainable products by developing sustainable product solutions
and using innovative materials.
Driving environmental improvements in our supply chain
In our supply chain, activities focus on helping suppliers establish
sound environmental management systems at their manufacturing
plants to best reduce their negative environmental impacts. We have
guidelines and training programmes in place for our suppliers, using the
environmental performance of our own production sites as best practice
examples.
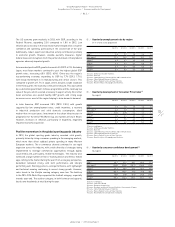
The majority of our footwear sourcing volume is produced in factories
which are OHSAS 18000 and/or ISO 14001 certified. The remaining
part of our footwear sourcing volume is produced in factories that
have management systems in place but have not yet been certified. All
footwear factories are regularly assessed against the adidas Group’s
standards on environment and workplace health and safety. We use
“Environmental Key Performance Indicators” to track the progress
of environmental efforts undertaken by our strategic suppliers.
Furthermore, we have established a database to collect environmental
data from the factories of our core suppliers. A range of other activities
have been implemented to reduce our carbon footprint in the supply and
distribution chain. Examples of these are in the areas of transportation
and energy use. In the transportation of our products, our policy is to
minimise the impacts, in particular from airfreight shipments, through
improved order and production planning tools.
Control and monitoring of restricted substances
We have specified clear standards that follow the strictest local
regulations and best practice standards for consumer care and
safety. These standards are mandatory for all business partners and
are updated regularly based on findings in our ongoing dialogue with
scientific organisations. They cover all general requirements for
eco-labels and green seals (e.g. ÖKO-Tex Standard 100, Toxproof TÜV
Rheinland, etc.) for footwear, apparel and hardware products. Both
our own quality assurance laboratories and external testing institutes
are used to constantly monitor material samples to ensure supplier
compliance with these requirements. Materials that do not meet our
standards and specifications are rejected.